|
Recognition
Recognition may refer to: Machine learning *Pattern recognition, a branch of machine learning which encompasses the meanings below Biometric * Recognition of human individuals, or biometrics, used as a form of identification and access control **Facial recognition system, a system to identify individuals by their facial characteristics **Fingerprint recognition, automated method of verifying a match between two human fingerprints ** Handwritten biometric recognition, identifies the author of specific handwriting, offline (static) or in real-time (dynamic) **Iris recognition, a method of biometric identification Linguistic *Language identification, the problem of identifying which natural language given content is in *Natural language understanding, the parsing of the meaning of text *Speech recognition, the conversion of spoken words into text *Speaker recognition, the recognition of a speaker from their voice Textual *Handwriting recognition, the conversion of handwritten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Recognition System
A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a Film frame, video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image. Development began on similar systems in the 1960s, beginning as a form of computer Application software, application. Since their inception, facial recognition systems have seen wider uses in recent times on smartphones and in other forms of technology, such as robotics. Because computerized facial recognition involves the measurement of a human's physiological characteristics, facial recognition systems are categorized as biometrics. Although the accuracy of facial recognition systems as a biometric technology is lower than iris recognition, fingerprint, fingerprint image acquisition, palm recognition or Speech recognition, voice recognition, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), computer speech recognition or speech-to-text (STT). It incorporates knowledge and research in the computer science, linguistics and computer engineering fields. The reverse process is speech synthesis. Some speech recognition systems require "training" (also called "enrollment") where an individual speaker reads text or isolated vocabulary into the system. The system analyzes the person's specific voice and uses it to fine-tune the recognition of that person's speech, resulting in increased accuracy. Systems that do not use training are called "speaker-independent" systems. Systems that use training are called "speaker dependent". Speech recognition applications include voice user interfaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity Recognition
Activity recognition aims to recognize the actions and goals of one or more agents from a series of observations on the agents' actions and the environmental conditions. Since the 1980s, this research field has captured the attention of several computer science communities due to its strength in providing personalized support for many different applications and its connection to many different fields of study such as medicine, human-computer interaction, or sociology. Due to its multifaceted nature, different fields may refer to activity recognition as plan recognition, goal recognition, intent recognition, behavior recognition, location estimation and location-based services. Types Sensor-based, single-user activity recognition Sensor-based activity recognition integrates the emerging area of sensor networks with novel data mining and machine learning techniques to model a wide range of human activities. Mobile devices (e.g. smart phones) provide sufficient sensor data and calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Recognitions
''The Recognitions'' is the 1955 debut novel of American author William Gaddis. The novel was initially poorly received by critics. After Gaddis won a National Book Award in 1975 for his second novel, ''J R'', his first work gradually received new and belated recognition as a masterpiece of American literature. In 2005, ''Time (magazine), Time'' included ''The Recognitions'' in its list of "100 Best English-language Novels from 1923 to 2005". Plot The story loosely follows the life of Wyatt Gwyon, son of a Calvinist minister from rural New England; his mother dies in Spain. He plans to follow his father into the ministry. But he is inspired to become a painter by ''The Seven Deadly Sins and the Four Last Things, The Seven Deadly Sins'', Hieronymous Bosch's noted painting which his father owned. Gwyon leaves New England and travels to Europe to study painting. Discouraged by a corrupt critic and frustrated with his career, he moves to New York City. He meets Recktall Brown, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Number Plate Recognition
Automatic number-plate recognition (ANPR; see also other names below) is a technology that uses optical character recognition on images to read vehicle registration plates to create vehicle location data. It can use existing closed-circuit television, road-rule enforcement cameras, or cameras specifically designed for the task. ANPR is used by police forces around the world for law enforcement purposes, including checking if a vehicle is registered or licensed. It is also used for electronic toll collection on pay-per-use roads and as a method of cataloguing the movements of traffic, for example by highways agencies. Automatic number-plate recognition can be used to store the images captured by the cameras as well as the text from the license plate, with some configurable to store a photograph of the driver. Systems commonly use infrared lighting to allow the camera to take the picture at any time of day or night. ANPR technology must take into account plate variations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess PR capabilities but their primary function is to distinguish and create emergent patterns. PR has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. Pattern recognition systems are commonly trained from labeled "training" data. When no labeled data are available, other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns. KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesture Recognition
Gesture recognition is an area of research and development in computer science and language technology concerned with the recognition and interpretation of human gestures. A subdiscipline of computer vision, it employs mathematical algorithms to interpret gestures. Gesture recognition offers a path for computers to begin to better understand and interpret computer processing of body language, human body language, previously not possible through text user interface, text or unenhanced graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Gestures can originate from any bodily motion or state, but commonly originate from the face or hand. One area of the field is emotion recognition derived from facial expressions and hand gestures. Users can make simple gestures to control or interact with devices without physically touching them. Many approaches have been made using cameras and computer vision algorithms to interpret sign language, however, the identification and recognition of posture, gait, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris Recognition
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometrics, biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the iris (anatomy), irises of an individual's Human eye, eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometrics, biometric technologies depend on the amount of Entropy (information theory), entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" (False positives and false negatives, False Matches) even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed. Retinal scanning is a different, ocul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Perception
Facial perception is an individual's understanding and interpretation of the face. Here, perception implies the presence of consciousness and hence excludes automated facial recognition systems. Although facial recognition is found in other species, this article focuses on facial perception in humans. The perception of facial features is an important part of social cognition. Information gathered from the face helps people understand each other's Identity (social science), identity, what they are thinking and feeling, anticipate their actions, Emotion recognition, recognize their emotions, build connections, and communicate through body language. Developing facial recognition is a necessary building block for complex societal constructs. Being able to perceive identity, mood, age, sex, and race lets people mold the way we interact with one another, and understand our immediate surroundings. Though facial perception is mainly considered to stem from visual intake, studies have s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Recognition
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different view points, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades. Approaches based on CAD-like object models * Edge detection * Primal sketch * Marr, Mohan and Nevatia * Lowe * Olivier Faugeras Recognition by parts * Generalized cylinders ( Thomas Binford) * Geons ( Irving Biederman) * Dickinson, Forsyth and Ponce Appearance-based methods * Use example images (called templates or exemplars) of the objects to perform recognition * Objects look differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
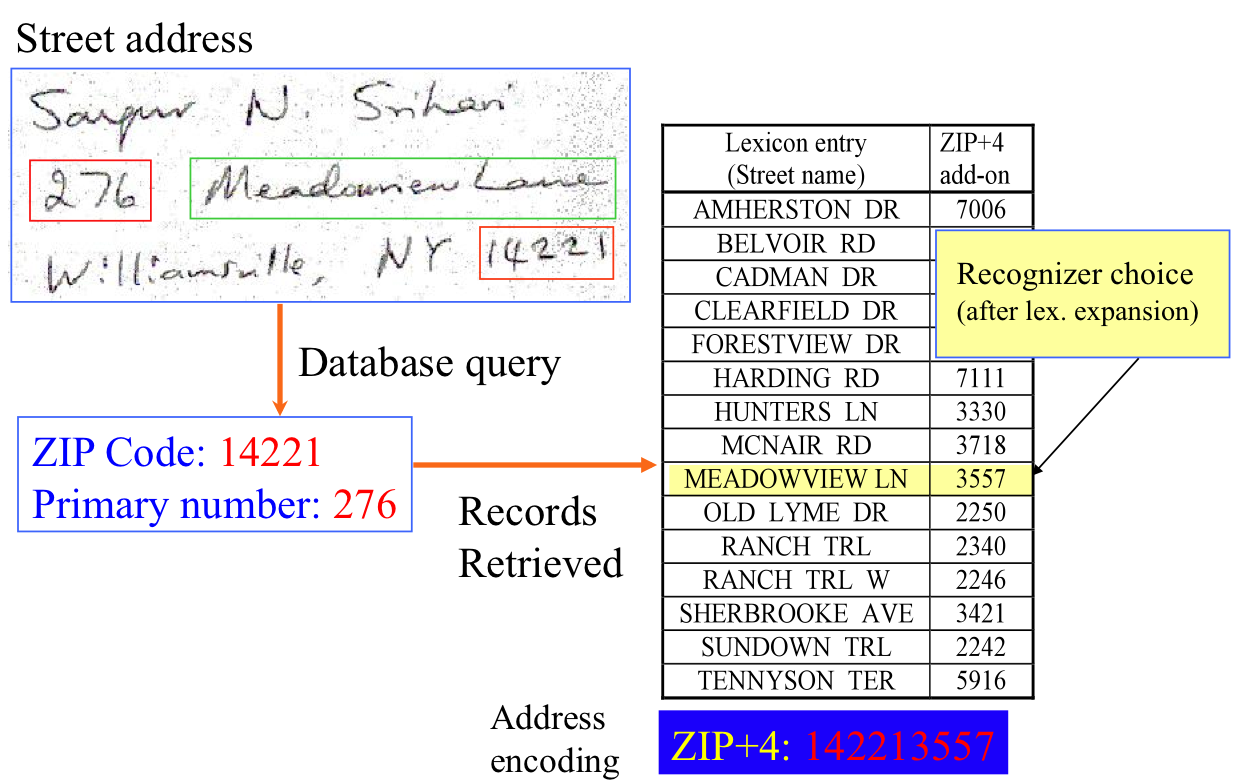
Handwriting Recognition
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwriting, handwritten input from sources such as paper documents, photographs, touch-screens and other devices. The image of the written text may be sensed "off line" from a piece of paper by optical scanning (optical character recognition) or intelligent word recognition. Alternatively, the movements of the pen tip may be sensed "on line", for example by a pen-based computer screen surface, a generally easier task as there are more clues available. A handwriting recognition system handles formatting, performs correct Segment (handwriting), segmentation into characters, and finds the most possible words. Offline recognition Offline handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text in an image into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications. The data obtained by this form is reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronics, electronic or machine, mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example: from a television broadcast). Widely used as a form of data entry from printed paper data recordswhether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized receipts, business cards, mail, printed data, or any suitable documentationit is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed online, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech, key data and text mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intelligen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |