|
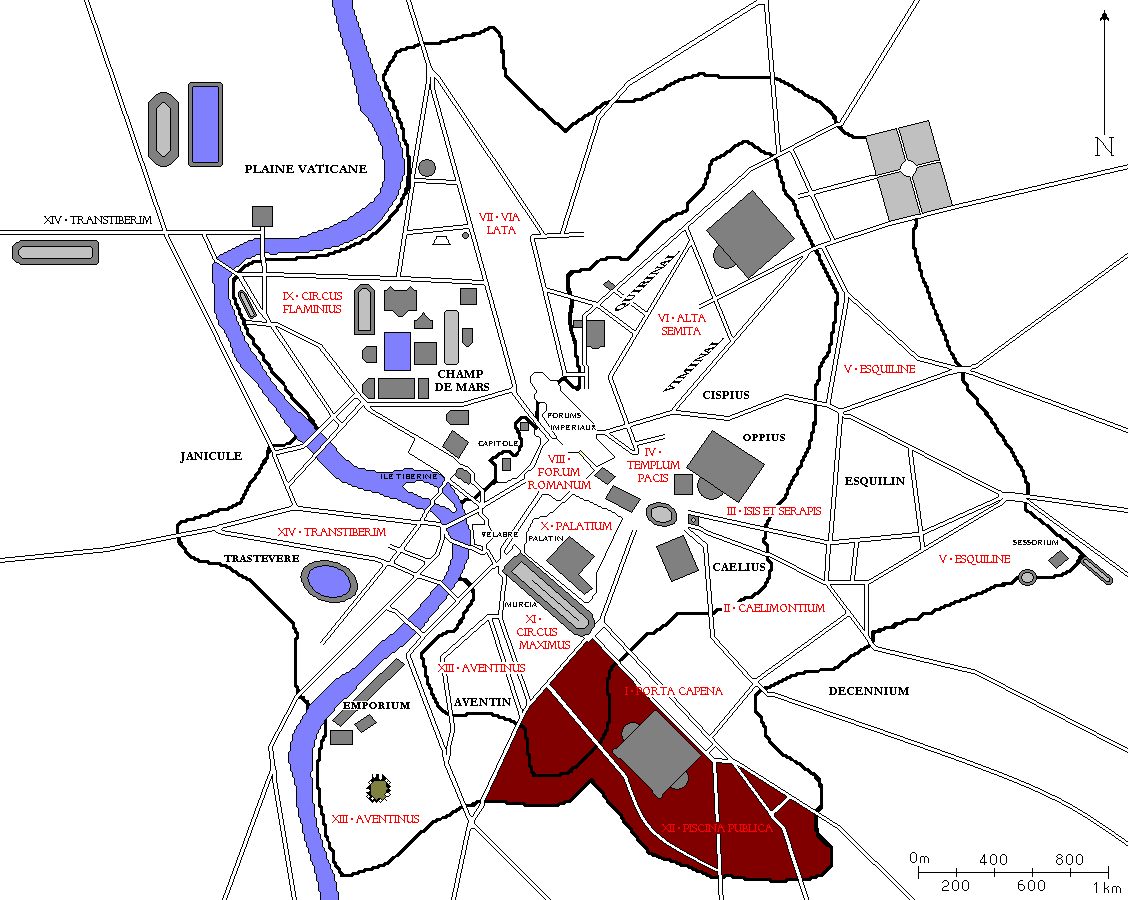
Regio XII Piscina Publica
The Regio XII Piscina Publica is the twelfth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio XII took its name from the ''Piscina Publica'', a swimming pool that disappeared during the middle imperial period. Geographic extent and important features Regio XII was named after the principal feature of this area during the reign of Augustus, the ''Piscina Publica'', a public reservoir and swimming pool, built around the 3rd century BCE. In extent, this region was bordered by the ''Vicus Piscinae Publicae'' to the north, the Via Ostiensis to the west, the Via Appia and the Via Latina to the east, and the Aurelian Walls to the south. Its principal gates through the walls were the Porta Appia and the Porta Ardeatina. A measurement taken at the end of the 4th century recorded that the perimeter of the region was 12,000 Roman feet (approximately 3.5 km), making it one of the smaller of the Augustan regions. The ''Piscina'' itself sat in the low-lying area b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Bona Dea
The Temple of Bona Dea was an ancient sanctuary in Ancient Rome, erected the 3rd century BC and dedicated to the goddess Bona Dea.Samuel Ball Platner, "Bona Dea Subsaxana", A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome, Oxford University Press, Londra, 1929 The date of the foundation is unknown. However, the cult was introduced in Rome after 272 BC, and the sanctuary was founded in that century. It is mentioned to have been repaired by the empress Livia, spouse of Emperor Augustus. The sanctuary was a center of healing in Rome. Domesticated snakes were housed in the temple, and medicinal herbs were sold. It was the center of the cult of the festival of Bona Dea, which was celebrated on 1 May. During the festival, no men were allowed within the borders of the sanctuary. The Temple of Bona Dea was still in use during the 3rd century. If still in use by the 4th-century, it would have been closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire. A church was erected in the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Magistrate
The Roman magistrates were elected officials in Ancient Rome. During the period of the Roman Kingdom, the King of Rome was the principal executive magistrate.Abbott, 8 His power, in practice, was absolute. He was the chief priest, lawgiver, judge, and the sole commander of the army.Abbott, 8Abbott, 15 When the king died, his power reverted to the Roman Senate, which then chose an Interrex to facilitate the election of a new king. During the transition from monarchy to republic, the constitutional balance of power shifted from the executive (the Roman king) to the Roman Senate. When the Roman Republic was founded in 509 BC, the powers that had been held by the king were transferred to the Roman consuls, of which two were to be elected each year. Magistrates of the republic were elected by the people of Rome, and were each vested with a degree of power called "major powers" (''maior potestas'').Abbott, 151 Dictators had more "major powers" than any other magistrate, and after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curators
A curator (from la, cura, meaning "to take care") is a manager or overseer. When working with cultural organizations, a curator is typically a "collections curator" or an "exhibitions curator", and has multifaceted tasks dependent on the particular institution and its mission. In recent years the role of curator has evolved alongside the changing role of museums, and the term "curator" may designate the head of any given division. More recently, new kinds of curators have started to emerge: "community curators", "literary curators", " digital curators" and " biocurators". Collections curator A "collections curator", a "museum curator" or a "keeper" of a cultural heritage institution (e.g., gallery, museum, library or archive) is a content specialist charged with an institution's collections and involved with the interpretation of heritage material including historical artifacts. A collections curator's concern necessarily involves tangible objects of some sort—artwork, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insula (Roman City)
The Latin word ''insula'' (literally meaning "island", plural ''insulae'') was used in Roman cities to mean either a city block in a city plan, i.e. a building area surrounded by four streets, or, later, a type of apartment building that occupied such a city block specifically in Rome and nearby Ostia. The latter type of ''Insulae'' were known to be prone to fire and rife with disease. A standard Roman city plan was based on a grid of orthogonal (laid out on right angles) streets. It was founded on ancient Greek city models, described by Hippodamus. It was used especially when new cities were established, e.g. in Roman '' coloniae''. The streets of each city were designated the decumani (east–west-oriented) and cardines (north–south). The principal streets, the Decumanus Maximus and Cardo Maximus, intersected at or close to the forum Forum or The Forum (plural forums or fora) may refer to: Common uses *Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicus
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (plural ) designated a village within a rural area () or the neighbourhood of a larger settlement. During the Republican era, the four of the city of Rome were subdivided into . In the 1st century BC, Augustus reorganized the city for administrative purposes into 14 regions, comprising 265 . Each had its own board of officials who oversaw local matters. These administrative divisions are recorded as still in effect at least until the mid-4th century. The word "" was also applied to the smallest administrative unit of a provincial town within the Roman Empire. It is also notably used today to refer to an ''ad hoc'' provincial civilian settlement that sprang up close to and because of a nearby military fort or state-owned mining operation. Local government in Rome Each ''vicus'' elected four local magistrates ('' vicomagistri'') who commanded a sort of local police force chosen from among the people of the ''vicus'' by lot. Occasionally the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balnea
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large Roman Empire, imperial public bath, bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed in great numbers throughout Rome. Most Roman cities had at least one – if not many – such buildings, which were centers not only for bathing, but socializing and reading as well. Bathhouses were also provided for wealthy private Roman villa, villas, domus, town houses, and castra, forts. They were supplied with water from an adjacent river or stream, or within cities by aqueduct (watercourse), aqueduct. The water would be heated by fire then channelled into the caldarium (hot bathing room). The design of baths is discussed by Vitruvius in ''De architectura'(V.10) Terminology '','' '','' '','' and may all be translated as 'bath' or 'baths', though Latin sources distinguish among these terms. or , derived from the Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horrea
A ''horreum'' (plural: ''horrea'') was a type of public warehouse used during the ancient Roman period. Although the Latin term is often used to refer to granaries, Roman ''horrea'' were used to store many other types of consumables; the giant Horrea Galbae in Rome were used not only to store grain but also olive oil, wine, foodstuffs, clothing and even marble.Lawrence Richardson, ''A New Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'', p. 193. JHU Press, 1992. By the end of the imperial period, the city of Rome had nearly 300 ''horrea'' to supply its demands. The biggest were enormous, even by modern standards; the Horrea Galbae contained 140 rooms on the ground floor alone, covering an area of some 225,000 square feet (21,000 m²).David Stone Potter, D. J. Mattingly, ''Life, Death, and Entertainment in the Roman Empire'', p. 180. University of Michigan Press, 1999. The amount of storage space available in the public ''horrea'' can be judged by the fact that when the emperor Septimius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domus
In Ancient Rome, the ''domus'' (plural ''domūs'', genitive ''domūs'' or ''domī'') was the type of town house occupied by the upper classes and some wealthy freedmen during the Republican and Imperial eras. It was found in almost all the major cities throughout the Roman territories. The modern English word '' domestic'' comes from Latin ''domesticus'', which is derived from the word ''domus''. The word in modern Slavic languages means "home" and is a cognate of the Latin word, going back to Proto-Indo-European. Along with a ''domus'' in the city, many of the richest families of ancient Rome also owned a separate country house known as a villa. Many chose to live primarily, or even exclusively, in their villas; these homes were generally much grander in scale and on larger acres of land due to more space outside the walled and fortified city. The elite classes of Roman society constructed their residences with elaborate marble decorations, inlaid marble paneling, door ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aedicula
In ancient Roman religion, an ''aedicula'' (plural ''aediculae'') is a small shrine, and in classical architecture refers to a niche covered by a pediment or entablature supported by a pair of columns and typically framing a statue,"aedicula, n." ''OED Online'', Oxford University Press, September 2020www.oed.com/view/Entry/3077 Accessed 29 September 2020."aedicule, n." ''OED Online'', Oxford University Press, September 2020www.oed.com/view/Entry/3079 Accessed 29 September 2020 the early Christian ones sometimes contained funeral urns. Aediculae are also represented in art as a form of ornamentation. The word ''aedicula'' is the diminutive of the Latin '' aedes'', a temple building or dwelling place. The Latin word has been Anglicised as "aedicule" and as "edicule". Classical aediculae Many aediculae were household shrines ( lararia) that held small altars or statues of the Lares and Di Penates. The Lares were Roman deities protecting the house and the family household gods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vigiles
The ''Vigiles'' or more properly the ''Vigiles Urbani'' ("watchmen of the City") or ''Cohortes Vigilum'' (" cohorts of the watchmen") were the firefighters and police of ancient Rome. History The ''Triumviri Nocturni'' (meaning ''three men of the night'') were the first men, being privately owned slaves, organized into a group that combated the common problems of fire and conflagrations in Rome. The privately operated system became ineffective, so in the interest of keeping himself and Rome safe, Augustus instituted a new public firefighting force called the ''Vigiles''. Augustus modelled the new firefighters after the fire brigade of Alexandria, Egypt. The Vigiles were also known by their nickname ''Spartoli'' or "little bucket fellows" which was given to them because of the buckets they carried water in, which were made of rope sealed with pitch. In AD 6, Augustus levied a 4% tax on the sale of slaves and used the proceeds to set up the new force. The first Vigiles units w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term '' mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



