|
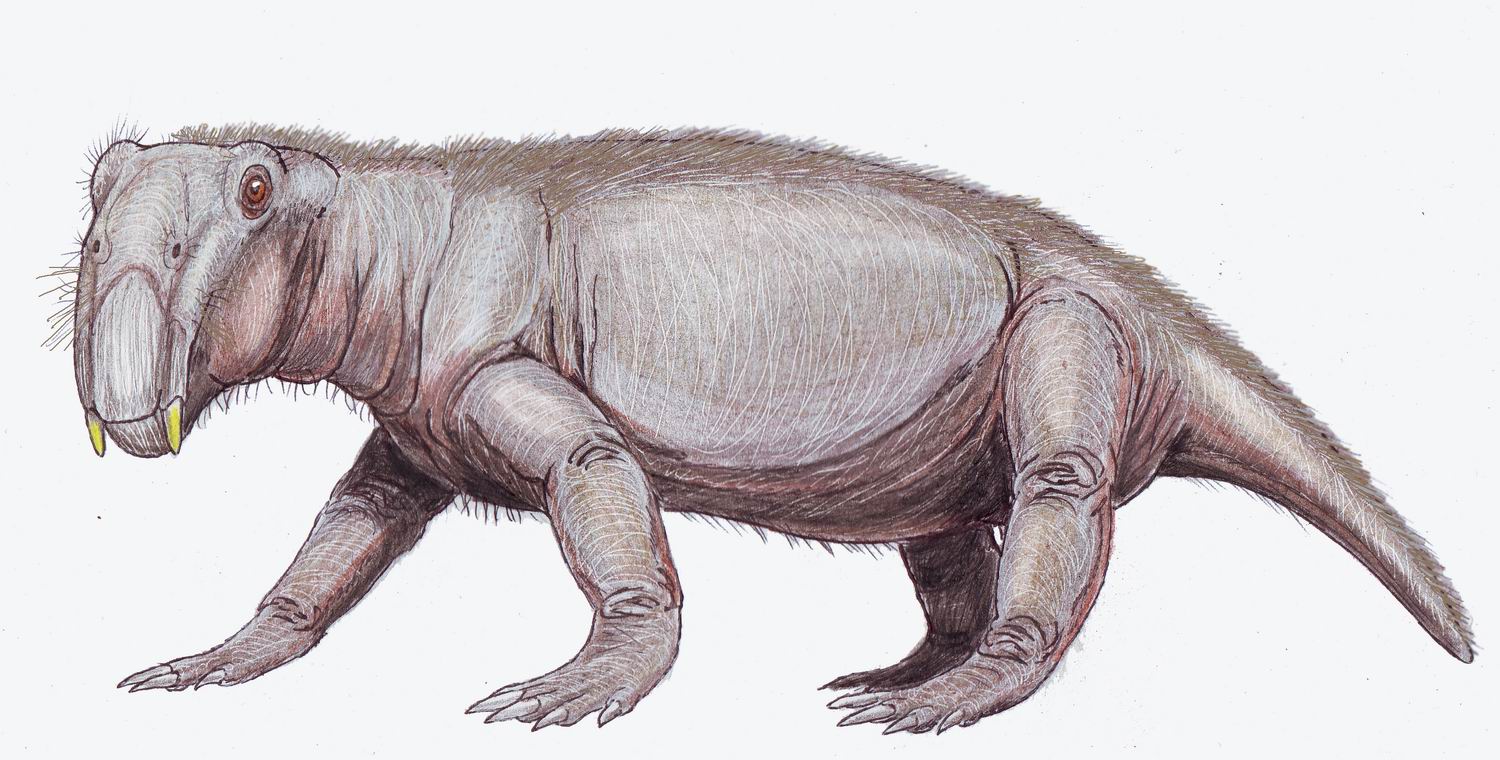
Redondasaurus
''Redondasaurus'' is an extinct genus of phytosaur from the Late Triassic (221.5 to 201.6 million years ago) of the southwestern United States. It was named by Hunt & Lucas in 1993, and contains two species, ''R. gregorii'' and ''R. bermani''. It is the youngest and most evolutionarily-advanced of the phytosaurs. History of discovery The first specimen now described with genus ''Redondasaurus'' was found in 1939 by D.E. Savage in the Travesser Formation in New Mexico. Savage originally described this find as '' Machaeroprosopus''. The 1947 discovery of another phytosaur skull in the Redonda Formation, New Mexico, by E.H. Colbert and J.T. Gregory led to the first recognition that both skulls represented a new taxon. In addition, they proposed that the skulls represented the most derived phytosaur in North America due to their supratemporal fenestrae being hidden in dorsal view. A third skull was discovered by D.S. Berman in the 1980s and was later identified as ''Pseudopalatus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
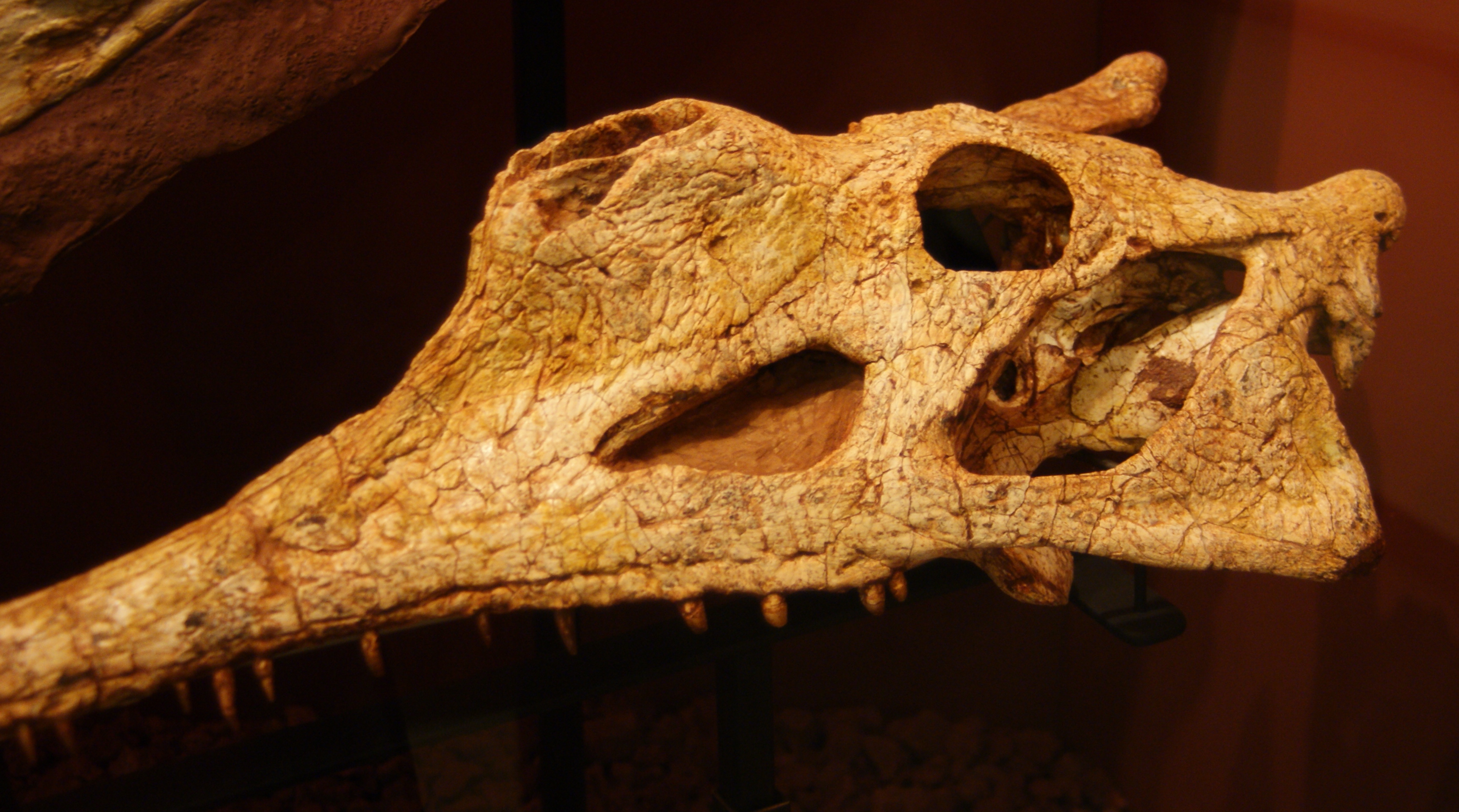
Redondasaurus Bermani Skull
''Redondasaurus'' is an extinct genus of phytosaur from the Late Triassic (221.5 to 201.6 million years ago) of the southwestern United States. It was named by Hunt & Lucas in 1993, and contains two species, ''R. gregorii'' and ''R. bermani''. It is the youngest and most evolutionarily-advanced of the phytosaurs. History of discovery The first specimen now described with genus ''Redondasaurus'' was found in 1939 by D.E. Savage in the Travesser Formation in New Mexico. Savage originally described this find as ''Machaeroprosopus''. The 1947 discovery of another phytosaur skull in the Redonda Formation, New Mexico, by E.H. Colbert and J.T. Gregory led to the first recognition that both skulls represented a new taxon. In addition, they proposed that the skulls represented the most derived phytosaur in North America due to their supratemporal fenestrae being hidden in dorsal view. A third skull was discovered by D.S. Berman in the 1980s and was later identified as ''Pseudopalatus'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redondasaurus
''Redondasaurus'' is an extinct genus of phytosaur from the Late Triassic (221.5 to 201.6 million years ago) of the southwestern United States. It was named by Hunt & Lucas in 1993, and contains two species, ''R. gregorii'' and ''R. bermani''. It is the youngest and most evolutionarily-advanced of the phytosaurs. History of discovery The first specimen now described with genus ''Redondasaurus'' was found in 1939 by D.E. Savage in the Travesser Formation in New Mexico. Savage originally described this find as '' Machaeroprosopus''. The 1947 discovery of another phytosaur skull in the Redonda Formation, New Mexico, by E.H. Colbert and J.T. Gregory led to the first recognition that both skulls represented a new taxon. In addition, they proposed that the skulls represented the most derived phytosaur in North America due to their supratemporal fenestrae being hidden in dorsal view. A third skull was discovered by D.S. Berman in the 1980s and was later identified as ''Pseudopalatus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Vertebrate Faunachron
Land vertebrate faunachrons (LVFs) are biochronological units used to correlate and date terrestrial sediments and fossils based on their tetrapod faunas. First formulated on a global scale by Spencer G. Lucas in 1998, LVFs are primarily used within the Triassic Period (252 - 201 Ma), though Lucas later designated LVFs for other periods as well. Eight worldwide LVFs are defined for the Triassic. The first two of these LVFs, the Lootsbergian and Nonesian, are based on South African synapsids and faunal assemblage zones estimated to correspond to the Early Triassic. These are followed by the Perovkan and Berdyankian, based on temnospondyl amphibians and Russian assemblages estimated to be from the Middle Triassic. The last four LVFs, the Otischalkian, Adamanian, Revueltian, and Apachean, are based on aetosaur and phytosaur reptiles common in the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States. The LVF system, though widely used, is also a controversial application of biostratigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosaurs
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek) are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalent groupings containing the same species, but some studies have identified non-phytosaurid phytosaurians. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters. The name is misleading because the sharp teeth in phytosaur jaws clearly show that they were predators. For many years, phytosaurs were considered to be the most basal group of Pseudosuchia (crocodile-line archosaurs), meaning that they were thought to be more closely related to the crocodilians than to birds (the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosaur
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek) are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalent groupings containing the same species, but some studies have identified non-phytosaurid phytosaurians. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters. The name is misleading because the sharp teeth in phytosaur jaws clearly show that they were predators. For many years, phytosaurs were considered to be the most basal group of Pseudosuchia (crocodile-line archosaurs), meaning that they were thought to be more closely related to the crocodilians than to birds (the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machaeroprosopus
''Machaeroprosopus'' is an extinct genus of mystriosuchin leptosuchomorph phytosaur from the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States. ''M. validus'', once thought to be the type species of ''Machaeroprosopus'', was named in 1916 on the basis of three complete skulls from Chinle Formation, Arizona. The skulls have been lost since the 1950s, and a line drawing in the original 1916 description is the only visual record of the specimen. Another species, ''M. andersoni'', was named in 1922 from New Mexico, and the species ''M. adamanensis'', ''M. gregorii'', ''M. lithodendrorum'', ''M. tenuis'', and ''M. zunii'' were named in 1930. Most species have been reassigned to the genera '' Smilosuchus'', '' Rutiodon'', or '' Phytosaurus''. Until recently, ''M. validus'' was considered to be the only species that has not been reassigned. Thus, ''Machaeroprosopus'' was considered to be a ''nomen dubium'' or "doubtful name" because of the lack of diagnostic specimens that can support it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redonda Formation
The Redonda Formation is a geologic formation exposed in eastern New Mexico.Dobrovolny and Summerson 1947 It contains vertebrate fossils of the late Triassic Period.Griggs and Read 1959 Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. Description The formation consists of interbedded fine-grained red-brown sandstone and mudstone. It conformably overlies the Bull Canyon FormationLucas and Hunt 1989 and underlies the Entrada Formation. The formation is interpreted as having been deposited in a lake with an area of about . Fossils The formation has few fossil plants, with only ''Neocalamites'' reported, but it contains abundant invertebrate fossils (conchostracans and ostracods) and a diverse assemblage of vertebrate fossils. Vertebrate fauna Fish Stereospondyls Synapsids Archosauriforms History of investigation The unit was first named as the Redonda Member of the Chinle Formation by Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopalatus Pristinus
''Machaeroprosopus'' is an extinct genus of mystriosuchin leptosuchomorph Leptosuchomorpha is a clade of phytosaurs. It is a node-based taxon defined as the last common ancestor of ''Leptosuchus studeri'' and '' Pseudopalatus pristinus'' and all of its descendants. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (fro ... phytosaur from the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States. ''M. validus'', once thought to be the type species of ''Machaeroprosopus'', was named in 1916 on the basis of three complete skulls from Chinle Formation, Arizona. The skulls have been lost since the 1950s, and a line drawing in the original 1916 description is the only visual record of the specimen. Another species, ''M. andersoni'', was named in 1922 from New Mexico, and the species ''M. adamanensis'', ''M. gregorii'', ''M. lithodendrorum'', ''M. tenuis'', and ''M. zunii'' were named in 1930. Most species have been reassigned to the genera ''Smilosuchus'', ''Rutiodon'', or ''Phytosaurus''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinle Formation
The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geological formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. In New Mexico, it is often raised to the status of a geological group, the Chinle Group. Some authors have controversially considered the Chinle to be synonymous to the Dockum Group of eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Texas, the Oklahoma panhandle, and southwestern Kansas. The Chinle Formation is part of the Colorado Plateau, Basin and Range, and the southern section of the Interior Plains.GEOLEX database entry for Chinle USGS (viewed 19 March 2006) A probable separate depositional basin within the Chinle is found in northwestern Colorado and northeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Species
Index (or its plural form indices) may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index'' * The Index, an item on a Halo megastructure in the ''Halo'' series of video games Periodicals and news portals * ''Index Magazine'', a publication for art and culture * Index.hr, a Croatian online newspaper * index.hu Index.hu is a Hungary, Hungarian news website covering both Hungarian and international news. In 2018, it was the most visited Hungarian website with an average of 1.5 million daily readers. While most of the website's articles are written in Hung ..., a Hungarian-language news and community portal * The Index (Kalamazoo College), ''The Index'' (Kalamazoo College), a student newspaper * ''The Index'', an 1860s European propaganda journal created by Henry Hotze to support the Confederate States of America * ''Truman State University Index'', a student newspaper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its west by Nevada. Utah also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the southwest, with more than 180,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin. Utah has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups such as the ancient Puebloans, Navajo and Ute. The Spanish were the first Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |