|
Read For Ownership
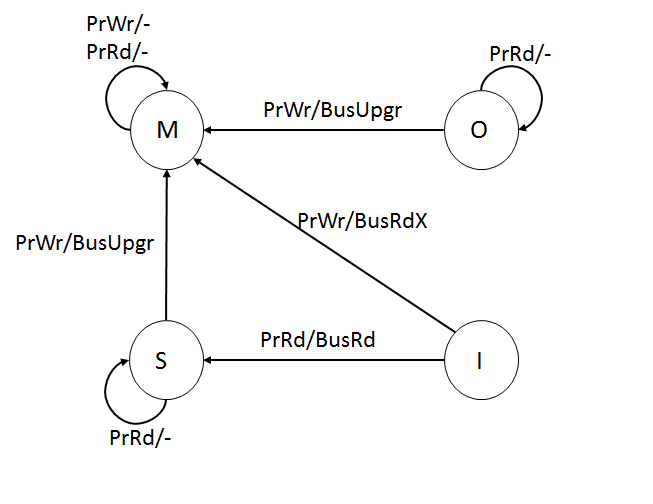
The MESI protocol is an invalidate-based cache coherence protocol, and is one of the most common protocols that support write-back caches. It is also known as the Illinois protocol due to its development at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Write back caches can save considerable bandwidth generally wasted on a write through cache. There is always a dirty state present in write-back caches that indicates that the data in the cache is different from that in the main memory. The Illinois Protocol requires a cache-to-cache transfer on a miss if the block resides in another cache. This protocol reduces the number of main memory transactions with respect to the MSI protocol. This marks a significant improvement in performance. States The letters in the acronym MESI represent four exclusive states that a cache line can be marked with (encoded using two additional bits): ;Modified (M): The cache line is present only in the current cache, and is ''dirty'' - it has been m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cache Coherency Protocols
Examples of coherency protocols for cache memory are listed here. For simplicity, all "miss" Read and Write status transactions which obviously come from state "I" (or miss of Tag), in the diagrams are not shown. They are shown directly on the new state. Many of the following protocols have only historical value. At the moment the main protocols used are the R-MESI type / MESIF protocols and the HRT-ST-MESI (MOESI type) or a subset or an extension of these. Cache coherency problem In systems as Multiprocessor system architecture#Symmetric multiprocessor system, Multiprocessor system, Multi-core processor, multi-core and Non-uniform memory access, NUMA system, where a dedicated cache for each ''processor'', ''core'' or ''node'' is used, a consistency problem may occur when a same data is stored in more than one cache. This problem arises when a data is modified in one cache. This problem can be solved in two ways: # Invalidate all the copies on other caches (broadcast-invalida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherency
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that is stored in multiple local caches. In a cache coherent system, if multiple clients have a cached copy of the same region of a shared memory resource, all copies are the same. Without cache coherence, a change made to the region by one client may not be seen by others, and errors can result when the data used by different clients is mismatched. A cache coherence protocol is used to maintain cache coherency. The two main types are snooping and directory-based protocols. Cache coherence is of particular relevance in multiprocessing systems, where each CPU may have its own local cache of a shared memory resource. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When one of the copies of data is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
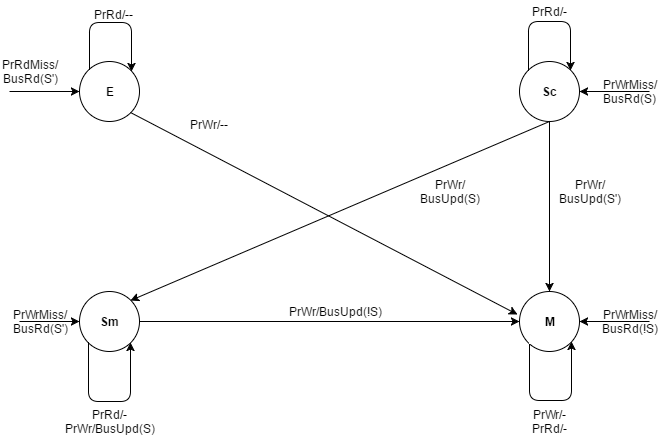
Dragon Protocol
The Dragon Protocol is an update based cache coherence protocol used in multi-processor systems. Write propagation is performed by directly updating all the cached values across multiple processors. Update based protocols such as the Dragon protocol perform efficiently when a write to a cache block is followed by several reads made by other processors, since the updated cache block is readily available across caches associated with all the processors. States Each cache block resides in one of the four states: exclusive-clean, shared-clean, shared-modified and modify. * Exclusive-clean (E): This means that the cache block was first fetched by the current processor and has not been accessed by any other processor since. * Shared clean (Sc): This means that the cache block definitely exists in multiple processor’s caches, and that the current processor is not the last one to write the block. States E and Sc are maintained separately by the protocol to prevent read-write operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSI Protocol
The MOSI protocol is an extension of the basic MSI cache coherency protocol. It adds the Owned state, which indicates that the current processor owns this block, and will service requests from other processors for the block. Overview of States Following are the permitted states of a given cache line: Modified (M) - Only one cache has a valid copy of the block and the value is likely to be different from the one in main memory. It has almost the same meaning as a dirty state in a write-back cache except for the difference that modified state also implies exclusive ownership of that block. Dirty state just means that the value of the block is different from the one in main memory, whereas, modified implies that the value is different than that of the main memory and that it is cached in only one location. Owned (O) - Multiple caches may hold the most recent and correct value of a block and the value in main memory may or may not be correct. At a time, only one cache can have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write-once (cache Coherency) , computer storage that can be written to once, but read from multiple times
{{disambig ...
Write once may refer to: * Write once, run anywhere, a slogan for the cross-platform benefits of Java * Write once, compile anywhere, a slogan for the cross-platform benefits of C * Write-once (cache coherency), a write-invalidate protocol in computer memory design * Write once read many Write once read many (WORM) describes a data storage device in which information, once written, cannot be modified. This write protection affords the assurance that the data cannot be tampered with once it is written to the device, excluding the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Protocol
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that is stored in multiple local caches. In a cache coherent system, if multiple clients have a cached copy of the same region of a shared memory resource, all copies are the same. Without cache coherence, a change made to the region by one client may not be seen by others, and errors can result when the data used by different clients is mismatched. A cache coherence protocol is used to maintain cache coherency. The two main types are snooping and directory-based protocols. Cache coherence is of particular relevance in multiprocessing systems, where each CPU may have its own local cache of a shared memory resource. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When one of the copies of data is ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESIF Protocol
The MESIF protocol is a cache coherency and memory coherence protocol developed by Intel for cache coherent non-uniform memory architectures. The protocol consists of five states, Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Shared (S), Invalid (I) and Forward (F). The M, E, S and I states are the same as in the MESI protocol. The F state is a specialized form of the S state, and indicates that a cache should act as a designated responder for any requests for the given line. The protocol ensures that, if any cache holds a line in the S state, at most one (other) cache holds it in the F state. In a system of caches employing the MESI protocol, a cache line request that is received by multiple caches holding a line in the S state will be serviced inefficiently. It may either be satisfied from (slow) main memory, or ''all'' the sharing caches could respond, bombarding the requestor with redundant responses. In a system of caches employing the MESIF protocol, a cache line request will be responded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOESI Protocol
Modified Owned Exclusive Shared Invalid (MOESI) is a full cache coherency protocol that encompasses all of the possible states commonly used in other protocols. In addition to the four common MESI protocol states, there is a fifth "Owned" state representing data that is both modified and shared. This avoids the need to write modified data back to main memory before sharing it. While the data must still be written back eventually, the write-back may be deferred . In order for this to be possible, direct cache-to-cache transfers of data must be possible, so a cache with the data in the modified state can supply that data to another reader without transferring it to memory. As discussed in AMD64 Architecture Programmer's Manual Vol. 2 ''System Programming'', each cache line is in one of five states: ;Modified: This cache has the only valid copy of the cache line, and has made changes to that copy. The cached copy may be further modified freely. ;Owned: This line is one of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAS Latency
Column address strobe latency, also called CAS latency or CL, is the delay in clock cycles between the READ command and the moment data is available. In asynchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in nanoseconds (absolute time). In synchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in clock cycles. Because the latency is dependent upon a number of clock ticks instead of absolute time, the actual time for an SDRAM module to respond to a CAS event might vary between uses of the same module if the clock rate differs. RAM operation background Dynamic RAM is arranged in a rectangular array. Each row is selected by a horizontal ''word line''. Sending a logical high signal along a given row enables the MOSFETs present in that row, connecting each storage capacitor to its corresponding vertical ''bit line''. Each bit line is connected to a ''sense amplifier'' that amplifies the small voltage change produced by the storage capacitor. This amplified signal is then output from the DRAM chip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write-back Cache
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches are effective in many areas of computing because typical computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested, and spatial locality, where data is requested that is stored near data that has already bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
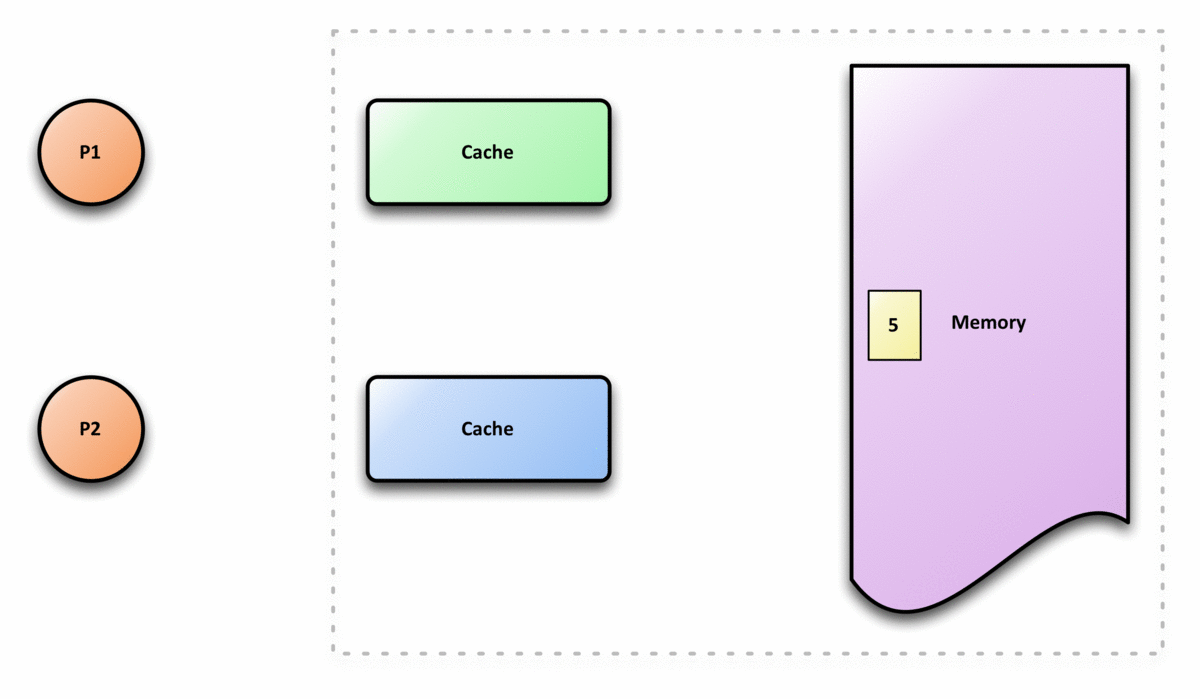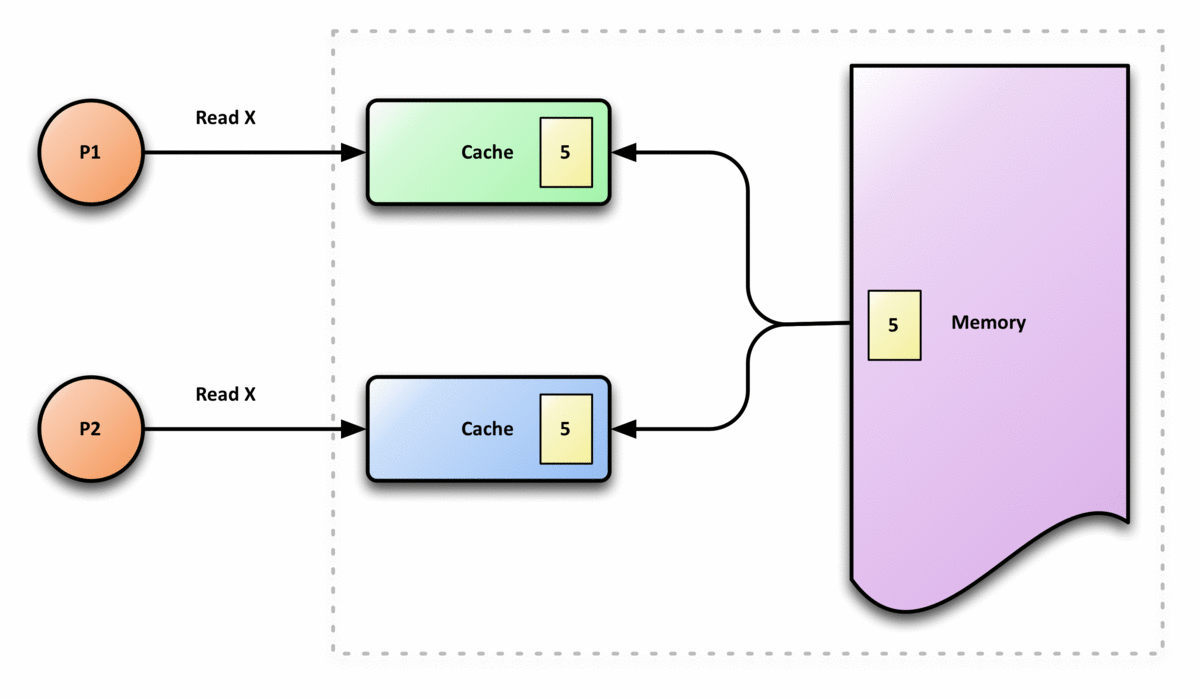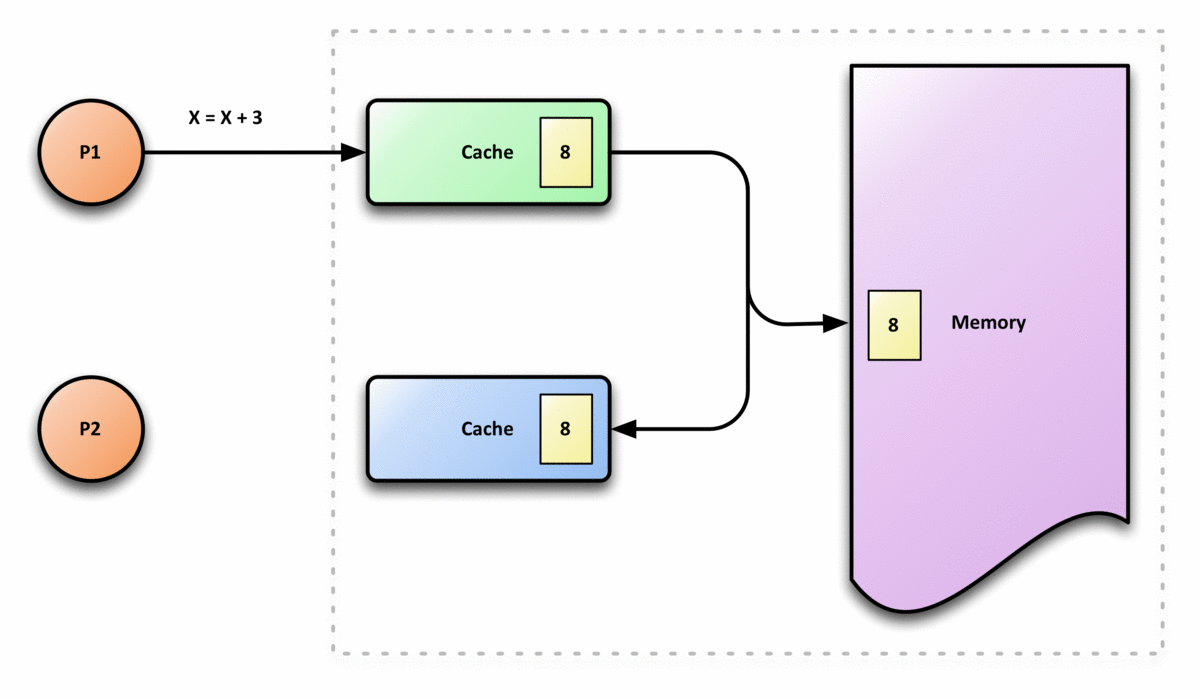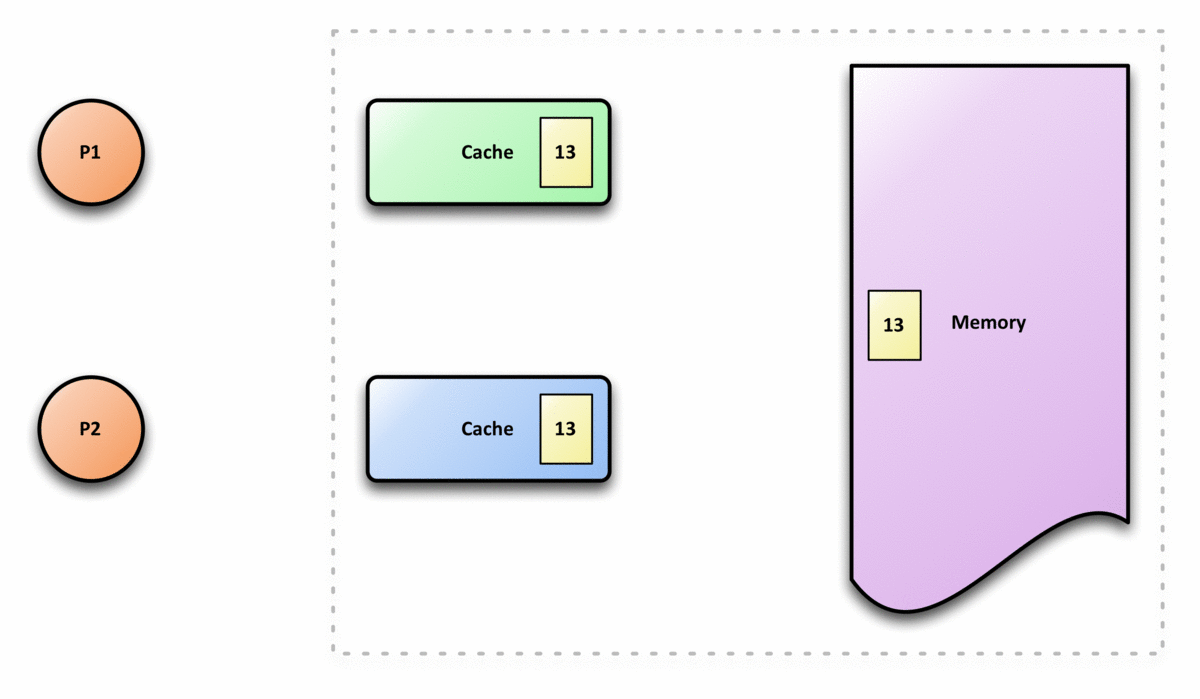
Bus Snooping
Bus snooping or bus sniffing is a scheme by which a coherency controller (snooper) in a cache (a snoopy cache) monitors or snoops the bus transactions, and its goal is to maintain a cache coherency in distributed shared memory systems. This scheme was introduced by Ravishankar and Goodman in 1983, under the name "write-once" cache coherency. A cache containing a coherency controller (snooper) is called a snoopy cache. How it works When specific data are shared by several caches and a processor modifies the value of the shared data, the change must be propagated to all the other caches which have a copy of the data. This change propagation prevents the system from violating cache coherency. The notification of data change can be done by bus snooping. All the snoopers monitor every transaction on a bus. If a transaction modifying a shared cache block appears on a bus, all the snoopers check whether their caches have the same copy of the shared block. If a cache has a copy of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |