|
Revived Cornish Stannary Parliament
The Revived Cornish Stannary Parliament ( Cornish: ''Seneth Stenegow Kernow''), was a pressure group which claimed to be a revival of the historic Cornish Stannary Parliament last held in 1753. It was established in 1974 and campaigned, up until 2008, against the government of the United Kingdom's position on the constitutional status of Cornwall. Status The historic Cornish Stannary Parliament last assembled at Truro in 1752, and continued until 11 September 1753. The RCSP formed in 1974 claims continuity from the historic parliament on the grounds that the English legal system does not recognise desuetude (laws lapsing through lack of use), and cites the precedent of the Court of Chivalry, which sat in 1952 for the first time in over 200 years. Their contention is that the Stannary Parliament, whilst not in session, still exists. They also point to the fact that the 1508 Charter of Pardon from which the historic parliament derived its powers, was confirmed as still being on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornish Language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or , ) is a Southwestern Brittonic language, Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. Along with Welsh language, Welsh and Breton language, Breton, Cornish descends from Common Brittonic, a language once spoken widely across Great Britain. For much of the Middle Ages, medieval period Cornish was the main language of Cornwall, until it was gradually pushed westwards by the spread of English language, English. Cornish remained a vernacular, common community language in parts of Cornwall until the mid-18th century, and there is some evidence for traditional speakers persisting into the 19th century. Cornish became extinct language, extinct as a living community language in Cornwall by the last speaker of the Cornish language, end of the 18th century, although knowledge of Cornish, including speaking ability to a certain extent, persisted within some families and individuals. Cornish language revival, A revival started in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Clay
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedron, tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedron, octahedral sheet of Aluminium oxide, alumina (). Kaolinite is a soft, earthy, usually white, mineral (dioctahedral phyllosilicate clay), produced by the chemical weathering of aluminium silicate minerals like feldspar. It has a low shrink–swell capacity and a low cation-exchange capacity (1–15 meq/100 g). Rocks that are rich in kaolinite, and halloysite, are known as kaolin () or china clay. In many parts of the world kaolin is colored pink-orange-red by iron oxide, giving it a distinct rust hue. Lower concentrations of iron oxide yield the white, yellow, or light orange colors of kaolin. Alternating lighter and darker layers are sometimes found, as at Providence Canyon State Park in Georgia, United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sine Die
Adjournment ''sine die'' (from Latin 'without a date') is the conclusion of a meeting by a deliberative assembly, such as a legislature or organizational board, without setting a date to reconvene. The assembly can reconvene, either in its present form or a reconstituted form, if preexisting laws and rules provide for this. Otherwise the adjournment effectively dissolves the assembly. A court may also adjourn a matter ''sine die'', which means that the matter is stayed until further notice. In a ''sine die'' adjournment of this type, the hearing stands open indefinitely, and could theoretically be resumed if the situation changed. For example, a case may be adjourned ''sine die'' if there is no possibility of proceeding in the foreseeable future, such as when the defendant is in prison and cannot participate in legal proceedings. United States usage The Congress of the United States customarily adjourns a session ''sine die'' on the morning of January 3, immediately before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord-lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility over the local militia was removed. However, it was not until 1921 that they formally lost the right to call upon able-bodied men to fight when needed. Lord-lieutenant is now an honorary titular position usually awarded to a notable person in the county, and despite the name, may be either male or female, peer or not. Origins England and Wales Lieutenants were first appointed to a number of English counties by King Henry VIII in the 1540s, when the military functions of the sheriffs were handed over to them. Each lieutenant raised and was responsible for the efficiency of the local militia units of his county, and afterwards of the yeomanry and volunteers. He was commander of these forces, whose officers he appointed. These commissions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magistrates' Court (England And Wales)
A magistrates' court is a lower court where, in several jurisdictions, all criminal proceedings start. Also some civil matters may be dealt with here, such as family proceedings. Courts * Magistrates' court (England and Wales) * Magistrates' court (Hong Kong) * District Court (Ireland), the main court of summary jurisdiction in Ireland * Magistrate's courts of Israel * Magistrate's Court of Jersey * Magistrates' Court (Kenya) * District Court (New Zealand), replaced magistrate's courts in 1980 * Magistrate's court (Russia) * Magistrate's court (South Africa) * Magistrate's court (Sri Lanka) * Magistrate court (West Virginia) Australian courts * Magistrates Court of the Australian Capital Territory * Magistrates court (Northern Territory) * Magistrates Court of Queensland * Magistrates Court of South Australia * Magistrates Court of Tasmania * Magistrates' Court of Victoria * Magistrates Court of Western Australia * Local Court of New South Wales * Federal Circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Austell
Saint Austell (, ; ) is a town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, south of Bodmin and west of the border with Devon. At the 2021 Census in the United Kingdom, census it had a population of 20,900. History St Austell was a village centred around the parish church, until the arrival of significant tin mining in the 18th century turned it into a town. St Austell is named after the 6th-century Cornish saint, St Austol, a disciple of St Mewan. In a Vatican manuscript there is a 10th-century list of Cornish parish saints. This includes Austoll, which means that the church and village existed at that time, shortly after 900. St Austell is not mentioned in Domesday Book (1086). However, A. L. Rowse, in his book ''St. Austell: Church, Town, and Parish'', cites records which show a church was dedicated on 9 October 1262 by Bishop Bronescombe, and other records show a church there in 1169, dedicated to "Sanctus Austolus". The current church dates from the 13th–14th centuries, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Office
The Home Office (HO), also known (especially in official papers and when referred to in Parliament) as the Home Department, is the United Kingdom's interior ministry. It is responsible for public safety and policing, border security, immigration, passports, and civil registration. Agencies under its purview include police in England and Wales, Border Force, UK Visas and Immigration, the Visas and Immigration authority, and the MI5, Security Service (MI5). It also manage policy on drugs, counterterrorism, and immigration. It was formerly responsible for His Majesty's Prison Service and the National Probation Service, but these have been transferred to the Ministry of Justice (United Kingdom), Ministry of Justice. The Cabinet minister responsible for the department is the Home Secretary, home secretary, a post considered one of the Great Offices of State; it has been held by Yvette Cooper since July 2024. The Home Office is managed from day to day by a civil servant, the Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
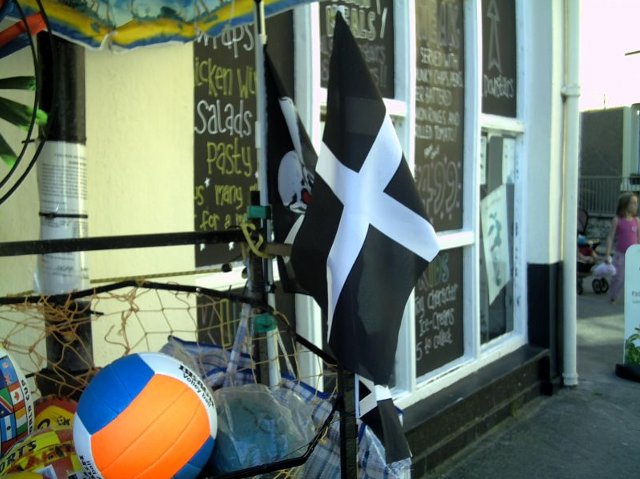
Saint Piran's Flag
Saint Piran's Flag () is the flag of Cornwall. The earliest known description of the flag, referred to as the Standard of Cornwall, was written in 1838. It is used by all Cornish people as a symbol of their identity. The flag is attributed to Saint Piran, a 5th-century Cornish abbot. But the white cross and black background design is also the coat of arms of the Saint-Perran (or Saint-Pezran) family from Cornouaille in Brittany, recorded from the 15th century. Origins The earliest known evidence of this flag was recorded by Davies Gilbert in his 1838 work: ''The Parochial History of Cornwall'', in which he gives reference to a white cross on a black ground hatwas formerly the banner of St Perran and the Standard of Cornwall; probably with some allusion to the black ore and the white metal of tin The fact that Gilbert identifies it as being "formerly" a standard of Cornwall implies that he believed it to have been used before 1838. However, Gilbert did not leave a rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Song Of The Western Men
"The Song of the Western Men", also known as "Trelawny", is a Cornish patriotic song, composed by Louisa T. Clare for lyrics by Robert Stephen Hawker. The poem was first published anonymously in ''The Royal Devonport Telegraph and Plymouth Chronicle'' in September 1826, over 100 years after the events. Background Hawker, a churchman, claimed authorship for the words except for the chorus. He assumed that the Trelawny mentioned in those three lines was Sir Jonathan Trelawny, the Bishop of Bristol, who had been imprisoned in the Tower of London by King James II in 1688. However it is more likely that it referred to his grandfather, Sir John Trelawny, a Cornish Royalist leader who had been imprisoned by parliament in 1628. The people of Cornwall did not actually march to rescue Trelawny, as told in the song. He was imprisoned in the Tower of London for three weeks, then tried and acquitted. Hawker's poem was set to music by Louisa T. Clare in 1861. Hawker was so pleased with C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornish National Tartan
Cornish is the adjective and demonym associated with Cornwall, the most southwesterly part of the United Kingdom. It may refer to: * Cornish language, a Brittonic Southwestern Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Cornwall * Cornish people ** Cornish Americans ** Cornish Australians ** Cornish Canadians ** Cornish diaspora * Culture of Cornwall Cornish may also refer to: Places United States * Cornish, Colorado * Cornish, Maine, a town ** Cornish (CDP), Maine, the primary village * Cornish, New Hampshire * Cornish, Oklahoma * Cornish, Utah * Cornish Township, Aitkin County, Minnesota * Cornish Township, Sibley County, Minnesota People * Cornish (surname) Animals and plants * Cornish Aromatic, apple cultivar * Cornish chicken * Cornish chough (''Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax''), a species in the family Corvidae * Cornish game hen * Cornish Rex, a breed of cat * Lucas Terrier, a Cornish breed of dog Sports * Cornish Wrestling, the ancient martial art, the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821), are published by Times Media, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'' were founded independently and have had common ownership only since 1966. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. ''The Times'' was the first newspaper to bear that name, inspiring numerous other papers around the world. In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as or , although the newspaper is of national scope and distribution. ''The Times'' had an average daily circulation of 365,880 in March 2020; in the same period, ''The Sunday Times'' had an average weekly circulation of 647,622. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |