|
Renlandian Orogeny
The Renlandian Orogeny is a Tonian (early Neoproterozoic) tectonic and metamorphic event that is found in East Greenland, on Svalbard, on Ellesmere Island and in Scotland. It takes its name from Renland in East Greenland, where the event was first recognised. Identification This tectonic and metamorphic event was first identified at Renland where the 1040–920 Ma (ages relate to the youngest detrital zircons and timing of later intrusions) Krummedal Succession is folded and cut by an augen gneiss with an interpreted crystallisation age of 915 ± 18 Ma. In northeastern Svalbard latest Mesoproterozoic to early Neoproterozoic siliciclastic rocks are affected by the Nordaustlandet Orogeny, which has been directly correlated with the Renlandian. This medium-grade metamorphism and associated felsic magmatism affects the Krossfjorden Group (west Svalbard) and the Brennvinsfjord Group and Helvetesflya Formation (east Svalbard). In Scotland, the Renlandian event has been recognised in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonian
The Tonian (from grc, τόνος, tónos, meaning "stretch") is the first geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era. It lasted from to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined by the ICS based on radiometric chronometry. The Tonian is preceded by the Stenian Period of the Mesoproterozoic Era and followed by the Cryogenian. Rifting leading to the breakup of supercontinent Rodinia, which had formed in the mid-Stenian, occurred during this period, starting from 900 to 850 Mya. Biology The first putative metazoan (animal) fossils are dated to the middle to late Tonian ( 890-800 Mya). The fossils of ''Otavia antiqua'', which has been described as a sponge by its discoverers and numerous other scholars, date back to about 800 mya. Even earlier sponge-like fossils have been reported in reefs dating back to 890 million years before the present, but their identity is highly debated. This dating is consistent with molecular data recove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wester Ross Supergroup
The Wester Ross Supergroup is one of the subdivisions of the Neoproterozoic sequence of sedimentary rocks (or their metamorphic equivalents) in the Scottish Highlands. It lies unconformably on medium to high-grade metamorphic rocks and associated igneous rocks of the Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age Lewisian complex or locally over the Mesoproterozoic sedimentary rocks of the Stoer Group. The contact between the Wester Ross Supergroup and the next youngest of the Neoproterozoic sequences in the Scottish Highlands, the Loch Ness Supergroup, is everywhere a tectonic one. Stratigraphy The Wester Ross Supergroup consists of several groups that are geographically or structurally isolated from each other. The certainty of the correlation between the groups is variable, with the Torridon, Sleat and Morar groups considered as very likely to be lateral equivalents of each other, while the Iona and Tarskavaig groups and those on Shetland are likely but not proven. Torridon Group The Tor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Greenland
Greenland is the largest island on Earth. Only one-fifth of its surface area is exposed bedrock, the rest being covered by ice. The exposed surface is approximately 410,000 km2. The geology of Greenland is dominated by crystalline rocks of the Precambrian Shield."Greenland Geology." ''Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland''. 20 June 2003 (retrieved 26 Dec 2010) The crystalline rocks of the Nuuk/Qeqertarsuatsiaat area comprise some of the oldest bedrock in Greenland which covers most of western Greenland. The surface has been altered several times and has an appearance as though it were shaped billions of years ago. This is one of the reasons why the Nuuk area is extraordinary and also because the particular climate zone for the area limits the vegetation which makes it possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
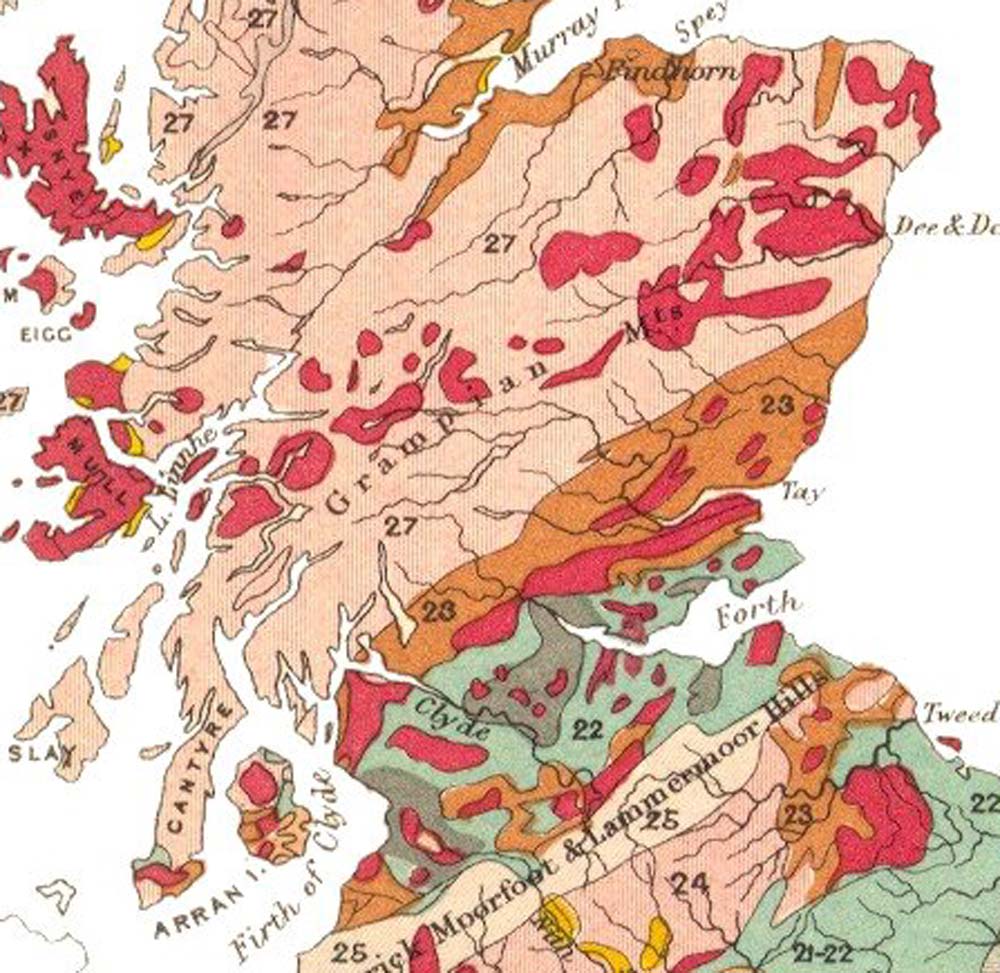
Geology Of Scotland
The geology of Scotland is unusually varied for a country of its size, with a large number of differing geological features.Keay & Keay (1994) page 415. There are three main geographical sub-divisions: the Highlands and Islands is a diverse area which lies to the north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault; the Central Lowlands is a rift valley mainly comprising Palaeozoic formations; and the Southern Uplands, which lie south of the Southern Uplands Fault, are largely composed of Silurian deposits. The existing bedrock includes very ancient Archean gneiss, metamorphic beds interspersed with granite intrusions created during the Caledonian mountain building period (the Caledonian orogeny), commercially important coal, oil and iron bearing carboniferous deposits and the remains of substantial Palaeogene volcanoes. During their formation, tectonic movements created climatic conditions ranging from polar to desert to tropical and a resultant diversity of fossil remains. Scotla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valhalla Orogeny
In Norse mythology Valhalla (;) is the anglicised name for non, Valhǫll ("hall of the slain").Orchard (1997:171–172) It is described as a majestic hall located in Asgard and presided over by the god Odin. Half of those who die in combat enter Valhalla, while the other half are chosen by the goddess Freyja to reside in Fólkvangr. The masses of those killed in combat (known as the Einherjar) along with various legendary Germanic heroes and kings, live in Valhalla until Ragnarök when they will march out of its many doors to fight in aid of Odin against the jötnar. Valhalla is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, in the ''Prose Edda'' (written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson), in ''Heimskringla'' (also written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson), and in stanzas of an anonymous 10th century poem commemorating the death of Eric Bloodaxe known as ''Eiríksmál'' as compiled in ''Fagrskinna''. Valhalla i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knoydartian Orogeny
The Knoydartian Orogeny is a Tonian (early Neoproterozoic) tectonic and metamorphic event, or group of events, that is recognised in the rocks of the Wester Ross and Loch Ness supergroups of the Scottish Highlands. It is dated to about 820–725 Ma (million years ago), predating the deposition of the Cryogenian to Cambrian Dalradian Supergroup. It is named after Knoydart, one of the localities where the event was first recognised. Identification Evidence for a Precambrian event affecting Moine rocks (as then understood) came from the identification of a set of "older" pegmatites, thought to predate Caledonian tectonic and metamorphic effects, in a number of localities, including Morar and Knoydart, in the 1960s. The terms "Morarian" and Knoydartian" were both used to describe this event. It was dated to about 740 Ma (million years ago). As more dating was carried out on samples covering a larger geographical area, using techniques with significantly greater precision, the full a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion (geology)
Accretion, in geology, is a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate at a subduction zone, frequently on the edge of existing continental landmasses. The added material may be sediment, volcanic arcs, seamounts, oceanic crust or other igneous features. Description Accretion involves the addition of material to a tectonic plate via subduction, the process by which one plate is forced under the other when two plates collide. The plate which is being forced down, the subducted plate, is pushed against the upper, over-riding plate. Sediment on the ocean floor of the subducting plate is often scraped off as the plate descends. This accumulated material is called an accretionary wedge (or accretionary prism), which is pushed against and attaches to the upper plate. In addition to accumulated ocean sediments, volcanic island arcs or seamounts present on the subducting plate may be amalgamated onto existing continental crust on the upper plate, increasing the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat-slab Subduction
Flat slab subduction is characterized by a low subduction angle (<30 degrees to horizontal) beyond the and a resumption of normal subduction far from the . A slab refers to the subducting lower plate. Although, some would characterize flat slab as any shallowly dipping lower plate as in western . Flat slab |
Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent. Rodinia formed at c. 1.23 Ga by accretion and collision of fragments produced by breakup of an older supercontinent, Columbia, assembled by global-scale 2.0–1.8 Ga collisional events.; Rodinia broke up in the Neoproterozoic with its continental fragments reassembled to form Pannotia 633–573 million years ago. In contrast with Pannotia, little is known yet about the exact configuration and geodynamic history of Rodinia. Paleomagnetic evidence provides some clues to the paleolatitude of individual pieces of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells brin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Ness Supergroup
The Loch Ness Supergroup is one of the subdivisions of the Neoproterozoic sequence of sedimentary rocks (or their metamorphic equivalents) in the Scottish Highlands. It is found everywhere in tectonic contact above the older Wester Ross Supergroup. It is thought to be unconformably overlain by the Cryogenian to Cambrian Dalradian Supergroup. Stratigraphy The supergroup is subdivided into three groups. Glenfinnan Group This group, which consists of amphibolite facies pelitic gneiss and interbanded pelite, semi-pelite, psammite, quartzite and migmatites, lies tectonically above the Sgurr Beag Thrust and below the Loch Eil Group. There is evidence of a true stratigraphic transition between these two groups in some areas. Slices of Lewisian-type gneisses are found above the Sgurr Beag Thrust and are interpreted to represent pieces of basement to the group, with a highly sheared unconformable contact, incorporated during the Caledonian orogeny. The original stratigraphic thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |