|
Rhombifera Bohemica
The Eocrinoidea were an extinct class of echinoderms that lived between the Early Cambrian and Late Silurian periods. They are the earliest known group of stalked, brachiole-bearing echinoderms, and were the most common echinoderms during the Cambrian. The earliest genera had a short holdfast and irregularly structured plates. Later forms had a fully developed stalk with regular rows of plates. They were benthic suspension feeders, with five ambulacra on the upper surface, surrounding the mouth and extending into a number of narrow arms. Phylogeny Eocrinoids were a paraphyletic group that are seen as the basal stock from which all other blastozoan groups evolved. Early evolution The following cladogram, after Nardin et al. 2017, shows the progression of early eocrinoid families, with all other eocrinoid families (including representatives ''Trachelocrinus'' and ''Ridersia'') grouped with "derived Blastozoans" as their relationships with each other and with other blastozoans ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Jaekel
Otto Max Johannes Jaekel (21 February 1863 – 6 March 1929) was a German paleontologist and geologist. Biography Jaekel was born in Nowa Sól, Neusalz (Nowa Sól), Prussian Silesia, the son of a builder and the youngest of seven children. He studied at the ''Ritterakademie'' in Legnica, Liegnitz (Legnica). After graduating in 1883, he came to study geology and paleontology under Ferdinand von Roemer, Ferdinand Roemer in Wrocław, Breslau (Wrocław) until 1885. Karl von Zittel awarded a PhD to Jaekel in Munich in 1886. Between 1887 and 1889, Jaekel was an assistant of E.W. Benecke at the Geologisch-Paläontologisches Institut in Straßburg, where he received his Habilitation. He worked at the Humboldt University of Berlin, Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Berlin and at the Natural History Museum, Berlin, Geologisch-Paläontologisches Museum (a combined post) from 1891. Jaekel was considered as an ordinary professor of geology at the University of Vienna in 1903, but this was block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
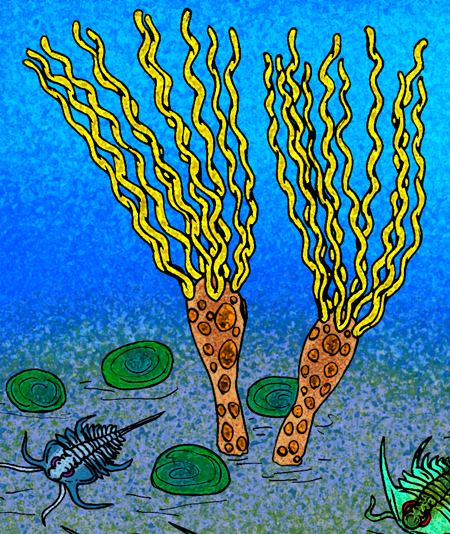
Gogia
''Gogia'' is a genus of primitive eocrinoid blastozoan from the early to middle Cambrian. ''G. ojenai'' dates to the late Early Cambrian; other species come from various Middle Cambrian strata throughout North America, but the genus has yet to be described outside this continent. Notable localities where species are found include the Wheeler Shale of Utah, and the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The species of ''Gogia'', like other eocrinoids, were not closely related to the true crinoids, instead, being more closely related to the blastoids. ''Gogia'' is distinguished from sea lilies, and most other blastoids, in that the plate-covered body was shaped like a vase, or a bowling pin (with the pin part stuck into the substrate), and that the five ambulacra were split into pairs of coiled or straight, ribbon-like strands. Six specimens of ''Gogia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed The Phyllopod bed, designated by USNM locality number 35k, is the most famous foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian First Appearances
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian Echinoderms
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Echinoderms
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic Echinoderms
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Greek ''palaiós'' (παλαιός, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (ζωή, "life") meaning "ancient lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastozoa
Blastozoa is a subphylum of extinct echinoderms characterized by the presence of specialized respiratory structures and brachiole plates used for feeding. It ranged from the Cambrian to the Permian. Biserial, triradiate, and pentaradiate ambulacral patterns have been identified in blastozoa specimens. The pentaradiate pattern in particular has been associated with several different classes. A significant species has been found at the Zaouïa Formation. References External linksHarvard: Subphylum Blastozoa Blastozoa, Paleozoic echinoderms Cambrian echinoderms Silurian echinoderms Ordovician echinoderms Devonian echinoderms Permian echinoderms Animal subphyla {{paleo-echinoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outgroup (cladistics)
In cladistics or phylogenetics, an outgroup is a more distantly related group of organisms that serves as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships of the ingroup, the set of organisms under study, and is distinct from sociological outgroups. Character states present in the ingroup but absent in the outgroup are (often) synapomorphies that provide empirical support for the inferred monophyly of the ingroup; character states that are present in the outgroup and some members of the ingroup are symplesiomorphies, and their complementary synapomorphies shared among some members of the ingroup provide hypotheses of relationship within the ingroup clade. The outgroup is used as a point of comparison for the ingroup and specifically allows for the phylogeny to be rooted. Because the polarity (direction) of character change can be determined only on a rooted phylogeny, the choice of outgroup is essential for understanding the evolution of traits along a phylogeny. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytomy
An internal node of a phylogenetic tree is described as a polytomy or multifurcation if (i) it is in a rooted tree and is linked to three or more child subtrees or (ii) it is in an unrooted tree and is attached to four or more branches. A tree that contains any multifurcations can be described as a multifurcating tree. Soft polytomies vs. hard polytomies Two types of polytomies are recognized, soft and hard polytomies. Soft polytomies are the result of insufficient phylogenetic information: though the lineages diverged at different times – meaning that some of these lineages are closer relatives than others, and the available data does not allow recognition of this. Most polytomies are soft, meaning that they would be resolved into a typical tree of dichotomies if better data were available. In contrast, a hard polytomy represents a true divergence event of three or more lineages. Applications Interpretations for a polytomy depend on the individuals that are represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurocystites
''Pleurocystites'' (meaning ''rib bag'' or ''side bladder'') is a genus of rhombiferan echinoderm (a cystoid) that lived in the Late Ordovician. Its fossils are known from Europe and North America. ''Pleurocystites'' grew to a height of 2 centimeters (3/4 of an inch) and fed on plankton. Sources * ''Fossils'' (Smithsonian Handbooks) by David Ward (Page 191) * Parker, Steve. Dinosaurus: the complete guide to dinosaurs. Firefly Books Inc, 2003. Pg. 75 External links''Pleurocystites''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Rhombifera Ordovician echinoderms of Europe Ordovician echinoderms of North America Late Ordovician first appearances Late Ordovician extinctions Paleozoic life of Ontario Paleozoic life of Quebec {{pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibrachicystis
''Dibrachicystis'' is an extinct genus of rhombiferan echinoderm from the early Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan, about 510 Ma). It is a stalked echinoderm within the family Dibrachicystidae which lived in what is now northernmost Iberian Chains, northern Spain. It is known from the holotype MPZ2009/1230 and from the paratypes MPZ2011/2–6. It was found in the uppermost part of the Murero Formation at Purujosa, Moncayo Natural Park, dating to the Lower Languedocian and referred to the ''Solenopleuropsis thorali'' Zone. It was first named by Samuel Zamora and A. B. Smith in 2011 and the type species is ''Dibrachicystis purujoensis''. Phylogeny Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... after Zamora & Smith, 2011 (all genera not part of a named bracket a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aethocrinus
''Aethocrinus'' is an early-diverging crinoid reported from the Early Ordovician. Its five arms bifurcate. The contested '' Echmatocrinus '' notwithstanding, it is a candidate for the earliest true member of the crinoid class – though not being a member of the crown group, quite where within the stem group to draw the distinction between eocrinoids and crinoids is a somewhat arbitrary decision. References Crinoidea {{Crinoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |