|
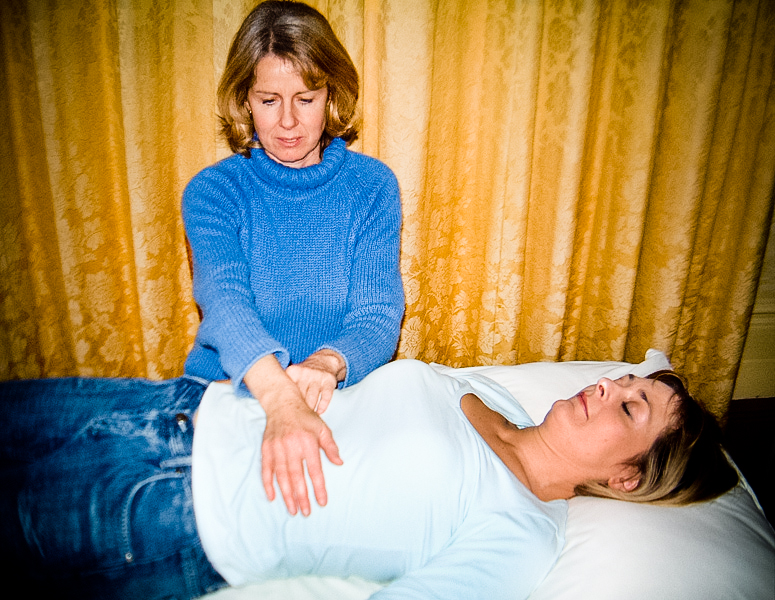
Reiki Practitioners
Reiki is a pseudoscientific form of energy healing, a type of alternative medicine originating in Japan. Reiki practitioners use a technique called ''palm healing'' or ''hands-on healing'' through which, according to practitioners, a " universal energy" is transferred through the palms of the practitioner to the client, to encourage emotional or physical healing. It is based on qi ("chi"), which practitioners say is a universal life force, although there is no empirical evidence that such a life force exists. Reiki is used as an illustrative example of pseudoscience in scholarly texts and academic journal articles. The marketing of reiki has been described as "fraudulent misrepresentation", and itself as a "nonsensical method", with a recommendation that the American government agency NCCAM should stop funding reiki research because it "has no substantiated health value and lacks a scientifically plausible rationale". Clinical research does not show reiki to be effective a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese ( or ) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and List of ethnic groups in China, many minority ethnic groups in China, as well as by various communities of the Chinese diaspora. Approximately 1.39 billion people, or 17% of the global population, speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic languages, Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be dialects of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered to be separate languages in a Language family, family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin with 66%, or around 800&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trends In Molecular Medicine
A fad, trend, or craze is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation, or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short time period. Fads are objects or behaviors that achieve short-lived popularity but fade away. Fads are often seen as sudden, quick-spreading, and short-lived events. Fads include diets, clothing, hairstyles, toys, and more. Some popular fads throughout history are toys such as yo-yos, hula hoops, and fad dances such as the Macarena, floss and the twist. Similar to habits or customs but less durable, fads often result from an activity or behavior being perceived as popular or exciting within a peer group, or being deemed " cool" as often promoted by social networks.Kornblum (2007), p. 213. A fad is said to "catch on" when the number of people adopting it begins to increase to the point of being noteworthy or going viral. Fads often fade quickly when the perception of novelty is gone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Publishers (United States)
Universal Publishers is the parent publishing company of three non-fiction book imprints specializing in nonfiction, how-to, technical and academic titles (Universal-Publishers, BrownWalker Press & Dissertation.com). It originally began in 1997 as "Dissertation.com," one of the first companies to use print on-demand and PDF (Portable Document Format) e-book technologies to publish academic theses and Ph.D. dissertations for sale online. The company was founded by Jeffrey R. Young, while he was in graduate school as a way to make academic dissertations widely available to other students and researchers at a reasonable price. The ''BrownWalker Press'' imprint was launched in 2001 to publish academic textbooks, scholarly monographs, and edited collections across a wide range of academic expertise. In 2010, BrownWalker Press added an academic conference proceeding publishing division (ConferencePaper Publisher). Universal Publishers has over 1500 nonfiction, how-to , and academic ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Journal
An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the dissemination, scrutiny, and discussion of research. Unlike professional magazines or Trade magazine, trade magazines, the articles are mostly written by researchers rather than staff writers employed by the journal. They nearly universally require peer review for Research Article, research articles or other scrutiny from contemporaries competent and established in their respective fields. Academic journals trace their origins back to the 17th century. , it is estimated that over 28,100 active academic journals are in publication, with scopes ranging from the general sciences, as seen in journals like ''Science (journal), Science'' and ''Nature (journal), Nature'', to highly specialized fields. These journals publish a variety of articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Dunning (author)
Brian Andrew Dunning (born 1965) is an American writer and producer who focuses on science and skepticism. He has hosted a weekly podcast, ''Skeptoid'', since 2006, and he is an author of a series of books on the subject of scientific skepticism, some of which are based on the podcast. ''Skeptoid'' has been the recipient of several podcast awards such as the Parsec Award. Dunning has also created the ''Skeptoid.org'' spin-off video series, ''inFact'', and ''The Feeding Tube'' both available on YouTube. Dunning has produced two educational films on the subject of critical thinking: ''Here Be Dragons'' in 2008, and ''Principles of Curiosity'' in 2017. Dunning co-founded Buylink, a business-to-business service provider, in 1996, and served at the company until 2002. He later became eBay's second-biggest affiliate marketer; he has since been convicted of wire fraud through a cookie stuffing scheme, for his company fraudulently obtaining between $200,000 and $400,000 from eBay. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council Against Health Fraud
The National Council Against Health Fraud (NCAHF) was a not-for-profit, US-based organization, that described itself as a "private nonprofit, voluntary health agency that focuses upon health misinformation, fraud, and quackery as public health problems." History According to archived website, the NCAHF evolved from three separate organizations. The Lehigh Valley Committee Against Health Fraud, Inc. (LVCAHF, now called Quackwatch) was founded in 1969 by Stephen Barrett and H. William Gross, Dental degree, D.D.S. in Allentown, Pennsylvania. The Southern California Council Against Health Fraud (SCCAHF) had its origin in 1976 at Loma Linda University with academic colleagues William T. Jarvis and Gordon Rick as co-founders. Thomas H. Jukes of University of California, Berkeley founded the third organization, an unnamed group in northern California. For a time between 1998 and 2000, the NCAHF operated under the name National Council for Reliable Health Information (NCRHI). The organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placebo Effect
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures. Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials to test the efficacy of medical treatments. In a placebo-controlled trial, any change in the control group is known as the ''placebo response'', and the difference between this and the result of no treatment is the ''placebo effect''. Placebos in clinical trials should ideally be indistinguishable from so-called verum treatments under investigation, except for the latter's particular hypothesized medicinal effect. This is to shield test participants (with their consent) from knowing who is getting the placebo and who is getting the treatment under test, as patients' and clinicians' expectations of efficacy can influence results. The idea of a placebo effect was discussed in 18th century psychology, but became more prominent in the 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Council Against Health Fraud
The National Council Against Health Fraud (NCAHF) was a not-for-profit, US-based organization, that described itself as a "private nonprofit, voluntary health agency that focuses upon health misinformation, fraud, and quackery as public health problems." History According to archived website, the NCAHF evolved from three separate organizations. The Lehigh Valley Committee Against Health Fraud, Inc. (LVCAHF, now called Quackwatch) was founded in 1969 by Stephen Barrett and H. William Gross, D.D.S. in Allentown, Pennsylvania. The Southern California Council Against Health Fraud (SCCAHF) had its origin in 1976 at Loma Linda University with academic colleagues William T. Jarvis and Gordon Rick as co-founders. Thomas H. Jukes of University of California, Berkeley founded the third organization, an unnamed group in northern California. For a time between 1998 and 2000, the NCAHF operated under the name National Council for Reliable Health Information (NCRHI). The organization bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William T
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will (given name), Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill (given name), Bill, Billie (given name), Billie, and Billy (name), Billy. A common Irish people, Irish form is Liam. Scottish people, Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma (given name), Wilma and Wilhelmina (given name), Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German language, German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors. Subjective well-being refers to how a person feels about and evaluates their life. Objective well-being encompasses factors that can be assessed from an external perspective, such as health, income, and security. Individual well-being concerns the quality of life of a particular person, whereas community well-being measures how well a group of people functions and thrives. Various types of well-being are categorized based on the domain of life to which they belong, such as physical, psychological, emotional, social, and economic well-being. Theories of well-being aim to identify the Essence, essential features of well-being. Hedonism argues that the balance of pleasure over pain is the only factor. Desire theories assert that the satisfact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |