|
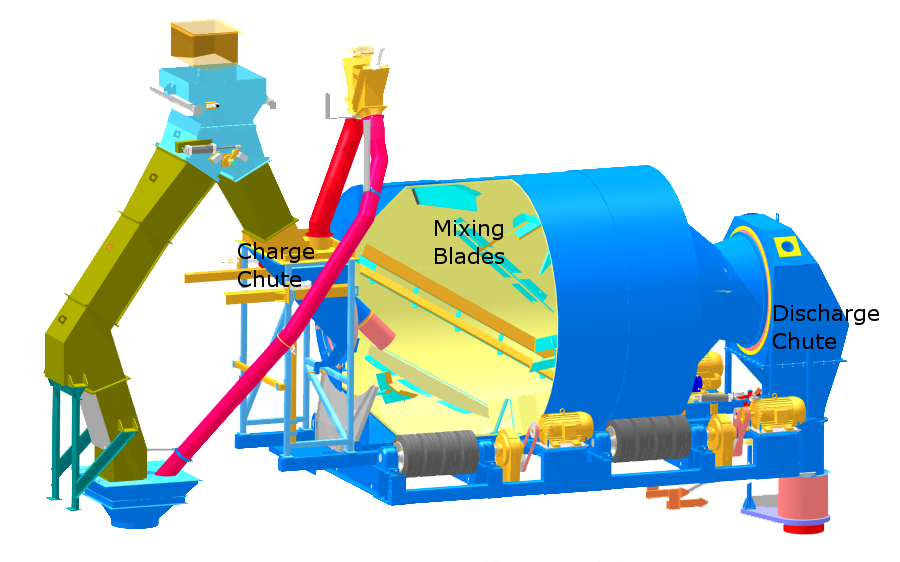
Reversing Drum Mixer
A reversing drum mixer (also commonly called a non-tilting mixer) is a type of concrete mixer that produces concrete in single batches. The entire drum rotates around its axis as materials are loaded through a charge chute at one end of the drum and exit through a discharge chute at the opposite end of the drum. Mixing Action Mixing blades are mounted on the inside surface of the drum, and as the drum rotates, the blades mix by lifting and dropping the materials during each rotation. Once the materials are sufficiently mixed the rotation of the drum is reversed and the blade arrangement pushes the concrete through to the discharge end of the mixer. Industrial sized reversing drum mixers can have a capacity of 9 m³ and can produce a mid quality concrete mix in as little as 40 seconds. Reversing drum mixers provide for efficient mixing and leave very little build up within the mixer. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete Mixer
A concrete mixer (also cement mixer) is a device that homogeneously combines cement, Construction aggregate, aggregate (e.g. sand or gravel), and water to form concrete. A typical concrete mixer uses a revolving drum to mix the components. For smaller volume works, portable concrete mixers are often used so that the concrete can be made at the construction site, giving the workers ample time to use the concrete before it hardens. An alternative to a machine is mixing concrete by hand. This is usually done in a wheelbarrow; however, several companies have recently begun to sell modified tarpaulin, tarps for this purpose. The concrete mixer was invented by Columbus, Ohio industrialist Gebhardt Jaeger. History One of the first concrete mixers ever was developed in 1900 by T.L. Smith in Milwaukee. The mixer already exhibited the still common basic construction with a tiltable conical drum (as double cone at that time) with blades. On February 9, 1904, the first portable concrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a ''center of rotation''. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientation (geometry), orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis, rotation around a axis. The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or ''autorotation''). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal ''spin axis'' can be called a ''pole''; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or ''orbit''), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chute (gravity)
A chute is a vertical or inclined plane, channel, or passage through which objects are moved by means of gravity. Landform A chute, also known as a race, flume, cat, or river canyon, is a steep-sided passage through which water flows rapidly. Akin to these, man-made chutes, such as the timber slide and log flume, were used in the logging industry to facilitate the downstream transportation of timber along rivers. These are no longer in common use. Man-made chutes may also be a feature of spillways on some dams. Some types of water supply and irrigation systems are gravity fed, hence chutes. These include aqueducts, puquios, and acequias. Building chutes Chutes are in common use in tall buildings to allow fast and efficient transport of items and materials from the upper floors to a central location on one of the lower floors, especially the basement. Chutes may be of a round, square or rectangular cross-section at the top and/or the bottom. * Laundry chutes in hotels are pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wear
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology. Wear in machine elements, together with other processes such as fatigue and creep, causes functional surfaces to degrade, eventually leading to material failure or loss of functionality. Thus, wear has large economic relevance as first outlined in the Jost Report. Abrasive wear alone has been estimated to cost 1–4% of the gross national product of industrialized nations. Wear of metals occurs by plastic displacement of surface and near-surface material and by detachment of particles that form wear debris. The particle size may vary from millimeters to nanometers. This process may occur by contact with other metals, nonmetallic solids, flowing liquids, solid particles or liquid droplets entrained in flowing gasses. The wear rate is affected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting in various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many List of polyurethane applications, different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, Potting (electronics), electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting a polymeric isocyanate with a polyol. Since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |