|
Redmi K30 Pro
Redmi K30 Pro is a line of Android-based smartphones manufactured by Xiaomi and marketed under its Redmi sub-brand. There are four models, the K30 Pro, K30 Pro Zoom, K30 Ultra and the POCO F2 Pro, which is a rebranded version of the K30 Pro. Design The K30 Pro line uses an anodized aluminum frame and Gorilla Glass on the front and back. Both the volume and power buttons are located on the right edge; the latter has a red accent. The front-facing camera is concealed by a motorized pop-up mechanism like on the K20 Pro. The camera protrusion on the back panel is a single unit with a dual-LED flash below, and a circular module. Colors available at launch were (Cyber) Grey, (Electric) Purple, (Phantom) White and (Neon) Blue. The K30 Ultra has unique Moonlight White, Midnight Black and Mint Green finishes. Specifications Hardware & software The Pro models are powered by the Snapdragon 865 and Adreno 650, while the K30 Ultra uses the MediaTek Dimensity 1000+ and Mali-G77 MC9. The K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaomi
Corporation (; ), commonly known as Xiaomi and registered as Xiaomi Inc., is a Chinese designer and manufacturer of consumer electronics and related software, home appliances, and household items. Behind Samsung, it is the second largest manufacturer of smartphones in the world, most of which run the MIUI operating system. The company is ranked 338th and is the youngest company on the ''Fortune'' Global 500. Xiaomi was founded in 2010 in Beijing by now multi-billionaire Lei Jun when he was 40 years old, along with six senior associates. Lei had founded Kingsoft as well as Joyo.com, which he sold to Amazon for $75 million in 2004. In August 2011, Xiaomi released its first smartphone and, by 2014, it had the largest market share of smartphones sold in China. Initially the company only sold its products online; however, it later opened brick and mortar stores. By 2015, it was developing a wide range of consumer electronics. In 2020, the company sold 146.3 million smartphon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4G LTE
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a Technical standard, standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution, EDGE and UMTS/High Speed Packet Access, HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequency bands, LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported. The standard is developed by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and is specified in its Release 8 document series, with minor enhancements described in Release 9. LTE is also called 3.95G and has been marketed as "4G LTE" and "Advanced 4G"; but it does not meet the technical criteria of a 4G wireless service, as specified in the 3GPP Relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabyte
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The prefix '' giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte is GB. This definition is used in all contexts of science (especially data science), engineering, business, and many areas of computing, including storage capacities of hard drives, solid state drives, and tapes, as well as data transmission speeds. However, the term is also used in some fields of computer science and information technology to denote (10243 or 230) bytes, particularly for sizes of RAM. Thus, prior to 1998, some usage of ''gigabyte'' has been ambiguous. To resolve this difficulty, IEC 80000-13 clarifies that a ''gigabyte'' (GB) is 109 bytes and specifies the term ''gibibyte'' (GiB) to denote 230 bytes. These differences are still readily seen for example, when a 400 GB drive's capacity is displayed by Microsoft Windows as 372&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older magnetic tapes and drum memory), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. RAM contains multiplexing and demultiplexing circuitry, to connect the data lines to the addressed storage for reading or writing the entry. Usually more than one bit of storage is accessed by the same address, and RAM devices often have multiple data lines and are said to be "8-bit" or "16-bit", etc. devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Stabilization
Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure. Generally, it compensates for pan and tilt (angular movement, equivalent to yaw and pitch) of the imaging device, though electronic image stabilization can also compensate for rotation. It is mainly used in high-end image-stabilized binoculars, still and video cameras, astronomical telescopes, and also smartphones. With still cameras, camera shake is a particular problem at slow shutter speeds or with long focal length lenses ( telephoto or zoom). With video cameras, camera shake causes visible frame-to-frame jitter in the recorded video. In astronomy, the problem of lens shake is added to variation in the atmosphere, which changes the apparent positions of objects over time. Application in still photography In photography, image stabilization can facilitate shutter speeds 2 to 5.5 stops slower (exposures 4 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autofocus
An autofocus (or AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication. Autofocus methods are distinguished as active, passive or hybrid types. Autofocus systems rely on one or more sensors to determine correct focus. Some AF systems rely on a single sensor, while others use an array of sensors. Most modern SLR cameras use through-the-lens optical sensors, with a separate sensor array providing light metering, although the latter can be programmed to prioritize its metering to the same area as one or more of the AF sensors. Through-the-lens optical autofocusing is usually speedier and more precise than manual focus with an ordinary viewfinder, although more precise manual focus can be achieved with special accessories such as focusing magnifiers. Autofocus ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although '' sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exmor
Exmor is the name of a technology Sony implemented on some of their CMOS sensor, CMOS image sensors. It performs on-chip Analog-to-digital converter, analog/digital signal conversion and two-step noise reduction in parallel on each column of the CMOS sensor. Exmor RS is the world's first stacked CMOS image sensor and was announced by Sony on 20 August 2012. Subsequently, Sony announced the first 3-layer stacked CMOS sensor, which added a Dynamic random-access memory, DRAM cell array in the middle. History In October 2015, Sony Semiconductor Solutions was established as a wholly owned group company to reinforce the CMOS image sensor business and integrate the semiconductor-related business operations of Sony Group. Following the incorporation, all the Exmor sensors are designed and manufactured by the company. On May 14, 2020, the Intelligent vision sensor, Intelligent Vision Sensor was announced with an introduction that reads: "the first image sensor in the world to be eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional electronic products, the largest video game console company and the largest video game publisher. Through Sony Entertainment Inc, it is one of the largest music companies (largest music publisher and second largest record label) and the third largest film studio, making it one of the most comprehensive media companies. It is the largest technology and media conglomerate in Japan. It is also recognized as the most cash-rich Japanese company, with net cash reserves of ¥2 trillion. Sony, with its 55 percent market share in the image sensor market, is the largest manufacturer of image sensors, the second largest camera manufacturer, and is among the semiconductor sales leaders. It is the world's largest player in the premium TV mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
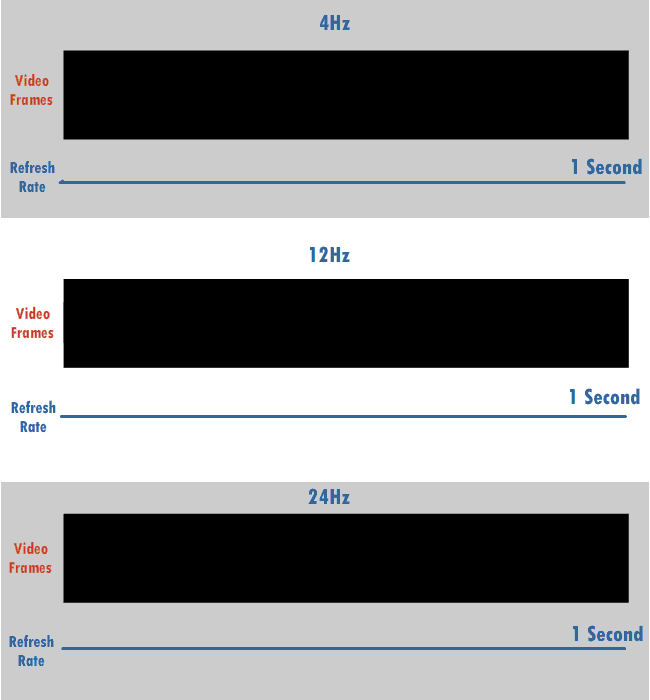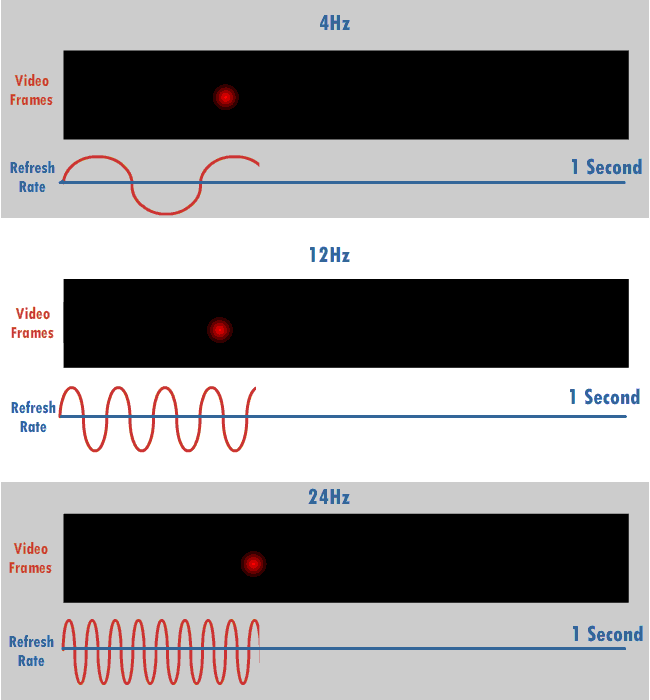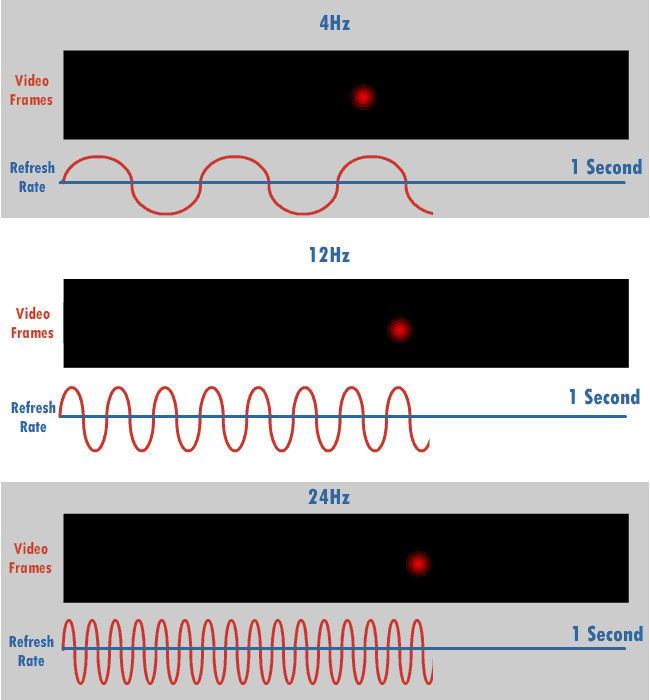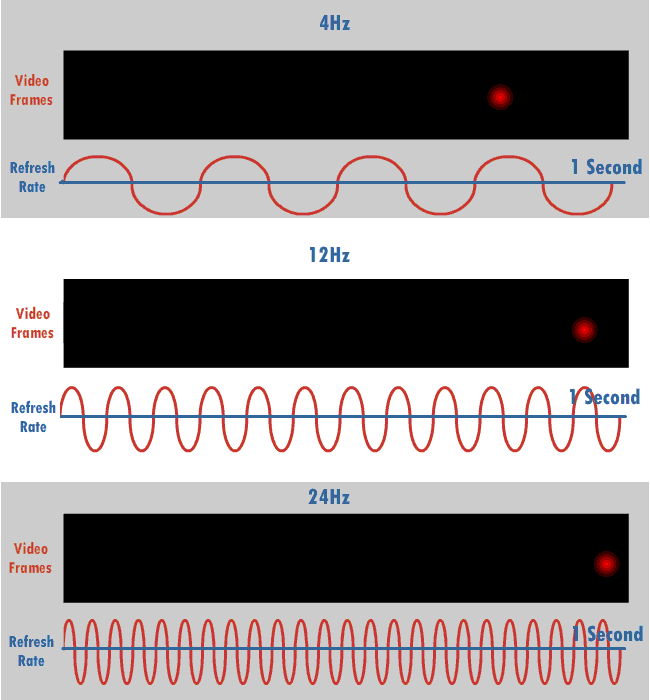
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate (or "vertical refresh rate", "vertical scan rate", terminology originating with the cathode ray tubes) is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a new external value from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |