|
Reid's Paradox Of Rapid Plant Migration
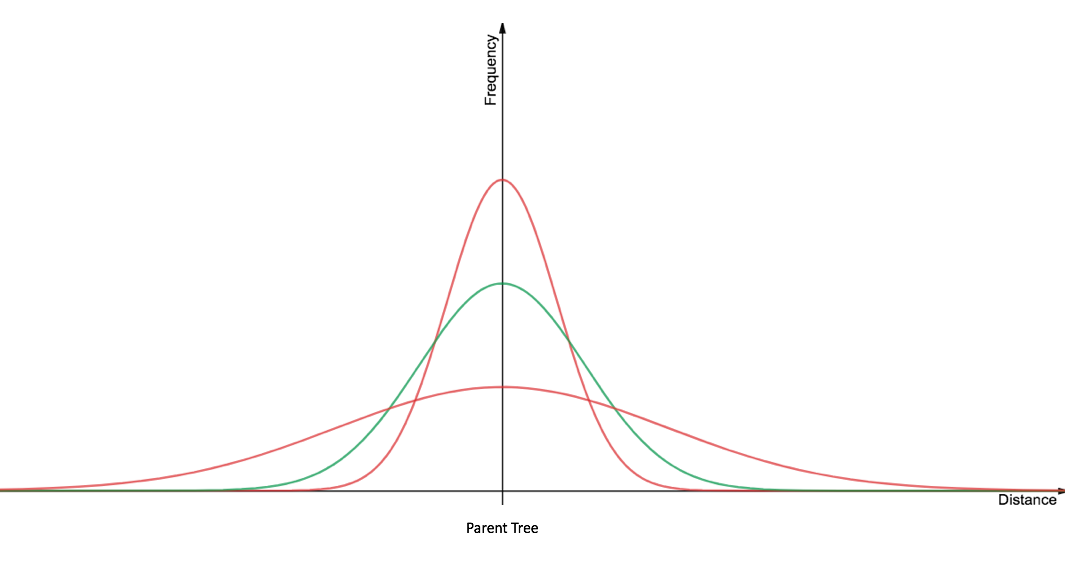
Reid's Paradox of Rapid Plant Migration or Reid's Paradox, describes the observation from the paleoecological record that plant ranges shifted northward, after the last glacial maximum, at a faster rate than the seed dispersal rates commonly occur. Rare long-distance seed dispersal events have been hypothesized to explain these fast migration rates, but the dispersal vector(s) are still unknown. The plant species' geographic range expansion rates are compared to the actualistic rates of seed dispersal using mathematical models, and are graphically visualized using dispersal kernels. These observations made in the paleontological record, which inspired Reid's Paradox, are from fossilized remains of plant parts, including needles, leaves, pollen, and seeds, that can be used to identify past shifts in plant species' ranges. Reid's Paradox is named after Clement Reid, a paleobotanist, who made the principle observations from the paleobotanical record in Europe in 1899. His comparison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoecology
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs a variety of fields including paleontology, ecology, climatology and biology. Paleoecology emerged from the field of paleontology in the 1950s, though paleontologists have conducted paleoecological studies since the creation of paleontology in the 1700s and 1800s. Combining the investigative approach of searching for fossils with the theoretical approach of Charles Darwin and Alexander von Humboldt, paleoecology began as paleontologists began examining both the ancient organisms they discovered and the reconstructed environments in which they lived. Visual depictions of past marine and terrestrial communities have been considered an early form of paleoecology. Overview of paleoecological approaches * Classic paleoecology uses data from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Jay
The blue jay (''Cyanocitta cristata'') is a passerine bird in the family Corvidae, native to eastern North America. It lives in most of the eastern and central United States; some eastern populations may be migratory. Resident populations are also in Newfoundland, Canada; breeding populations are found across southern Canada. It breeds in both deciduous and coniferous forests, and is common in residential areas. Its coloration is predominantly blue, with a white chest and underparts, and a blue crest; it has a black, U-shaped collar around its neck and a black border behind the crest. Males and females are similar in size and plumage, and plumage does not vary throughout the year. Four subspecies have been recognized. The blue jay feeds mainly on seeds and nuts, such as acorns, which it may hide to eat later; soft fruits; arthropods; and occasionally small vertebrates. It typically gleans food from trees, shrubs, and the ground, and sometimes hawks insects from the air. Blue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Biology
Conservation biology is the study of the conservation of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions. It is an interdisciplinary subject drawing on natural and social sciences, and the practice of natural resource management. The conservation ethic is based on the findings of conservation biology. Origins The term conservation biology and its conception as a new field originated with the convening of "The First International Conference on Research in Conservation Biology" held at the University of California, San Diego in La Jolla, California, in 1978 led by American biologists Bruce A. Wilcox and Michael E. Soulé with a group of leading university and zoo researchers and conservationists including Kurt Benirschke, Sir Otto Frankel, Thomas Lovejoy, and Jared Diamond. The meeting was prompted due to concern over tropical deforestation, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Ecology
Forest ecology is the scientific study of the interrelated patterns, processes, flora, fauna and ecosystems in forests. The management of forests is known as forestry, silviculture, and forest management. A forest ecosystem is a natural woodland unit consisting of all plants, animals, and micro-organisms ( Biotic components) in that area functioning together with all of the non-living physical ( abiotic) factors of the environment. Surrounding issues Forests have an enormously important role to play in the global ecosystem. Forests produce approximately 28% of the Earth's oxygen (the vast majority being created by oceanic plankton), they also serve as homes for millions of people, and billions depend on forests in some way. Likewise, a large proportion of the world's animal species live in forests. That's why we absolutely must protect them. Forest ecology helps to understand life in the forest. It shows how living organisms behave, live and survive. Furthermore, forest ecolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Beech
''Fagus grandifolia'', the American beech or North American beech, is a species of beech tree native to the eastern United States and extreme southeast of Canada. Description ''Fagus grandifolia'' is a large deciduous tree growing to tall, with smooth, silver-gray bark. The leaves are dark green, simple and sparsely-toothed with small teeth that terminate each vein, long (rarely ), with a short petiole. The winter twigs are distinctive among North American trees, being long and slender ( by ) with two rows of overlapping scales on the buds. Beech buds are distinctly thin and long, resembling cigars; this characteristic makes beech trees relatively easy to identify. The tree is monoecious, with flowers of both sexes on the same tree. The fruit is a small, sharply-angled nut, borne in pairs in a soft-spined, four-lobed husk. It has two means of reproduction: one is through the usual dispersal of seedlings, and the other is through root sprouts, which grow into new trees. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Maple
''Acer saccharum'', the sugar maple, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is native to the hardwood forests of eastern Canada and eastern United States. Sugar maple is best known for being the primary source of maple syrup and for its brightly colored fall foliage. It may also be known as "rock maple", "sugar tree", "birds-eye maple", "sweet maple", "curly maple", or "hard maple", particularly when referring to the wood. Description ''Acer saccharum'' is a deciduous tree normally reaching heights of , and exceptionally up to . A 10-year-old tree is typically about tall. As with most trees, forest-grown sugar maples form a much taller trunk and narrower canopy than open-growth ones. The leaves are deciduous, up to long and wide, palmate, with five lobes and borne in opposite pairs. The basal lobes are relatively small, while the upper lobes are larger and deeply notched. In contrast with the angular notching of the silver maple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugium (population Biology)
Refugium, plural refugia, the Latin for "refuge" or "hideaway", may refer to: * Refugium (fishkeeping), an appendage to a marine, brackish, or freshwater fish tank that shares the same water supply * Refugium (population biology), a location of an isolated or relict population of a once widespread animal or plant species ** Last Glacial Maximum refugia specifically, in anthropology * Refugium Range, a mountain range on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada See also * Refuge (Buddhism) * Refugium Peccatorum {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Dispersal
In Spermatophyte plants, seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant. Plants have limited mobility and rely upon a variety of dispersal vectors to transport their seeds, including both abiotic vectors, such as the wind, and living (biotic) vectors such as birds. Seeds can be dispersed away from the parent plant individually or collectively, as well as dispersed in both space and time. The patterns of seed dispersal are determined in large part by the dispersal mechanism and this has important implications for the demographic and genetic structure of plant populations, as well as migration patterns and species interactions. There are five main modes of seed dispersal: gravity, wind, ballistic, water, and by animals. Some plants are serotinous and only disperse their seeds in response to an environmental stimulus. These modes are typically inferred based on adaptations, such as wings or fleshy fruit. However, this simplified view may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurtosis
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from el, κυρτός, ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") is a measure of the "tailedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. Like skewness, kurtosis describes a particular aspect of a probability distribution. There are different ways to quantify kurtosis for a theoretical distribution, and there are corresponding ways of estimating it using a sample from a population. Different measures of kurtosis may have different interpretations. The standard measure of a distribution's kurtosis, originating with Karl Pearson, is a scaled version of the fourth moment of the distribution. This number is related to the tails of the distribution, not its peak; hence, the sometimes-seen characterization of kurtosis as " peakedness" is incorrect. For this measure, higher kurtosis corresponds to greater extremity of deviations (or outliers), and not the configuration of data near the mean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoarding (animal Behavior)
Hoarding or caching in animal behavior is the storage of food in locations hidden from the sight of both conspecifics (animals of the same or closely related species) and members of other species. Most commonly, the function of hoarding or caching is to store food in times of surplus for times when food is less plentiful. However, there is evidence that some amount of caching or hoarding is done in order to ripen the food, called ripening caching. The term hoarding is most typically used for rodents, whereas caching is more commonly used in reference to birds, but the behaviors in both animal groups are quite similar. Hoarding is done either on a long-term basis – cached on a seasonal cycle, with food to be consumed months down the line – or on a short-term basis, in which case the food will be consumed over a period of one or several days. Some common animals that cache their food are rodents such as hamsters and squirrels, and many different bird species, such as rook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Gray Squirrel
The eastern gray squirrel (''Sciurus carolinensis''), also known, particularly outside of North America, as simply the grey squirrel, is a tree squirrel in the genus '' Sciurus''. It is native to eastern North America, where it is the most prodigious and ecologically essential natural forest regenerator. Widely introduced to certain places around the world, the eastern gray squirrel in Europe, in particular, is regarded as an invasive species. In Europe, ''Sciurus carolinensis'' is included since 2016 in the list of Invasive Alien Species of Union concern (the Union list). This implies that this species cannot be imported, bred, transported, commercialized, or intentionally released into the environment in the whole of the European Union. Distribution ''Sciurus carolinensis'' is native to the eastern and midwestern United States, and to the southerly portions of the central provinces of Canada. The native range of the eastern gray squirrel overlaps with that of the fox sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Equation
The diffusion equation is a parabolic partial differential equation. In physics, it describes the macroscopic behavior of many micro-particles in Brownian motion, resulting from the random movements and collisions of the particles (see Fick's laws of diffusion). In mathematics, it is related to Markov processes, such as random walks, and applied in many other fields, such as materials science, information theory, and biophysics. The diffusion equation is a special case of the convection–diffusion equation, when bulk velocity is zero. It is equivalent to the heat equation under some circumstances. Statement The equation is usually written as: where is the density of the diffusing material at location and time and is the collective diffusion coefficient for density at location ; and represents the vector differential operator del. If the diffusion coefficient depends on the density then the equation is nonlinear, otherwise it is linear. The equation above applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |