|
Renewables Advisory Board
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind power, and hydropower. Bioenergy and geothermal power are also significant in some countries. Some also consider Nuclear power proposed as renewable energy, nuclear power a renewable power source, although this is controversial, as nuclear energy requires mining uranium, a nonrenewable resource. Renewable energy installations can be large or small and are suited for both urban and rural areas. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification. This has several benefits: electricity can heat pump, move heat and Electric vehicle, vehicles efficiently and is clean at the point of consumption. Variable renewable energy sources are those that have a fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power. In contrast, ''contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downstream of the Three Gorges. The List of reservoirs by volume, world's 27th largest dam by reservoir volume, and the List of largest power stations, world's largest power station by installed capacity (22,500 Megawatt, MW), the Three Gorges Dam generates 95±20 TWh of electricity per year on average, depending on the amount of precipitation in the river basin. After the extensive monsoon rainfalls of 2020, the dam produced nearly 112 TWh in a year, breaking the previous world record of ~103 TWh set by the Itaipu Dam in 2016. The dam's body was completed in 2006; the power plant became fully operational in 2012, when the last of the main water turbines in the underground plant began production. The last major component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that uses electricity to transfer heat from a colder place to a warmer place. Specifically, the heat pump transfers thermal energy using a heat pump and refrigeration cycle, cooling the cool space and warming the warm space. In winter a heat pump can move heat from the cool outdoors to warm a house; the pump may also be designed to move heat from the house to the warmer outdoors in summer. As they transfer heat rather than generating heat, they are more energy-efficient than heating by gas boiler. A gaseous refrigerant is compressed so its pressure and temperature rise. When operating as a heater in cold weather, the warmed gas flows to a heat exchanger in the indoor space where some of its thermal energy is transferred to that indoor space, causing the gas to condense into a liquid. The liquified refrigerant flows to a heat exchanger in the outdoor space where the pressure falls, the liquid evaporates and the temperature of the gas falls. It is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
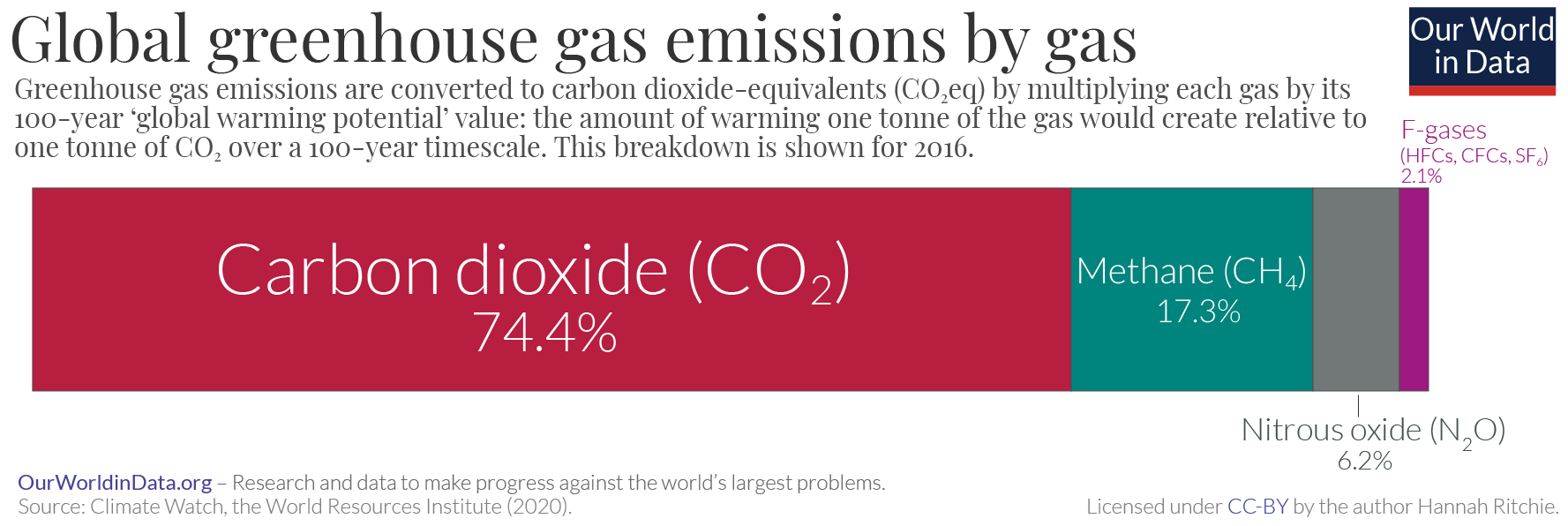
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality. It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a registered charity in England and Wales, and was founded by Max Roser, a social historian and development economist. The research team is based at the University of Oxford. The organization is chaired by Hetan Shah. Content Our World in Data uses interactive charts and maps to illustrate research findings, often taking a long-term view to show how global living conditions have changed over time. Two-centuries-World-as-100-people.png, Compilation of graphs from the organization, showing the overall global percentages of the last two centuries, in six factors: extreme poverty, democracy, basic education, vaccination, literacy, and child mortality Global annual CO2 emissions by world region since 1750.svg, Global emi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Energy
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geological formations. Reservoirs of such compound mixtures, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas, can be extracted and burnt as fuel for human consumption to provide energy for direct use (such as for cooking, heating or lighting), to power heat engines (such as steam or internal combustion engines) that can propel vehicles, or to generate electricity via steam turbine generators. Some fossil fuels are further refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and diesel, or converted into petrochemicals such as polyolefins ( plastics), aromatics and synthetic resins. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The conversion from these organic materials to high-carbon fossil fuels is typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity generation. Today, wind power is generated almost completely using wind turbines, generally grouped into wind farms and connected to the electrical grid. In 2024, wind supplied over 2,494 TWh of electricity, which was 8.1% of world electricity. With about 100 Gigawatt, GW added during 2021, mostly Wind power in China, in China and the Wind power in the United States, United States, global installed wind power capacity exceeded 800 GW. 30 countries generated more than a tenth of their electricity from wind power in 2024 and wind generation has nearly tripled since 2015. To help meet the Paris Agreement goals to Climate change mitigation, limit climate change, analysts say it should expand much faster – by over 1% of electricity generation p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaic System
A photovoltaic system, also called a PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. Many utility-scale PV systems use tracking systems that follow the sun's daily path across the sky to generate more electricity than fixed-mounted systems. Photovoltaic systems convert light directly into electricity and are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling. A solar array only encompasses the solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as the balance of system (BOS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Renewable Energy Production By Countries And Sources In 2023
Global may refer to: General *Globe, a spherical model of celestial bodies *Earth, the third planet from the Sun Entertainment * ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003 * ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007 * ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989 * ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015 * Bruno J. Global, a character in the anime series ''The Super Dimension Fortress Marcoss'' Companies and brands Television * Global Television Network, in Canada ** Canwest Global, former parent company of Global Television Network ** Global BC, on-air brand of CHAN-TV, a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Calgary ** Global Edmonton ** Global Halifax ** Global Montreal ** Global News, the news division of the Global Television Network ** Global Okanagan, on-air brand of CHBC-TV, a television station in Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Toronto, a television station in Toronto * Global TV (Venezuela), a regional channel in Venezuela * Global TV, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that is derived from plants and animal waste. The Biomass (energy), biomass that is used as input materials consists of recently living (but now dead) organisms, mainly plants. Thus, Fossil fuel, fossil fuels are not regarded as biomass under this definition. Types of biomass commonly used for bioenergy include wood, food crops such as corn, energy crops and waste from forests, yards, or farms. Bioenergy can help with climate change mitigation but in some cases the required biomass production can increase greenhouse gas emissions or lead to local biodiversity loss. The environmental impacts of biomass production can be problematic, depending on how the biomass is produced and harvested. But it still produces CO2; so long as the energy is derived from breaking chemical bonds. The International Energy Agency, IEA's Net Zero by 2050 scenario calls for traditional bioenergy to be phased out by 2030, with modern bioenergy's share increasing fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Renewable Energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or bioenergy, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |