|
Rehabilitation (neuropsychology)
Rehabilitation of sensory and cognitive function typically involves methods for retraining neural pathways or training new neural pathways to regain or improve neurocognitive functioning that have been diminished by disease or trauma. The main objective outcome for rehabilitation is to assist in regaining physical abilities and improving performance. Three common neuropsychological problems treatable with rehabilitation are attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), concussion, and spinal cord injury. Rehabilitation research and practices are a fertile area for clinical neuropsychologists, rehabilitation psychologists, and others. Methods Physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, hot and cold therapy, and other methods that "exercise" specific brain functions are used. For example, eye–hand coordination exercises may rehabilitate certain motor deficits, or well-structured planning and organizing exercises might help rehabilitate executive function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Function
Cognitive skills are skills of the mind, as opposed to other types of skills such as motor skills, social skills or life skills. Some examples of cognitive skills are literacy, self-reflection, logical reasoning, abstract thinking, critical thinking, introspection and mental arithmetic. Cognitive skills vary in processing complexity, and can range from more fundamental processes such as perception and various memory functions, to more sophisticated processes such as decision making, problem solving and metacognition. Specialisation of functions Cognitive science has provided theories of how the brain works, and these have been of great interest to researchers who work in the empirical fields of brain science. A fundamental question is whether cognitive functions, for example visual processing and language, are autonomous modules, or to what extent the functions depend on each other. Research evidence points towards a middle position, and it is now generally accepted that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurocognitive
Neurocognitive functions are cognitive functions closely linked to the function of particular areas, neural pathways, or cortical networks in the brain, ultimately served by the substrate of the brain's neurological matrix (i.e. at the cellular and molecular level). Therefore, their understanding is closely linked to the practice of neuropsychology and cognitive neuroscience – two disciplines that broadly seek to understand how the structure and function of the brain relate to cognition and behaviour. A neurocognitive deficit is a reduction or impairment of cognitive function in one of these areas, but particularly when physical changes can be seen to have occurred in the brain, such as aging related physiological changes or after neurological illness, mental illness, drug use, or brain injury. A clinical neuropsychologist may specialise in using neuropsychological tests to detect and understand such deficits, and may be involved in the rehabilitation of an affected person. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benton Visual Retention Test
The Benton Visual Retention Test (or simply Benton test or BVRT) is an individually administered test for people aged from eight years to adulthood that measures visual perception and visual memory. It can also be used to help identify possible learning disabilities among other conditions that might affect an individual's memory. The individual examined is shown ten designs, one at a time, and asked to reproduce each one as exactly as possible on plain paper from memory. The test is untimed, and the results are professionally scored by form, shape, pattern, and arrangement on the paper. History Arthur Benton was a psychologist who worked with neurologist Morris Bender during his military assignment to the San Diego Naval Hospital. His experiences in the treatment of servicemen who had traumatic brain injuries led to his development of the Benton Visual Retention Test. Dr. Benton developed the test to provide a shorter assessment for immediate nonverbal memory to supplement the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
The Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) is a neuropsychological test of set-shifting, which is the capability to show flexibility when exposed to changes in reinforcement.E. A. Berg. (1948). A simple objective technique for measuring flexibility in thinking J. Gen. Psychol. 39: 15-22. The WCST was written by David A. Grant and Esta A. Berg. ''The Professional Manual for the WCST'' was written by Robert K. Heaton, Gordon J. Chelune, Jack L. Talley, Gary G. Kay, and Glenn Curtiss. Method Stimulus cards are shown to the participant and the participant is then instructed to match the cards. They are not given instructions on how to match the cards but are given feedback when the matches they make are right or wrong. When the test was first released the method of showing the cards was done with an evaluator using paper cards with the evaluator on one side of the desk facing the participant on the other. The test takes approximately 12–20 minutes to carry out using manual scoring whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
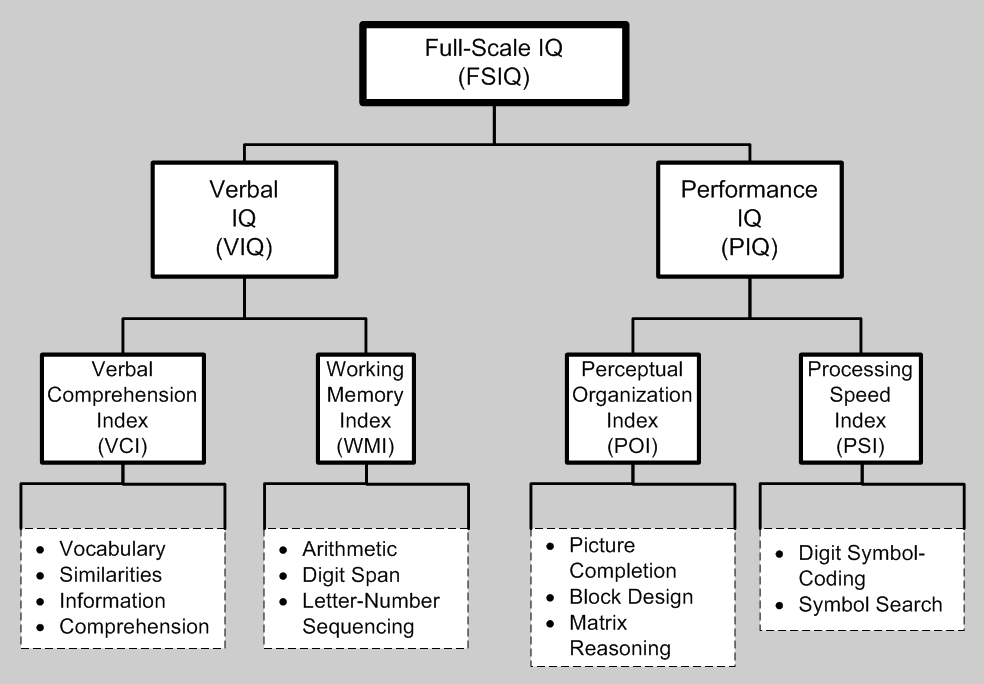
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. For children between the ages of 6 and 16, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is commonly used. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, Chief Psychologist at Bellevue Hospital (1932–1967) in NYC, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale released in 1939. It is currently in its fifth edition (''WAIS-5''), released in 2024 by Pearson. It is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS was founded to get to know Wechsler's patients at Bellevue Hospital and on his definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardized
Standardization (American English) or standardisation (British English) is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, efficiency, and quality. It can also facilitate a normalization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of ''standardization'' is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions. Divergent national standards impose costs on consumers and can be a form of non-tariff trade barrier. History Early examples Standard weights and measures were developed by the Indus Valley civilization.Iwata, Shigeo (2008), "Weights and Measures in the Indus Valley", ''Encyclopaedia of the History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurocognitive
Neurocognitive functions are cognitive functions closely linked to the function of particular areas, neural pathways, or cortical networks in the brain, ultimately served by the substrate of the brain's neurological matrix (i.e. at the cellular and molecular level). Therefore, their understanding is closely linked to the practice of neuropsychology and cognitive neuroscience – two disciplines that broadly seek to understand how the structure and function of the brain relate to cognition and behaviour. A neurocognitive deficit is a reduction or impairment of cognitive function in one of these areas, but particularly when physical changes can be seen to have occurred in the brain, such as aging related physiological changes or after neurological illness, mental illness, drug use, or brain injury. A clinical neuropsychologist may specialise in using neuropsychological tests to detect and understand such deficits, and may be involved in the rehabilitation of an affected person. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropsychological Test
Neuropsychological tests are specifically designed tasks that are used to measure a psychological function known to be linked to a particular brain structure or pathway. Tests are used for cognitive neuropsychology, research into brain function and in a clinical neuropsychology, clinical setting for the diagnosis of deficits. They usually involve the systematic administration of clearly defined procedures in a formal environment. Neuropsychological tests are typically administered to a single person working with an examiner in a quiet office environment, free from distractions. As such, it can be argued that neuropsychological tests at times offer an estimate of a person's peak level of cognitive performance. Neuropsychological tests are a core component of the process of conducting neuropsychological assessment, along with personal, interpersonal and contextual factors. Most neuropsychological tests in current use are based on traditional psychometric theory. In this model, a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Some Brain Areas
Some may refer to: *''some'', an English word used as a determiner and pronoun; see use of ''some'' *The term associated with the existential quantifier *"Some", a song by Built to Spill from their 1994 album ''There's Nothing Wrong with Love'' *Socialist-oriented market economy, the Vietnamese economic system occasionally abbreviated SOME *Social market economy, the German socioeconomic model abbreviated SOME *So Others Might Eat (SOME), a Washington, D.C.–based non-profit organization *SoMe, short for social media * ''Some'' (film), a 24 film * "Some" (song), a duet by Junggigo and Soyou *Some & Any Some & Any was a German pop duo, formed during the eighth season of the German television talent show ''Popstars''. The group consisted of then-18-year-old Vanessa Meisinger and 20-year-old half-Brazilian, half-Swiss Leonardo Ritzmann. The seas ..., German pop duo See also * Some (surname) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. The person may experience respiratory and circulatory problems due to the body's inability to maintain normal bodily functions. People in a coma often require extensive medical care to maintain their health and prevent complications such as pneumonia or blood clots. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be the result of natural causes, or can be Induced coma, medically induced, for example, during General anaesthesia, general anesthesia. Clinically, a coma can be defined as the consistent inability to follow a one-step command. For a patient to maintain consciousness, the components of ''wakefulness'' and ''awareness'' must be maintained. Wak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Function
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing, and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing that information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencephalon, subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Brain Injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury. TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism (closed head injury, closed or penetrating head injury) or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death. Causes include Falling (accident), falls, vehicle collisions, and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration of the brain within the skull or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |