|
Receptor Potential
A receptor potential, also known as a generator potential, a type of graded potential, is the transmembrane potential difference produced by activation of a sensory receptor. A receptor potential is often produced by sensory transduction. It is generally a depolarizing event resulting from inward current flow. The influx of current will often bring the membrane potential of the sensory receptor towards the threshold for triggering an action potential. Receptor potential can work to trigger an action potential either within the same neuron or on an adjacent cell. Within the same neuron, a receptor potential can cause local current to flow to a region capable of generating an action potential by opening voltage-gated ion channels. A receptor potential can also cause the release of neurotransmitters from one cell that will act on another cell, generating an action potential in the second cell. The magnitude of the receptor potential determines the frequency with which action pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graded Potential
Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary according to the size of the stimulus, as opposed to being all-or-none. They include diverse potentials such as receptor potentials, electrotonic potentials, subthreshold membrane potential oscillations, slow-wave potential, pacemaker potentials, and synaptic potentials. The magnitude of a graded potential is determined by the strength of the stimulus. They arise from the summation of the individual actions of ligand-gated ion channel proteins, and decrease over time and space. They do not typically involve voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels, but rather can be produced by neurotransmitters that are released at synapses which activate ligand-gated ion channels. They occur at the postsynaptic dendrite in response to presynaptic neuron firing and release of neurotransmitter, or may occur in skeletal, smooth, or cardiac muscle in response to nerve input. These impulses are incremental and may be excitatory or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taste Bud
Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the cheek, and epiglottis. These structures are involved in detecting the five elements of taste perception: saltiness, sourness, bitterness, sweetness and savoriness (umami). A popular assumption assigns these different tastes to different regions of the tongue; in actuality, these tastes can be detected by any area of the tongue. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with the taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptors , a device for the reception of electromagnetic ...
Receptor may refer to: *Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse *Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a neurotransmitter, or other substance **Cell surface receptor, a receptor on the outer surface of a cell membrane, that takes part in communication between the cell and the outside world **Nuclear receptor, a receptor found within cells that is responsible for sensing steroid and thyroid hormones and certain other molecules **Immune receptor, a receptor that occurs on the surface of immunocytes and binds to antigens *Receiver (radio) In radio, radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of Membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and myocyte, muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell interaction, cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward axon terminal, synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
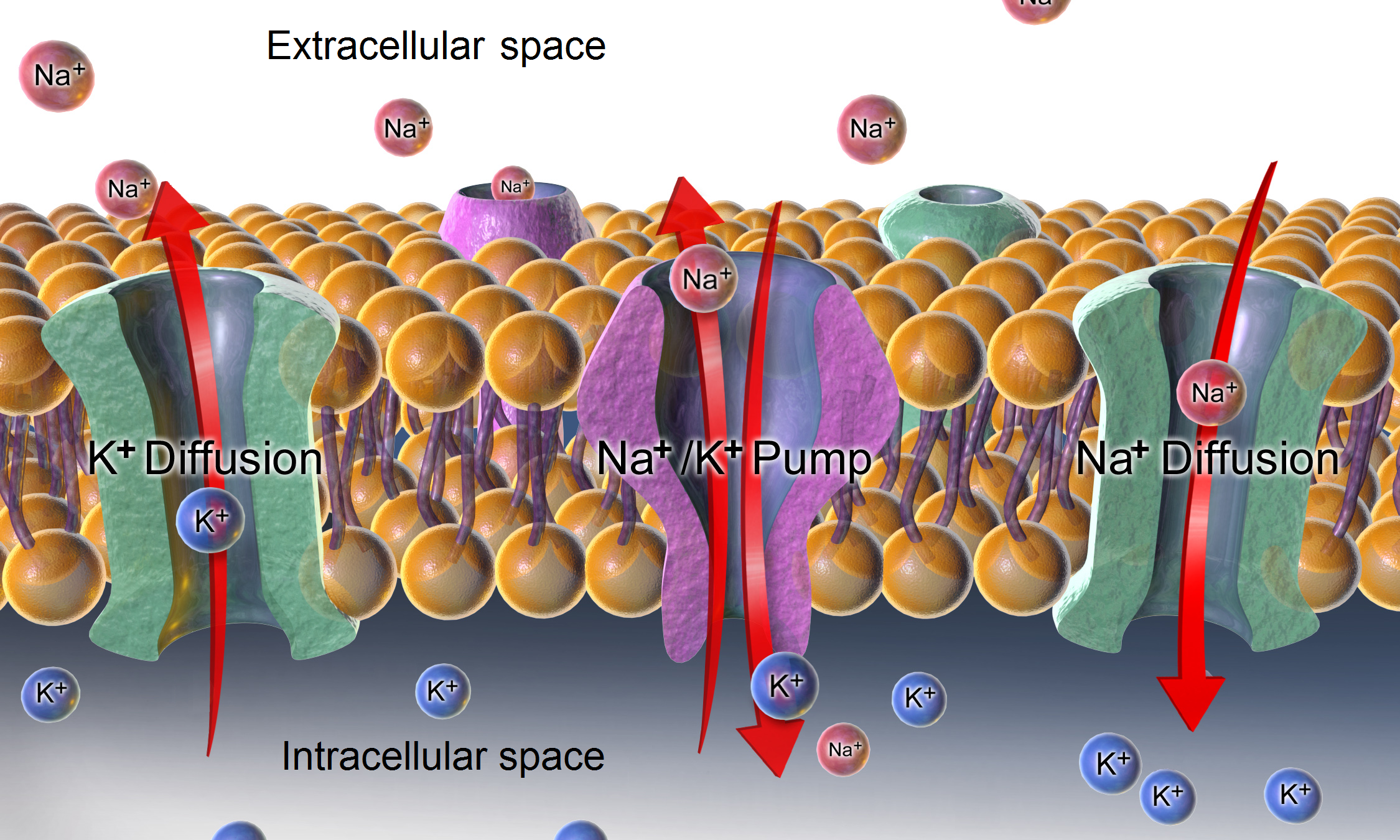
Resting Potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential has a value of approximately −70 mV or −0.07 V. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Because the membrane pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postsynaptic
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body. At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are contained within small sacs called synaptic vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cell. Finally, the neurotransmitters are cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Cleft
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in neuromuscular junction, muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form biological neural network, circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body. At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the #Structure, synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are contained within small sacs called synaptic vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cell. Finally, the neurotransmitters are cleared from the synapse through one of several Action potential, potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presynaptic
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are exocytosis, released at the chemical synapse, synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicle (biology), Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell (biology), cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis is a crucial transport mechanism that enables polar molecules to flow through the cell membranes’ hydrophobic lipid bilayer. The transport process is essential to hormone secretion, immune response and neurotransmission. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes undergo exocytosis. Prokaryotes secrete molecules and cellular waste through translocons that are localized to the cell membrane. In addition, they secrete molecules to other cells through specialized organs. Eukaryotes rely on multiple cellular processes to perform the exocytosis process. Eukaryotes have several organelles and a nucleus in the cytoplasm that are connected through multiple transport routes, that is formally known as the secretory pathway. This is a complex pathway with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. Some neurotransmitters are also stored in large dense core vesicles. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds to. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include Glutamate (neurotransmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Potential Difference
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. It equals the interior potential minus the exterior potential. This is the energy (i.e. work) per charge which is required to move a (very small) positive charge at constant velocity across the cell membrane from the exterior to the interior. (If the charge is allowed to change velocity, the change of kinetic energy and production of radiation must be taken into account.) Typical values of membrane potential, normally given in units of milli volts and denoted as mV, range from −80 mV to −40 mV. For such typical negative membrane potentials, positive work is required to move a positive charge from the interior to the exterior. However, thermal kinetic energy allows ions to overcome the potential difference. For a selectively permeable membrane, this permits a net flow against the gradient. This is a kind of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |