|
Reichskolonialbund
The ''Reichskolonialbund'' (RKB) () was a collective body that absorbed all German colonial organisations during the time of the Third Reich. It was led by Franz Ritter von Epp. The ''Reichskolonialbund'' was active between 1936 and 1943. History Background The purpose of the ''Reichskolonialbund'' was to reclaim the overseas colonies that Germany had lost as a result of the Treaty of Versailles at the end of World War I. The first efforts in rallying support for a re-establishment of a German Colonial Empire in Germany can be traced back to 1923. As a result, a number of pro-colonial organisations, supported by both conservative-minded Germans and nationalists, were established in different parts of Germany. Founded in 1925, the foremost outfit was the ''Koloniale Reichsarbeitsgemeinschaft'' (KORAG). This organisation, along with other groups, led to the foundation of the preliminary Reichskolonialbund in 1933. The establishment was made in two steps, the second one being i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Colonial Empire
The German colonial empire () constituted the overseas colonies, dependencies, and territories of the German Empire. Unified in 1871, the chancellor of this time period was Otto von Bismarck. Short-lived attempts at colonization by Kleinstaaterei, individual German states had occurred in preceding centuries, but Bismarck resisted pressure to construct a colonial empire until the Scramble for Africa in 1884. Claiming much of the remaining uncolonized areas of Africa, Germany built the third-largest colonial empire at the time, after the British Empire, British and Second French colonial empire, French. The German colonial empire encompassed parts of Africa and Oceania. Germany lost control of most of its colonial empire at the beginning of the World War I, First World War in 1914, but some German forces held out in German East Africa until the end of the war. After the Armistice of 11 November 1918, German defeat in World , Germany's colonial empire was officially confiscated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSDAP Office Of Colonial Policy
The NSDAP Office of Colonial Policy (German: ''Kolonialpolitisches Amt der NSDAP'', ''K.P.A.'' or ''KPA'') was a Nazi Party office formed in 1934. Its stated objective was to formulate plans for the re-taking of the former German colonies. The office lost much of its meaning after the start of World War II, and was dissolved after the reversal of Nazi Germany's military victories in 1943. History There were several predecessor organization created in response to the German colonial problem in the Nazi Party. The last was the Colonial Section of the paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party, under the central command of the SA-leadership. After the purge of the SA in the Night of the Long Knives, it was reformed as the Colonial Political Office in 1934, with Franz Ritter von Epp as its leader. From then on, its task was to provide clear directives and policy guidelines for the party and its press in regard to every colonial, political and economic problems. In addition, the office als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
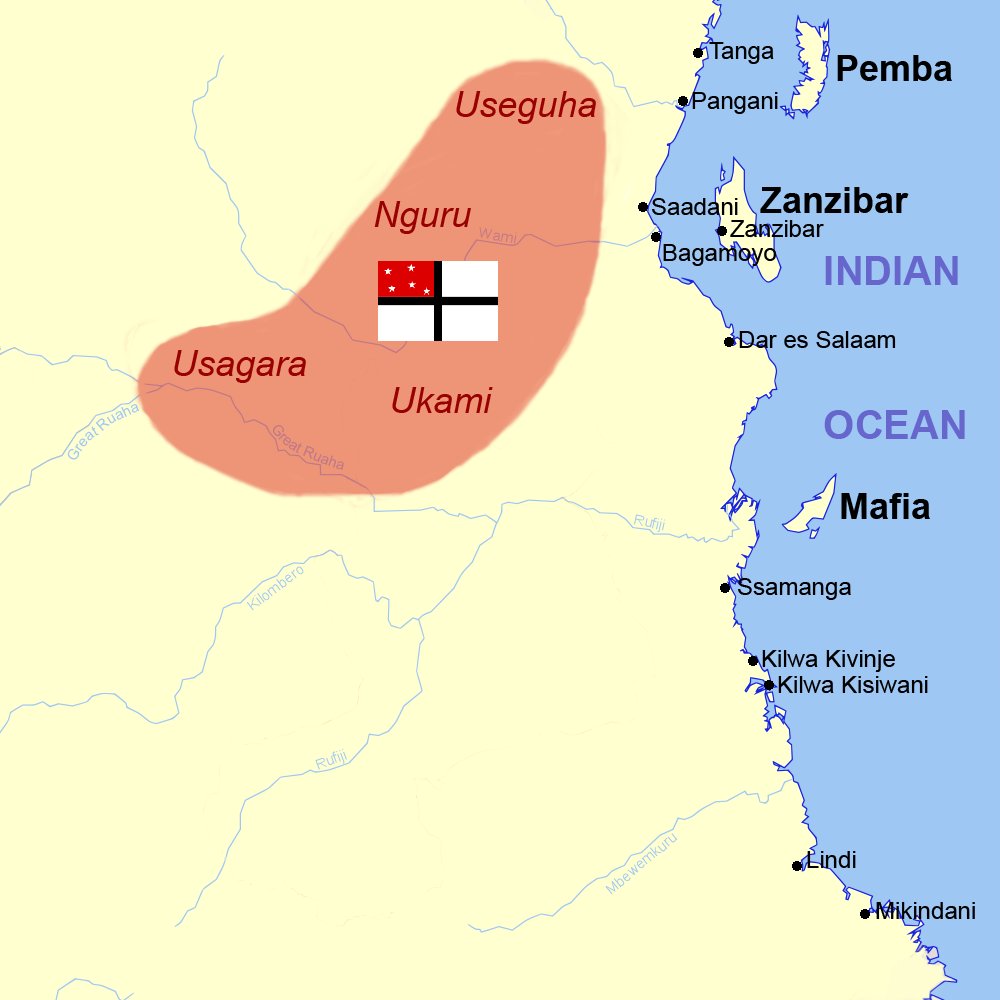
German East Africa Company
The German East Africa Company (, abbreviated DOAG) was a chartered colonial organization that brought about the establishment of German East Africa, a territory which eventually comprised the areas of modern Tanzania, Burundi, and Rwanda. The company originated in 1884 as the ( Society for German Colonisation) with the aim of trading in Africa. The German protectorate of Wituland (within modern Kenya) originated as a separate German sphere of influence in 1885. In April of the same year, the company leased the coastal strip opposite Zanzibar from Sultan Khalifa bin Said for 50 years. Its attempt to take over the administration led to a general revolt along the coast of what is now Tanzania. The company could hold Dar es Salaam and Bagamoyo only with the help of the German navy. In 1889 it had to request the assistance of the German government to put down the rebellion. In 1891, after it became apparent that the company could not handle its dominions, it sold out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Colonial Society
The German Colonial Society () (DKG) was a German organisation formed on 19 December 1887 to promote German colonialism. The Society was formed through the merger of the (; established in 1882 in Frankfurt) and the Society for German Colonization (; established in 1884). The Society was headquartered in Berlin. The German Colonial Society worked in close cooperation with the Pan-German League and became influential in the German Empire. Among its leaders were Hermann, Prince of Hohenlohe-Langenburg, Carl Peters and several members of parliament. Upon its formation the Society had approximately 15,000 members and by 1914 the number of members had increased to 42,000. The foremost goal of the Society was to work for a more expansive German colonial policy. From 1916 plans were made for a German colonial empire in Africa, the so-called , as well as annexations in East Asia. After Germany lost its colonies at the end of the First World War, the Society propagated for their reoccupatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Schnee
Heinrich Albert Schnee (Albert Hermann Heinrich Schnee; 4 February 1871 – 23 June 1949) was a German lawyer, colonial civil servant, politician, writer, and association official. He served as the last Governor of German East Africa. Early life and education Schnee was born in Neuhaldensleben, the son of the district court Councillor Hermann Schnee (1829–1901) and his wife Emily (née Scheibe). He attended high school in Nordhausen, and studied law in Heidelberg (as a member of the Corps Rhenania Heidelberg), Kiel, and Berlin (Dr. jur., 1893). Career In 1897, he began working in the Federal Foreign Office, and in 1898 he became a judge and the Deputy Governor of German New Guinea. In 1900, he became a District Officer and Deputy Governor of German Samoa. When in New York, Schnee, in 1901 married Ada Adeline Woodhill (1873-1969), a New Zealand actress of English and Irish extraction. After 1904, he again served as a Legation Councillor in the Colonial Departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Ritter Von Epp
Franz Ritter von Epp (born Franz Epp; from 1918 as Ritter von Epp; 16 October 1868 – 31 January 1947)Lilla, Joachim: Epp, Franz Ritter v.'. In: Staatsminister, leitende Verwaltungsbeamte und (NS-)Funktionsträger in Bayern 1918 bis 1945. Bayerische Landesbibliothek Online. Retrieved on 12 November 2015.Epp's death date is often erroneously given as 31 December 1946. According to Lilla, Staatsminister, this error was replicated from the . The correct date, 31 January 1947, is confirmed by Epp's death certificate in the civil registry of Munich. was a German general and politician who started his military career in the Bavarian Army. Successful wartime military service earned him a knighthood in 1916. After the end of World War I and the dissolution of the German Empire, Epp was a commanding officer in the and the . His unit, the ''Freikorps Epp'', was responsible for numerous massacres during the crushing of the Bavarian Soviet Republic. He was a member of Bavarian Peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers' Party (; DAP), existed from 1919 to 1920. The Nazi Party emerged from the Extremism, extremist German nationalism, German nationalist ("Völkisch nationalism, ''Völkisch'' nationalist"), racism, racist, and populism, populist paramilitary culture, which fought against communism, communist uprisings in post–World War I Germany. The party was created to draw workers away from communism and into nationalism. Initially, Nazi political strategy focused on anti-big business, anti-bourgeoisie, and anti-capitalism, disingenuously using socialist rhetoric to gain the support of the lower middle class; it was later downplayed to gain the support of business leaders. By the 1930s, the party's main focus shifted to Antisemit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Führer
( , spelled ''Fuehrer'' when the umlaut is unavailable) is a German word meaning "leader" or " guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with Adolf Hitler, the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Hitler officially called himself ''der Führer und Reichskanzler'' (the Leader and Chancellor of the Reich) after the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934, as well as the subsequent merging of the offices of ''Reichspräsident'' and '' Reichskanzler''. Nazi Germany cultivated the ("leader principle"), and Hitler was generally known as simply ("the Leader"). In compound words, the use of remains common in German and is used in words such as ( travel guide), ( museum docent), ( mountain guide), or (leader of the opposition). However, because of its strong association with Hitler, the isolated word itself usually has negative connotations when used with the meaning of "leader", especially in political contexts. The word has cognates in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebensraum
(, ) is a German concept of expansionism and Völkisch movement, ''Völkisch'' nationalism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, ''[Also in:]'' became a Geopolitics, geopolitical goal of German Empire, Imperial Germany in World War I (1914–1918), as the core element of the of territorial expansion. The most extreme form of this ideology was supported by the Nazi Party and Nazi Germany, the ultimate goal of which was to establish a Greater Germanic Reich, Greater German Reich. was a leading motivation of Nazi Germany to initiate World War II, and it would continue this policy until End of World War II in Europe, the end of the conflict. Following Adolf Hitler's rise to power, became an ideological principle of Nazism and provided justification for the German territorial expansion into Central and Eastern Europe. The Nazi policy () was based on its tenets. It stipulated that Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Bormann
Martin Ludwig Bormann (17 June 1900 – 2 May 1945) was a German Nazi Party official and head of the Nazi Party Chancellery, private secretary to Adolf Hitler, and a war criminal. Bormann gained immense power by using his position as Hitler's private secretary to control the flow of information and access to Hitler. He used his position to create an extensive bureaucracy and involve himself as much as possible in the decision-making. Bormann joined a paramilitary ''Freikorps'' organisation in 1922 while working as manager of a large estate. He served nearly a year in prison as an accomplice to his friend Rudolf Höss (later commandant of Auschwitz concentration camp) in the murder of Walther Kadow. Bormann joined the Nazi Party in 1927 and the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) in 1937. He initially worked in the party's insurance service, and transferred in July 1933 to the office of Deputy Führer Rudolf Hess, where he served as chief of staff. Bormann gained acceptance into Hitler's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For German Colonization
The Society for German Colonization (, GfdK) was founded on 28 March 1884 in Berlin by Carl Peters. Its goal was to accumulate capital for the acquisition of German Colony, colonial territories in overseas countries. History Peters had just returned from London, where he lived with his well-off uncle Carl Engel (musicologist), Carl Engel and studied the principles of History of colonialism, European colonialism. In the autumn of 1884 he proceeded, together with his friends Karl Ludwig Jühlke and Count Joachim von Pfeil, to the Sultanate of Zanzibar. Peters had initially planned to prospect for gold in Southern African Mashonaland (in present-day Zimbabwe) but discovered that the territory had already been claimed by the British. Peters' Zanzibar expedition was a nuisance to the German Empire, German government of Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, Bismarck, focused on good relations with both Sultan Barghash bin Said of Zanzibar, Barghash bin Said and the British Empire, and the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |