|
Relicinopsis
''Relicina'' is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. It contains 60 species. Taxonomy ''Relicina'' was originally conceived as a series of the large genus '' Parmelia'' by lichenologists Mason Hale and Syo Kurokawa in 1964. A decade later, they promoted it to the status of genus. The genus ''Relicinopsis'', proposed by Australian lichenologists John Elix and Doug Verdon in 1986 as a segregate of '' Pseudoparmelia'', was shown to be nested within ''Relicina'' in a 2017 molecular phylogenetics study. Description ''Relicina'' lichens have a leaf-like (foliose) body (thallus) with flat, two-sided that are typically attached by a somewhat swollen, bulbous base. The edge of each lobe is lined with short, black, hair-like structures called . The upper surface is generally yellow to yellow-green and may sometimes show small spots; it lacks the typical hairs and minute pores (pseudocyphellae) seen in some other lichens. Instead, the surface is cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoparmelia
''Pseudoparmelia'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Parmeliaceae. The genus has a pantropical distribution. Taxonomy It was circumscribed by Bernt Arne Lynge in 1914, who distinguished the genus from '' Parmelia'' by the presence of pseudocyphellae on the underside of the lichen thallus. However, this distinguishing characteristic was later shown to be an artifact caused by torn rhizines. The genus was not widely accepted until it was redefined by Mason Hale in the 1970s to include lichens with a pored and narrow, non-ciliate lobes. Further research revealed that this broader definition included a heterogeneous group of species, leading to a more restricted circumscription with most species being transferred to other genera. Molecular phylogenetics studies have shown that ''Pseudoparmelia'' forms a distinct lineage within the Parmeliaceae, closely related to the genera '' Relicina'' and ''Relicinopsis''. These three genera share features including a pored , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmeliaceae
The Parmeliaceae is a large and diverse family of Lecanoromycetes. With over 2700 species in 71 genera, it is the largest family of lichen-forming fungi. The most speciose genera in the family are the well-known groups: '' Xanthoparmelia'' ( 822 species), '' Usnea'' (355 species), '' Parmotrema'' ( 255 species), and '' Hypotrachyna'' (262 species). Nearly all members of the family have a symbiotic association with a green alga (most often ''Trebouxia'' spp., but ''Asterochloris'' spp. are known to associate with some species).Miadlikowska, J. ''et al.'' (2006). New insights into classification and evolution of the Lecanoromycetes (Pezizomycotina, Ascomycota) from phylogenetic analyses of three ribosomal RNA- and two protein-coding genes. ''Mycologia'' 98: 1088-1103. http://www.mycologia.org/cgi/reprint/98/6/1088.pdf The majority of Parmeliaceae species have a foliose, fruticose, or subfruticose growth form. The morphological diversity and complexity exhibited by this group i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmelia (fungus)
''Parmelia'' is a genus of medium to large foliose lichen, foliose (leafy) lichens.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, It has a global distribution, extending from the ArcticSkult H (1985) A New Subspecies of ''Parmelia omphalodes'' Ascomycetes Described from the Arctic. Annales Botanici Fennici 22, 201-6. to the Antarctic continentD.C. Lindsay (1973) Notes on Antarctic lichens: IV. The genera ''Cetraria'' Hoffm., ''Hypogymnia'' (Nyl.) Nyl., ''Menegazzia'' Massal, ''Parmelia'' Ach. and ''Platismatia'' Culb. et Culb. British Antarctic Survey Bulletin 36, 105-114. but concentrated in temperate regions. There are about 40 species in ''Parmelia''. In recent decades, the once large genus ''Parmelia'' has been divided into a number of smaller genera according to thallus (tissue), thallus morphology and phylogenetic relatedness. It is a foliaceous lichen, resembling a leaf in shape. The ends of the leaf-like lobes are often squarish-tippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebouxia
''Trebouxia'' is a unicellular green alga. It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions.Erokhina, L. G., Shatilovich, A. V., Kaminskaya, O. P., & Gilichinskii, D. A. (2004). Spectral Properties of the Green Alga ''Trebouxia'', a Phycobiont of Cryptoendolithic Lichens in the Antarctic Dry Valley. Microbiology,73(4), 420-424. doi:10.1023/b:mici.0000036987.18559Lukesova, A., & Frouz, J. (2007). Soil and Freshwater Micro-Algae as a Food Source for Invertebrates in Extreme Environments. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments,265-284. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7_14Seckbach, J. (2007). Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Dordrecht: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7Seckbach, J. (2002). Symbiosis: Mechanisms and model systems. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.John, D. M., Whitton, B. A., & Brook, A. J. (2002). The freshwater algal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnidia
A pycnidium (plural pycnidia) is an asexual fruiting body produced by mitosporic fungi, for instance in the order Sphaeropsidales ( Deuteromycota, Coelomycetes) or order Pleosporales (Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes). It is often spherical or inversely pearshaped ( obpyriform) and its internal cavity is lined with conidiophore A conidium ( ; : conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (: chlamydoconidia), is an Asexual reproduction, asexual, non-motility, motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word f ...s. When ripe, an opening generally appears at the top, through which the pycnidiospores escape. References {{reflist Further reading *Kulik, Martin M. "Symptomless infection, persistence, and production of pycnidia in host and non-host plants by Phomopsis batatae, Phomopsis phaseoli, and Phomopsis sojae, and the taxonomic implications." Mycologia(1984): 274–291. *Calpouzos, L., and D. B. Lapis. "Effects of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are o ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
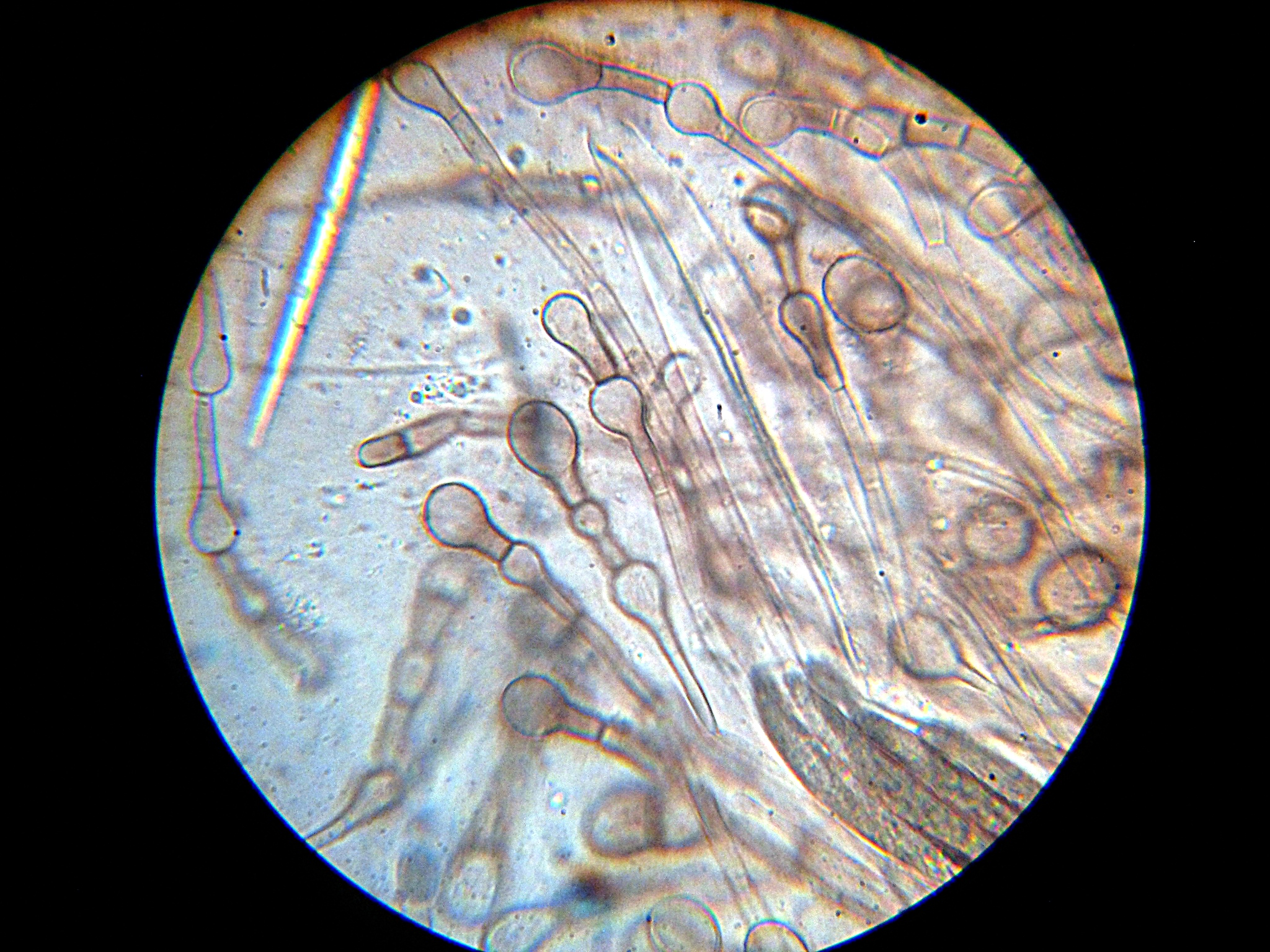
Ascus
An ascus (; : asci) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. '' Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. '' Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some '' Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism. ''Photosynthesis'' usually refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms store the chemical energy so produced within intracellular organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism's cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth. Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
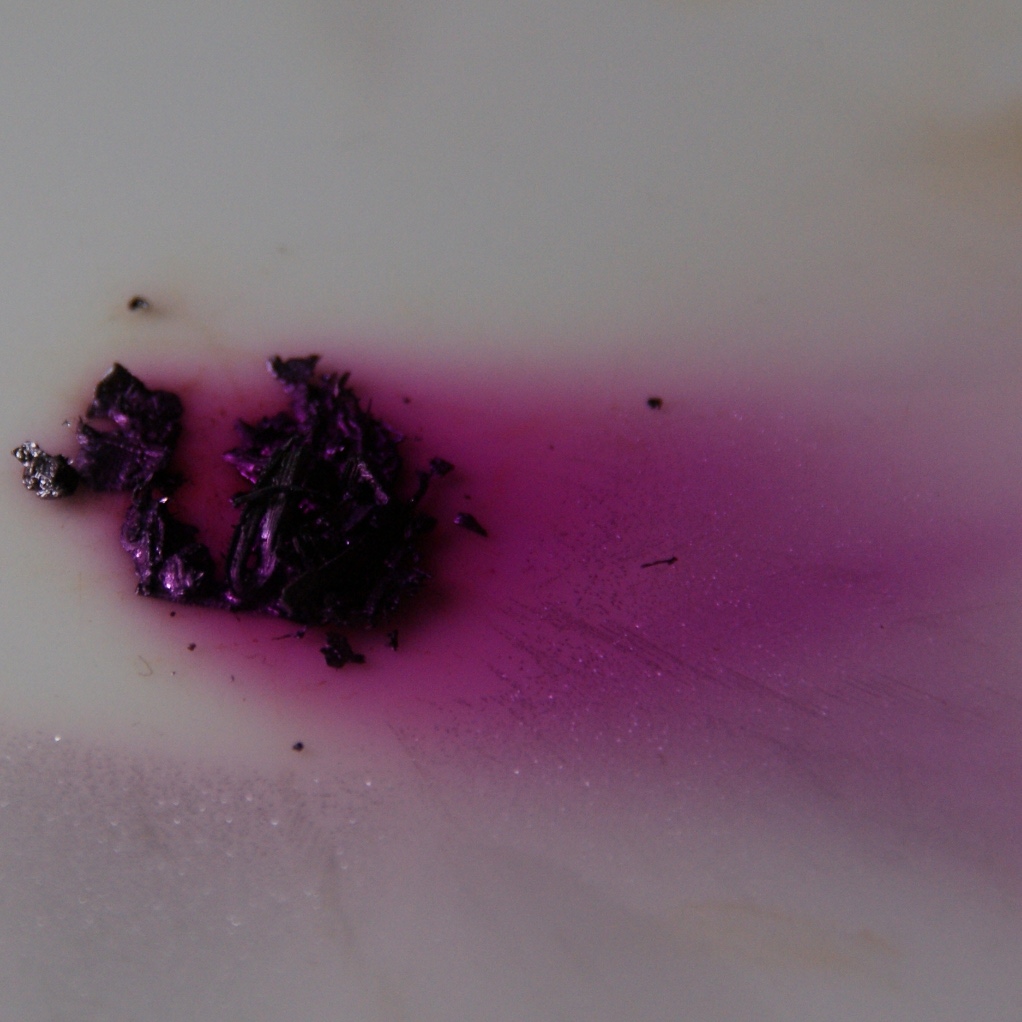
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |