|
Reynolds-Alberta Museum
The Reynolds-Alberta Museum is an agricultural museum, agricultural, industrial, and transportation museum in Wetaskiwin, Alberta, Canada. The museum is situated on an property containing the main museum building, an aviation display hangar, and its storage facility. The museum was initially conceived by Stan Reynolds, who had amassed a large collection of agricultural machinery, airplanes, and automobiles during the mid-20th century. During the 1980s, Reynolds donated 850 artifacts to the government of Alberta for the purposes of showcasing these items in a public museum. The provincial government opened the Reynolds-Alberta Museum to exhibit these items to the public on 12 September 1992. The institution was named after Reynolds, who eventually donated over 1,500 artifacts to the institution before his death. The museum collection presently contains over 6,600 agricultural, industrial, and transportation artifacts. The majority of the artifacts are held in the museum's storage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetaskiwin
Wetaskiwin ( ) is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. The city is located south of the provincial capital of Edmonton. The city name comes from the Cree word , meaning "the hills where peace was made". Wetaskiwin is home to the Reynolds-Alberta Museum, a museum dedicated to celebrating "the spirit of the machine" as well as the Wetaskiwin and District Heritage Museum, which documents the pioneer arrival and lifestyle in Wetaskiwin's early years. Southeast of Wetaskiwin, the Alberta Central Railway Museum acknowledges the impact that the railway had on Central Alberta. The city is well known in Western Canada for the slogan and jingle "Cars cost less in Wetaskiwin", from the Wetaskiwin Auto Dealers Association. Both have been in print, radio, and television advertisements since the mid-1970s. History The future location of Wetaskiwin was once the site of a battle between the Cree and the Blackfoot, known as ''Wee-Tas-Ki-Win-Spatinow'' for "the place where peace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 13
Highway 13 is an east–west highway through central Alberta. It runs from Alder Flats, Alberta, Alder Flats, west of Alberta Highway 22, Highway 22, to the Alberta-Saskatchewan border, where it becomes Saskatchewan Highway 14. Highway 13 is about long. East of the City of Wetaskiwin, it generally parallels the Canadian Pacific Kansas City Prairie North Line. Route description From the west, Highway 13 begins at Alder Flats before intersecting Highway 22. It continues east, passing south of Buck Lake, Alberta, Buck Lake and Winfield, Alberta, Winfield before crossing Alberta Highway 20, Highway 20. The highway then passes south of Battle Lake (Alberta), Battle Lake, the headwaters of the Battle River, and then south of Pigeon Lake (Alberta), Pigeon Lake, passing through the hamlets of Westerose, Alberta, Westerose and Falun, Alberta, Falun prior to intersecting Alberta Highway 2, Highway 2 (Queen Elizabeth II Highway), approximately south of Edmonton. East of Highway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën
Citroën ()The double-dot diacritic over the 'e' is a diaeresis () indicating the two vowels are sounded separately, and not as a diphthong. is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded on 4 June 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën has been owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 89.95% share in 1976. Citroën's head office is located in the Stellantis Poissy Plant in Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine since 2021 (previously in Rueil-Malmaison) and its offices studies and research in Vélizy-Villacoublay, Poissy (CEMR), Carrières-sous-Poissy and Sochaux-Montbéliard. In 1934, the firm established its reputation for innovative technology with the Citroën Traction Avant, Traction Avant. This was the world's first car to be mass-produced with front-wheel drive and four-wheel independent suspension, as well as unibody construction, omitting a separate chassis, and instead using the body of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedan (automobile)
A sedan (American English) or saloon (British English) is a passenger car in a three-box configuration with separate compartments for an engine, passengers, and cargo. The first recorded use of ''sedan'' in reference to an automobile body occurred in 1912. The name derives from the 17th-century litter known as a sedan chair, a one-person enclosed box with windows and carried by porters. Variations of the sedan style include the close-coupled sedan, club sedan, convertible sedan, fastback sedan, hardtop sedan, notchback sedan, and sedanet. Definition A sedan () is a car with a closed body (i.e., a fixed metal roof) with the engine, passengers, and cargo in separate compartments. This broad definition does not differentiate sedans from various other car body styles. Still, in practice, the typical characteristics of sedans are: * a B-pillar (between the front and rear windows) that supports the roof; * two rows of seats; * a three-box design with the engine at the front and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1932 Ford
The term 1932 Ford may refer to three models of automobile produced by Ford Motors between 1932 and 1934: the Model B, the Model 18, and the Model 40. These succeeded the Model A. The Model B had an updated four-cylinder engine and was available from 1932 to 1934. The Model 18 was the first Ford fitted with the flathead V-8, and it was available in the Model 40 too in 1933 and 1934. The company also replaced the Model AA truck with the Model BB, available with either the four- or eight-cylinder engine. The three car models were replaced by the streamlined Model 48 in 1935 which used the same chassis as its predecessor. The 1937 Ford would be the last to use the old 1932 chassis until 1940 when the car line of Ford was completely redesigned. Technical Rather than just updating the Model A, Ford launched a completely new vehicle for 1932. The V8 was marketed as the Model 18 in its initial year, but was commonly known as the Ford V‑8. It had t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
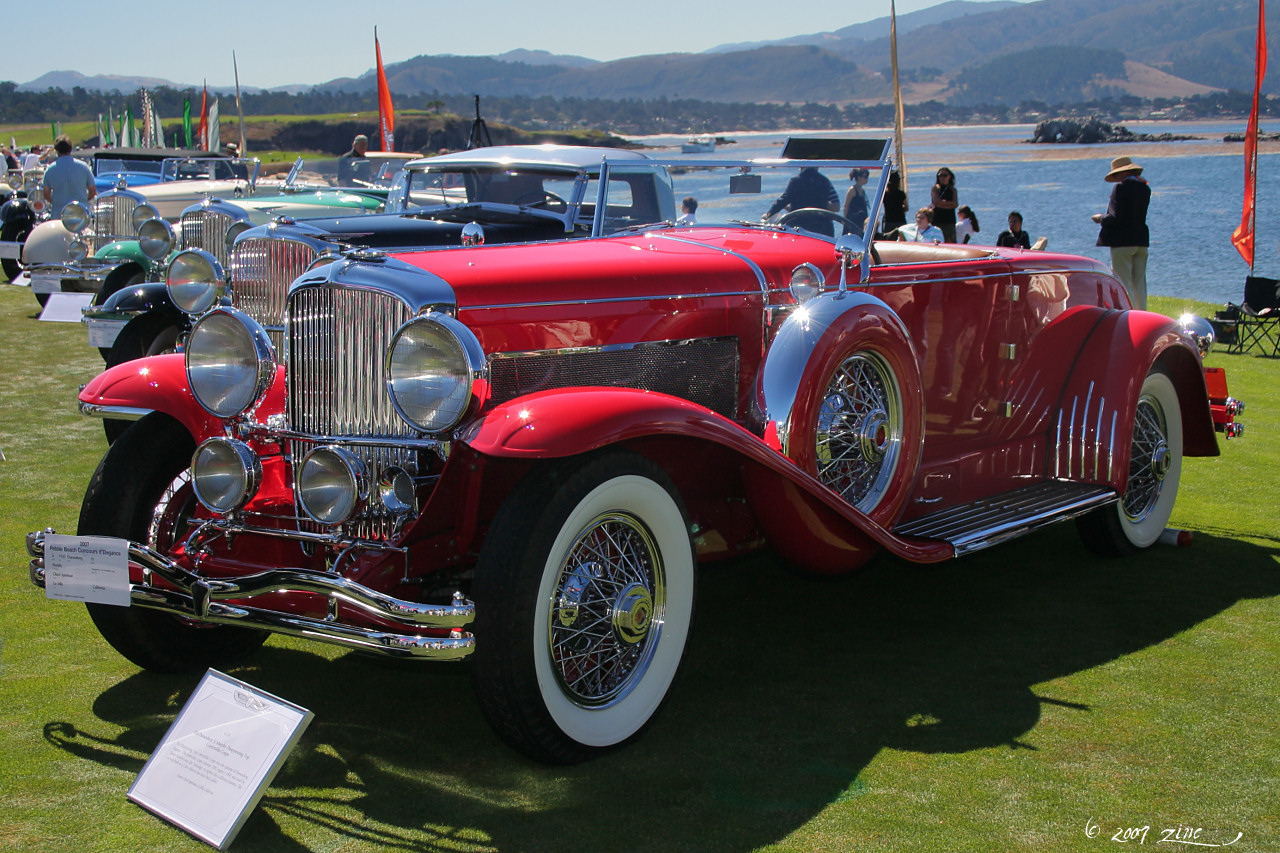
Duesenberg Model J
The Duesenberg Model J was a luxury automobile made by Duesenberg exclusively in 1928 and offered for ten subsequent years. Intended to compete with the most luxurious and powerful cars in the world, it was introduced in 1928, the year before the stock market crash that led to the Great Depression. Duesenberg Motors Company went bankrupt in 1937. Background E. L. Cord, the owner of Auburn Automobile Company, and other transportation firms, bought the Duesenberg Motor Corporation on October 26, 1926, for the brothers' engineering skills, talent and brand name. He intended to produce a car to rival the size, power, and luxury of top European brands such as Hispano-Suiza and Rolls-Royce. After Cord's takeover, the new company was renamed "Duesenberg, Inc." Fred Duesenberg would continue in the new organization with the title of vice president in charge of engineering and experimental work. Fred's brother August, who had played an important role in the development of the Model A an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hupp-Yeats
The Hupp-Yeats was an early American electric car manufactured in Detroit, Michigan from 1911 to 1916. The parent company was begun by Robert Craig Hupp, previously of the Hupp Motor Company as the R.C.H. Corporation through 1912, later becoming the Hupp-Yeats Electric Car Company. The Hupp-Yeats used Westinghouse motors with five selective speeds. The cars were built as four-seaters in both open and closed models, and came with standard solid rubber tires. Legacy Only a few of these cars are still known to exist completely. Most of these are in museums. References * External links Photo of the Hupp-Yeatsat the Reynolds-Alberta Museum in Wetaskiwin, Alberta Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ..., Canada. Defunct motor vehicle manufacturers of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
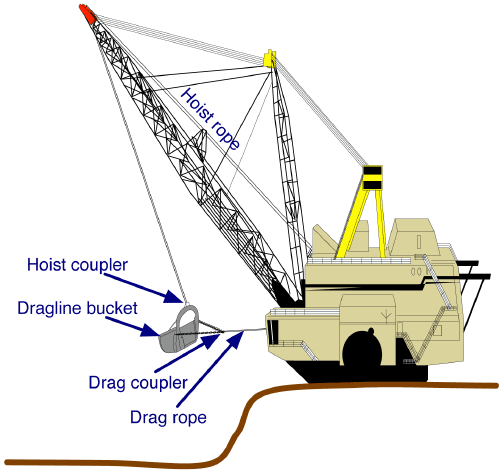
Dragline Excavator
A dragline excavator is a heavy-duty excavator used in civil engineering and surface mining. It was invented in 1904, and presented an immediate challenge to the steam shovel and its diesel and electric powered descendant, the power shovel. Much more efficient than even the largest of the latter, it enjoyed a heyday in extreme size for most of the 20th century, first becoming challenged by more efficient rotary excavators in the 1950s, then superseded by them on the upper end from the 1970s on. The largest ever walking dragline was Big Muskie, a Bucyrus-Erie 4250-W put online in 1969 that swung a , 325 ton capacity bucket, had a boom, and weighed 13,500 tons. The largest walking dragline produced as of 2014 was Joy Global’s digital AC drive control P&H 9020XPC, which has a bucket capacity of and boom lengths ranging from ; working weights vary between 7,539 and 8,002 tons. Types Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting crane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Shovel
A power shovel, also known as a motor shovel, stripping shovel, front shovel, mining shovel or rope shovel, is a bucket-equipped machine usually powered by steam, diesel fuel, gasoline or electricity and used for digging and loading earth or fragmented rock and for mineral extraction. Power shovels are a type of rope/cable excavator, where the digging arm is controlled and powered by winches and steel ropes, rather than hydraulics like in the modern hydraulic excavators. Basic parts of a power shovel include the track system, cabin, cables, rack, stick, boom foot-pin, saddle block, boom, boom point sheaves and bucket. The size of bucket varies from 0.73 to 53 cubic meters. Design Power shovels normally consist of a revolving deck with a power plant, drive and control mechanisms, usually a counterweight, and a front attachment, such as a crane ("boom") which supports a handle ("dipper" or "dipper stick") with a digger (" bucket") at the end. The term "dipper" is also sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucyrus-Erie
Bucyrus-Erie was an American surface and underground mining equipment company. It was founded as Bucyrus Foundry and Manufacturing Company in Bucyrus, Ohio, in 1880. Bucyrus moved its headquarters to South Milwaukee, Wisconsin, in 1893. In 1927, Bucyrus merged with the Erie Steam Shovel Company to form Bucyrus-Erie. In 1997, it was renamed Bucyrus International, Inc. In 2010 the enterprise was purchased by Caterpillar in a US$7.6 billion ($8.6 billion including net debt) transaction that closed on July 8, 2011. At the time of its acquisition, the Bucyrus product line included a range of material removal and material handling products used in both surface and underground mining. History 1880-1927 Bucyrus was an early producer of steam shovels in its Bucyrus, Ohio headquarters and manufacturing facility. In 1893, Bucyrus moved its operations to South Milwaukee, Wisconsin. In 1904 Bucyrus supplied 77 of the 102 steam shovels used to dig the Panama Canal. These were 95 ton model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travelling Exhibition
A travelling exhibition, also referred to as a "travelling exhibit" or a "touring exhibition", is a type of exhibition that is presented at more than one venue. Temporary exhibitions can bring together objects that might be dispersed among several collections, to reconstruct an original context such as an artist's career or a patron's collection, or to propose connections – perhaps the result of recent research – which give new insights or a different way of understanding items in museum collections. The whole exhibition, usually with associated services, including insurance, shipping, storage, conservation, mounting, set up, etc., can then be loaned to one or more venues to lengthen the life of the exhibition and to allow the widest possible audiences – regionally, nationally or internationally – to experience these objects and the stories they contain. Such collaborations can add interest to museums where displays of permanent collections might change only slowly, helpin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1917 Bucyrus Class 24 Dragline And 1929 Bucyrus Erie 200-B Stripping Shovel (2535705692)
Events Below, the events of World War I have the "WWI" prefix. January * January 9 – WWI – Battle of Rafa: The last substantial Ottoman Army garrison on the Sinai Peninsula is captured by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force's Desert Column. * January 10 – Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition: Seven survivors of the Ross Sea party are rescued after being stranded for several months. * January 11 – Unknown saboteurs set off the Kingsland Explosion at Kingsland (modern-day Lyndhurst, New Jersey), one of the events leading to United States involvement in WWI. * January 16 – The Danish West Indies is sold to the United States for $25 million (equivalent to $ million in ). * January 22 – WWI: United States President Woodrow Wilson calls for "peace without victory" in Germany. * January 25 – WWI: British armed merchantman is sunk by mines off Lough Swilly (Ireland), with the loss of 354 of the 475 aboard. * January 26 – The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |