|
Reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection involves plasma flows at a substantial fraction of the Alfvén wave speed, which is the fundamental speed for mechanical information flow in a magnetized plasma. The concept of magnetic reconnection was developed in parallel by researchers working in solar physics and in the interaction between the solar wind and magnetized planets. This reflects the bidirectional nature of reconnection, which can either disconnect formerly connected magnetic fields or connect formerly disconnected magnetic fields, depending on the circumstances. Ron Giovanelli is credited with the first publication invoking magnetic energy release as a potential mechanism for particle acceleration in Solar flare, solar flares. Giovanelli propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dungey
James Wynne Dungey (1923–2015) was a British space scientist who was pivotal in establishing the field of space weather and made significant contributions to the fundamental understanding of plasma physics. Early life and education Dungey grew up in Stamford, Lincolnshire, the son of a schoolteacher. During World War II, he worked at British Thompson-Houston in Rugby, on developments for radar. After the end of the war, he gained a degree in 1947 from Magdalene College, Cambridge, part of the University of Cambridge. He then completed a Ph.D. at the same institution, under the supervision of Fred Hoyle. Career and research From 1950 to 1953 Dungey worked at the University of Sydney with Ron Giovanelli, from 1953 to 1954 at Pennsylvania State University, and from 1954 to 1957 back at the University of Cambridge. From 1957 to 1959 he was a mathematics lecturer at King's College, Newcastle upon Tyne (now Newcastle University) and from 1959 to 1963 he worked at the UK Atomic Wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ron Giovanelli
Ronald Gordon Giovanelli, Doctor of Science, DSc, Australian Academy of Science, FAA (International Phonetic Alphabet, /dʒoʊvɑ’nɛli/; 30 April 1915 — 27 January 1984) was an Australian solar researcher, astronomer and physicist, who contributed to the fields of astrophysics, solar physics, radiative transfer, and astronomical optics. His career spanned more than 40 years, commencing prior to World War II. Giovanelli was the recipient of the 1949 Edgeworth David Medal by the Royal Society of New South Wales for the discipline of astrophysics, which recognises distinguished contributions by scientists under the age of 35 in their respective fields. He was also elected into the Fellowship of the Australian Academy of Science in 1962 for his contributions in the field of physics. Giovanelli served as Chief of the Physics Division of the CSIRO, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) from 1958 to 1976, during which he also became Chairman of the Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Topology
In plasma physics, the magnetic topology of a plasma is the structure and linkage of its magnetic field. The magnetic topology of a plasma can be changed through magnetic diffusion and reconnection Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle accelerati .... In the limit of a large magnetic Reynolds number, however, diffusion and reconnection of the magnetic field cannot occur, and the magnetic topology is preserved. See also * Helmet streamer#Pseudostreamers References {{Plasma-stub Plasma theory and modeling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfvén's Theorem
In ideal magnetohydrodynamics, Alfvén's theorem, or the frozen-in flux theorem, states that electrically conducting fluids and embedded magnetic fields are constrained to move together in the limit of large magnetic Reynolds numbers. It is named after Hannes Alfvén, who put the idea forward in 1943. Alfvén's theorem implies that the magnetic topology of a fluid in the limit of a large magnetic Reynolds number cannot change. This approximation breaks down in current sheets, where magnetic reconnection can occur. History The concept of magnetic fields being frozen into fluids with infinite electrical conductivity was first proposed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1943 paper titled "On the Existence of Electromagnetic-Hydrodynamic Waves", published in the journal '' Arkiv för matematik, astronomi och fysik''. He wrote: "On the Existence of Electromagnetic-Hydrodynamic Waves" interpreted the results of Alfvén's earlier paper "Existence of Electromagnetic-Hydrodynamic Waves", publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
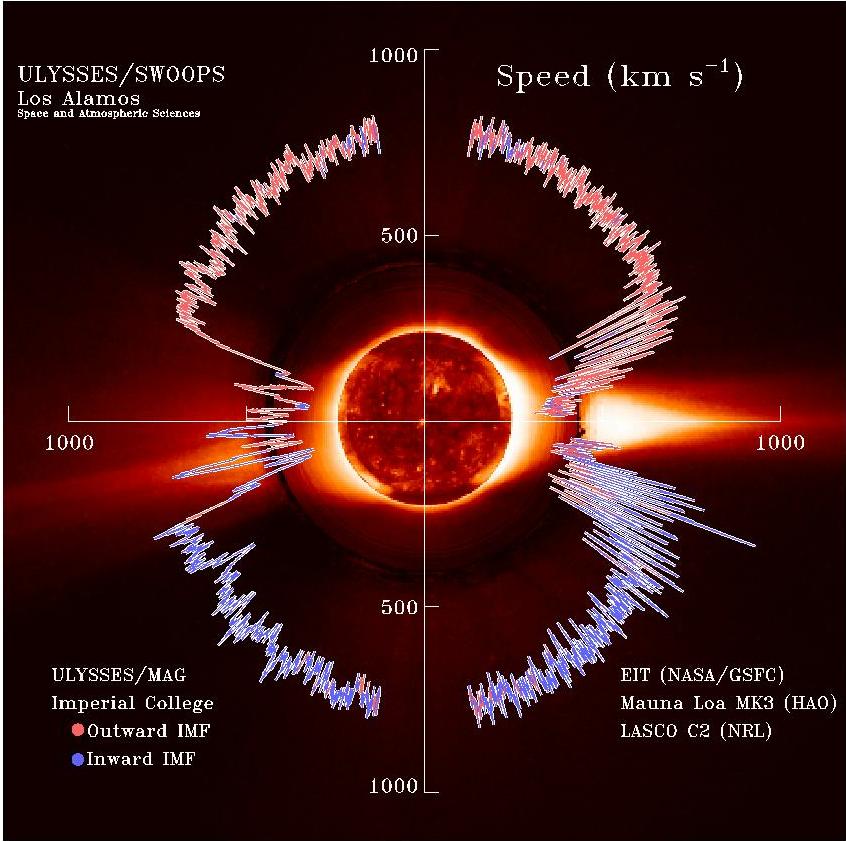
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually affect the entire solar atmosphere. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other eruptive solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. The typical time profile of these emissions features three identifiable phases: a ''precursor phase'', an ''impulsive phase'' when particle acceleration dominates, and a ''gradual phase'' in which hot plasma injected into the corona by the flare cools by a combination of radiation and conduction of energy back down to the lower atmosphere. The extreme ultraviolet and X-ray radiation from solar flares is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Sheet
A current sheet is an electric current that is confined to a surface, rather than being spread through a volume of space. Current sheets feature in magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), a model of electrically conductive fluids: if there is an electric current through part of the volume of such a fluid, magnetic forces tend to expel it from the fluid, compressing the current into thin layers that pass through the volume. The largest occurring current sheet in the Solar System is the so-called heliospheric current sheet, which is about 10,000 km thick, and extends from the Sun and out beyond the orbit of Pluto. In astrophysical plasmas such as the solar corona, current sheets theoretically might have an aspect ratio (breadth divided by thickness) as high as 100,000:1. By contrast, the pages of most books have an aspect ratio close to 2000:1. Because current sheets are so thin in comparison to their size, they are often treated as if they have zero thickness; this is a result of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lundquist Number
In plasma physics, the Lundquist number (denoted by S) is a dimensionless ratio which compares the timescale of an Alfvén wave crossing to the timescale of resistive diffusion. It is a special case of the magnetic Reynolds number when the Alfvén velocity is the typical velocity scale of the system, and is given by :S = \frac , where L is the typical length scale of the system, \eta is the magnetic diffusivity and v_A is the Alfvén velocity of the plasma. High Lundquist numbers indicate highly conducting plasmas, while low Lundquist numbers indicate more resistive plasmas. Laboratory plasma experiments typically have Lundquist numbers between 10^2-10^8, while in astrophysical situations the Lundquist number can be greater than 10^. Considerations of Lundquist number are especially important in magnetic reconnection Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo theory, dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body with a dipole magnetic field such as Earth, the field lines resemble a simple magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma (physics), plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation. Interactions of particles and atmospheres with magnetospheres are studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics, and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert (astronomer), W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Parker
Eugene Newman Parker (June 10, 1927 – March 15, 2022) was an American solar and plasma physicist. In the 1950s he proposed the existence of the solar wind and that the magnetic field in the outer Solar System would be in the shape of a Parker spiral, predictions that were later confirmed by spacecraft measurements. In 1987, Parker proposed the existence of nanoflares, a leading candidate to explain the coronal heating problem. Parker obtained his PhD from Caltech and spent four years as a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Utah. He joined University of Chicago in 1955 and spent the rest of his career there, holding positions in the physics department, the astronomy and astrophysics department, and the Enrico Fermi Institute. Parker was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1967. In 2017, NASA named its Parker Solar Probe in his honor, the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person. Biography Parker was born in Houghton, Michigan to Glenn and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |