|
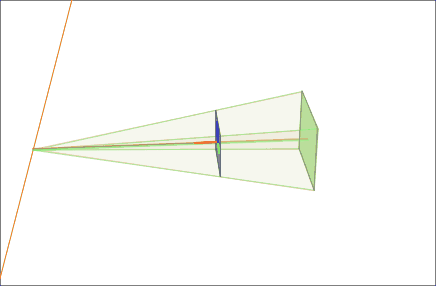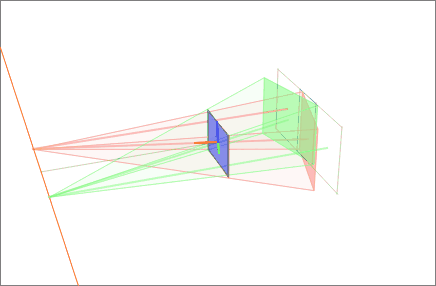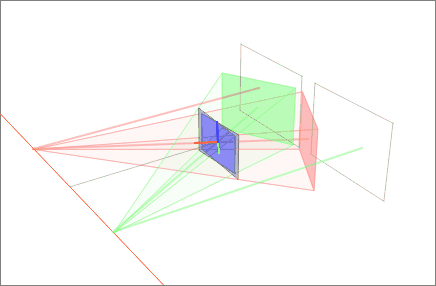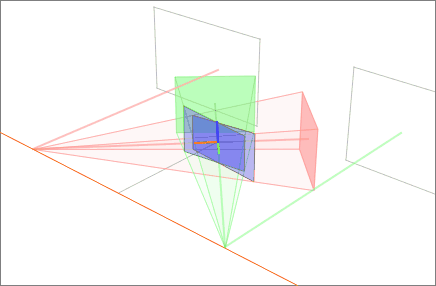
Rectified 5-cell 10 3 Configuration
Rectification has the following technical meanings: Mathematics * Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points * Rectifiable curve, in mathematics * Rectifiable set, in mathematics Science * GHK flux equation#Rectification, in biology, a process in cell membranes Technology * Image rectification, adjustment of images to simplify stereo vision or to map images to a map coordinate system (GIS) * The function of a rectifier, a device that converts alternating electrical current to direct current * Rectified airspeed, a means of displaying the airspeed of high-speed aircraft * Rectification (chemical/process engineering), countercurrent distillation, a unit operation also used for the production of rectified spirit (see Distillation#Fractional distillation) Other uses * Rectification (law), an equitable legal remedy whereby a court orders a change in a written document to reflect what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectification (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, rectification, also known as critical truncation or complete-truncation, is the process of truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points. The resulting polytope will be bounded by vertex figure facets and the rectified facets of the original polytope. A rectification operator is sometimes denoted by the letter with a Schläfli symbol. For example, is the rectified cube, also called a cuboctahedron, and also represented as \begin 4 \\ 3 \end. And a rectified cuboctahedron is a rhombicuboctahedron, and also represented as r\begin 4 \\ 3 \end. Conway polyhedron notation uses for ambo as this operator. In graph theory this operation creates a medial graph. The rectification of any regular self-dual polyhedron or tiling will result in another regular polyhedron or tiling with a tiling order of 4, for example the tetrahedron becoming an octahedron As a special case, a square til ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectifiable Curve
Arc length is the distance between two points along a section of a curve. Development of a formulation of arc length suitable for applications to mathematics and the sciences is a problem in vector calculus and in differential geometry. In the most basic formulation of arc length for a vector valued curve (thought of as the trajectory of a particle), the arc length is obtained by integrating the magnitude of the velocity vector over the curve with respect to time. Thus the length of a continuously differentiable curve (x(t),y(t)), for a\le t\le b, in the Euclidean plane is given as the integral L = \int_a^b \sqrt\,dt, (because \sqrt is the magnitude of the velocity vector (x'(t),y'(t)), i.e., the particle's speed). The defining integral of arc length does not always have a closed-form expression, and numerical integration may be used instead to obtain numerical values of arc length. Determining the length of an irregular arc segment by approximating the arc segment as connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectifiable Set
In mathematics, a rectifiable set is a set that is smooth in a certain measure-theoretic sense. It is an extension of the idea of a rectifiable curve to higher dimensions; loosely speaking, a rectifiable set is a rigorous formulation of a piece-wise smooth set. As such, it has many of the desirable properties of smooth manifolds, including tangent spaces that are defined almost everywhere. Rectifiable sets are the underlying object of study in geometric measure theory. Definition A Borel subset E of Euclidean space \mathbb^n is said to be m-rectifiable set if E is of Hausdorff dimension m, and there exist a countable collection \ of continuously differentiable maps :f_i:\mathbb^m \to \mathbb^n such that the m-Hausdorff measure \mathcal^m of :E\setminus \bigcup_^\infty f_i\left(\mathbb^m\right) is zero. The backslash here denotes the set difference. Equivalently, the f_i may be taken to be Lipschitz continuous without altering the definition. Other authors have different defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GHK Flux Equation
GHK may refer to: * Gahcho Kue Aerodrome, in the Northwest Territories, Canada * Geko Karen, a language of Burma * GHK algorithm, a regression model * Ghotki railway station, in Pakistan * Glasgow High Kelvinside, a Scottish rugby union club * Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz flux equation * Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz voltage equation * Gush Katif Airport Gush Katif Airport is a small abandoned airfield in Gaza Strip, Palestine approximately north of the town of Khan Yunis, and adjacent to the UNRWA Khan Yunis refugee camp. It was located immediately west of the former Israeli settlement of G ..., in the Gaza Strip * Wood and Plastic Union, a former German trade union {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Rectification
Image rectification is a transformation process used to project images onto a common image plane. This process has several degrees of freedom and there are many strategies for transforming images to the common plane. Image rectification is used in computer stereo vision to simplify the problem of finding matching points between images (i.e. the correspondence problem), and in geographic information systems (GIS) to merge images taken from multiple perspectives into a common map coordinate system. In computer vision Computer stereo vision takes two or more images with known relative camera positions that show an object from different viewpoints. For each pixel it then determines the corresponding scene point's depth (i.e. distance from the camera) by first finding matching pixels (i.e. pixels showing the same scene point) in the other image(s) and then applying triangulation (computer vision), triangulation to the found matches to determine their depth. Finding matches in stereo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |