|
Reinhold Rehs
Reinhold Rehs (12 October 1901 – 4 December 1971) was a German politician and chairman of the Federation of Expellees in 1967-70. Rehs was born in Klinthenen (now Znamenka in Pravdinsky District), district of Gerdauen, East Prussia (today Russia) as a son of a teacher of Huguenot descent, his family lived in East Prussia since their flight from France. He visited school in Königsberg and studied law at the Universities of Königsberg and Heidelberg. He worked as a journalist for the "Ostpreußische Zeitung" in Königsberg (1923–24) and became a lawyer there in 1928.Biography at munzinger.de He joined the SA in 1933 and the |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Königsberg
The University of Königsberg () was the university of Königsberg in Duchy of Prussia, which was a fief of Poland. It was founded in 1544 as the world's second Protestant Reformation, Protestant academy (after the University of Marburg) by Duke Albert, Duke of Prussia, Albert of Prussia and charted by the King Sigismund II Augustus. It was commonly known as the Albertina and served as a Protestant counterpart to the Catholic Jagiellonian University in Kraków. Following World War II, the city of Königsberg was transferred to the Soviet Union according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement, and renamed Kaliningrad in 1946. The Albertina was closed and the remaining German population Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), expelled, by the terms of the Potsdam Agreement. Today, the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University in Kaliningrad claims to maintain the traditions of the Albertina. History Albert, former Grand Master of the Teutonic Order and first Duchy of Prussia, Duke of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Warsaw (1970)
The Treaty of Warsaw (, ) was a treaty between the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) and the Polish People’s Republic. It was signed by Chancellor Willy Brandt and Prime Minister Józef Cyrankiewicz at the Presidential Palace on 7 December 1970, and it was ratified by the West German Bundestag on 17 May 1972. In the treaty, both sides committed themselves to nonviolence and accepted the existing border—the Oder–Neisse line, imposed on Germany by the Soviet Union in 1945 following the end of World War II. This had been a quite sensitive topic since then, as Poland was concerned that a German government might seek to reclaim some of the former eastern territories. From the Polish perspective, the transfer of these regions was considered to be a compensation for the former Polish territory east of the Curzon Line (" Kresy"), which had been annexed by the Soviet Union in 1939. In West Germany, Brandt was heavily criticised by the conservative CDU/ CSU opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostpolitik
''Neue Ostpolitik'' (German for "new eastern policy"), or ''Ostpolitik'' () for short, was the normalization of relations between the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG, or West Germany) and Eastern Europe, particularly the German Democratic Republic (GDR, or East Germany) beginning in 1969. Influenced by Egon Bahr, who proposed "change through rapprochement" in a 1963 speech at the Evangelische Akademie Tutzing, the policies were implemented beginning with Willy Brandt, fourth Chancellor of the FRG from 1969 to 1974, and winner of the 1971 Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts to place this policy at the acme of the FRG. ''Ostpolitik'' was an effort to break with the policies of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), which was the elected government of West Germany from 1949 until 1969. The Christian Democrats under Konrad Adenauer and his successors tried to combat the Communist government of East Germany, while Brandt's Social Democrats tried to achieve a certain degree of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
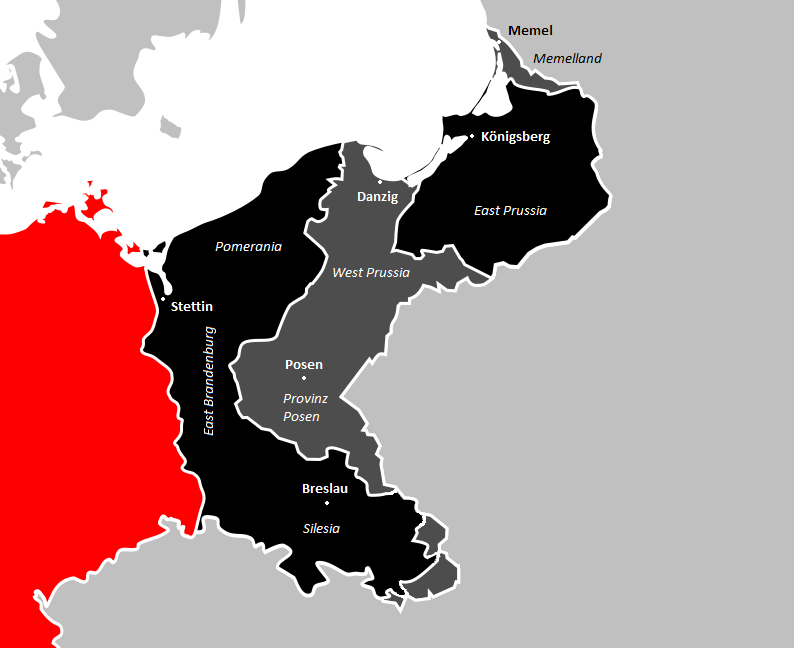
Former Eastern Territories Of Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union after World War II. In contrast to the lands awarded to the restored Polish state by the Treaty of Versailles after World War I, the German territories lost with the post-World War II Potsdam Agreement were either almost exclusively inhabited by Germans before 1945 (the bulk of East Prussia, Lower Silesia, Farther Pomerania, and parts of Western Pomerania, Lusatia, and Neumark), mixed German– Polish with a German majority (the Posen–West Prussia Border March, Lauenburg and Bütow Land, the southern and western rim of East Prussia, Ermland, Western Upper Silesia, and the part of Lower Silesia east of the Oder), or mixed German– Czech with a German majority ( Glatz). Virtually the entire German popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willy Brandt
Willy Brandt (; born Herbert Ernst Karl Frahm; 18 December 1913 – 8 October 1992) was a German politician and statesman who was leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) from 1964 to 1987 and concurrently served as the Chancellor of Germany, chancellor of West Germany from 1969 to 1974. He was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1971 Nobel Peace Prize, 1971 for his efforts to strengthen cooperation in Western Europe through the EEC and to achieve reconciliation between West Germany and the countries of Eastern Europe. He was the first Social Democratic chancellor since 1930. Fleeing to Norway and then Sweden during the Nazi regime and working as a left-wing politics, left-wing journalist, he took the name Willy Brandt as a pseudonym to avoid detection by Nazi agents, and then formally adopted the name in 1948. Brandt earned initial fame as Governing Mayor of Berlin, governing mayor of West Berlin. He served as the Minister for Foreign Affairs (Germany), foreign minis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsmannschaft Ostpreussen
Landsmanschaft could refer to: * Landsmanshaft, a type of Jewish mutual-aid organisation * Landsmannschaft (Studentenverbindung), a German students' fraternity * Organizations of German refugees from former eastern territories ** Landsmannschaft Schlesien ** Landsmannschaft Ostpreußen ** Landsmannschaft Westpreußen ** Landsmannschaft Weichsel-Warthe Bundesverband ** Landsmannschaft der Banater Schwaben ** Landsmannschaft der Bessarabiendeutschen ** Landsmannschaft der Buchenlanddeutschen ** Landsmannschaft der Deutschen aus Russland ** Landsmannschaft der Deutschen aus Ungarn ** Landsmannschaft der Siebenbürger Sachsen in Deutschland ** Landsmannschaft der Deutschen aus Litauen ** Karpatendeutsche Landsmannschaft Slowakei ** Pommersche Landsmannschaft ** Sudetendeutsche Landsmannschaft ** Deutsch-Baltische Gesellschaft See also * All-German Bloc/League of Expellees and Deprived of Rights * Federation of Expellees * Organised persecution of ethnic Germans * German eastward set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag Of Schleswig-Holstein
The Schleswig-Holstein Landtag is the state parliament of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It convenes in the state's capital Kiel and currently consists of 69 members of five parties. The current majority consists of a coalition of the Christian Democratic Union and the Greens, supporting the cabinet of Minister President Daniel Günther. The Landtag maintains partnerships with the parliament of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, the Oblast Duma of the Kaliningrad Oblast and the parliament of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. Location Since 1950, the Landtag convenes in the Landeshaus in Kiel, which was built in 1888 as the Royal Marine Academy. During the Nazi era, the Landeshaus served as the seat of the German Navy's Baltic Sea Command. Up to 1950, the Landtag convened in Lübeck, Flensburg and Eckernförde as well as in Kiel. Since its renovation in 2003, the Landtag sits in a new chamber in the Landeshaus. Electoral system The Landtag is elected via mixed-member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. Schleswig, named South Jutland at the time, was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it became a duchy within Denmark due to infighting in the Danish Royal House. It bordered Holstein, which was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. Beginning in 1460, the King of Denmark ruled both Schleswig and Holstein as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Hannibal
Operation Hannibal was a German naval operation involving the evacuation by sea of German troops and civilians from the Courland Pocket, East Prussia, West Prussia and Pomerania from mid-January to May 1945 as the Red Army advanced during the East Prussian and East Pomeranian Offensives and subsidiary operations. The operation was one of the largest evacuations by sea in history. Background Planning for Operation Hannibal started in late 1944, although it was done quietly since Hitler opposed such measures. The coordination of the evacuations was entrusted to Rear Admiral . By the end of 1944, Engelhardt had assembled a fleet of 22 former passenger liners, each weighing over . Overall responsibility of the operation went to Admiral Oskar Kummetz. In early 1945, the Germans had two Escort Divisions in the area, the and the . () The 9th Escort Division mainly consisted of lightly armed minesweepers. The East Prussian Offensive by the Red Army's 3rd Belarusian Front under Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |