|
Raymo, M.E.
Maureen E. Raymo (born 1959) is an American paleoclimatologist and marine geologist. She is the Co-Founding Dean Emerita of the Columbia Climate School and the G. Unger Vetlesen Professor of Earth & Environmental Sciences at Columbia University. From 2011 to 2022, she was also Director of Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory's (LDEO) Core Repository and, until 2024, was the Founding Director of the LDEO Hudson River Field Station. From 2020 to 2023, she was first Interim Director then Director of Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, the first climate scientist and first female scientist to head the institution. Raymo has done pioneering work on the origin of the ice ages, the geologic temperature record of the Earth, and past sea level change, publishing over 100 peer-reviewed scientific articles. Her work underlies fundamental ideas in paleoceanography including the uplift weathering hypothesis, the "41,000-year problem," the Pliocene sea-level paradox, and the Lisiecki-Raymo δ18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, cultural center of Southern California. With an estimated 3,878,704 residents within the city limits , it is the List of United States cities by population, second-most populous in the United States, behind only New York City. Los Angeles has an Ethnic groups in Los Angeles, ethnically and culturally diverse population, and is the principal city of a Metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area of 12.9 million people (2024). Greater Los Angeles, a combined statistical area that includes the Los Angeles and Riverside–San Bernardino metropolitan areas, is a sprawling metropolis of over 18.5 million residents. The majority of the city proper lies in Los Angeles Basin, a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Climate
The Mid-Piacenzian Warm Period (mPWP) (prior to 2009 known as the Middle Pliocene Warm Period ), or the Pliocene Thermal Maximum, was an interval of warm climate during the Pliocene epoch that lasted from 3.3 to 3.0 million years ago (Ma). Climate The global average temperature in the mid-Pliocene was 2–3 °C higher than today, global sea level 25 meters higher, and the Northern Hemisphere ice sheet was ephemeral before the onset of extensive glaciation over Greenland that occurred in the late Pliocene around 3 Ma. Near-surface permafrost extent was substantially lower relative to the present. Global precipitation was marginally increased by 0.09 mm/yr according to CCSM4 simulations. Annual Northern Hemisphere Hadley circulation was weakened, but annual Southern Hemisphere Hadley circulation was enhanced. As during the Quaternary glaciation, glacial-interglacial cycles existed during the mPWP and it was not a uniform and stable climatic interval. Polar amplification duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
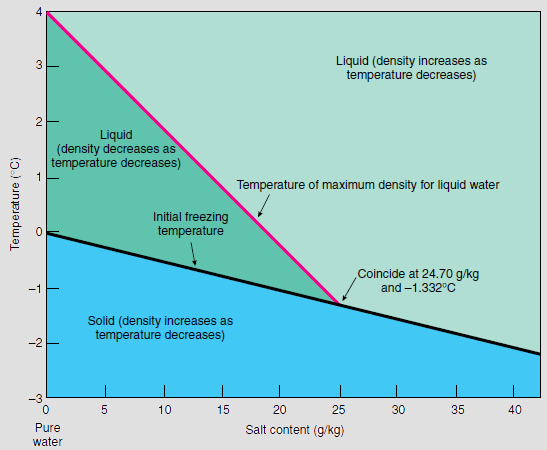
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale Ocean current, ocean circulation driven by global density gradients formed by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The name ''thermohaline'' is derived from ''wikt:thermo-, thermo-'', referring to temperature, and ', referring to salinity, salt content—factors which together determine the Water (molecule)#Density of saltwater and ice, density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel Polar regions of Earth, polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling and sinking en-route to higher latitudes - eventually becoming part of the North Atlantic Deep Water - before flowing into the ocean basins. While the bulk of thermohaline water upwelling, upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of approximately 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific; extensive mixing takes place between the ocean basins, reducing the difference in their densities, forming the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
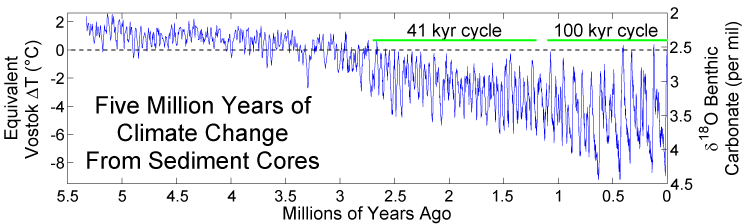
Five Myr Climate Change
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple ( 3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not tile the plane with copies of itself. It is the largest face any of the five regular three-dimensional regular Platonic solid can have. A conic i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to air. Strontium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of its two vertical neighbors in the periodic table, calcium and barium. It occurs naturally mainly in the minerals celestine and strontianite, and is mostly mined from these. Both strontium and strontianite are named after Strontian, a village in Scotland near which the mineral was discovered in 1790 by Adair Crawford and William Cruickshank; it was identified as a new element the next year from its crimson-red flame test color. Strontium was first isolated as a metal in 1808 by Humphry Davy using the then newly discovered process of electrolysis. During the 19th century, strontium was mostly used in the production of sugar from sugar beets (see strontian proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or Qingzang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, and East Asia. Geographically, it is located to the north of Himalayas and the Indian subcontinent, and to the south of Tarim Basin and Mongolian Plateau. Geopolitically, it covers most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces, southern Xinjiang province in Western China, Bhutan, the Administrative divisions of India, Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti district, Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of . With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Uplift
Tectonic uplift is the orogeny, geologic uplift of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While Isostasy, isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of Thrust tectonics, crustal thickening (such as Mountain formation, mountain building events), changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying Mantle (geology), mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere. Tectonic uplift results in denudation (processes that wear away the earth's surface) by raising buried rocks closer to the surface. This process can redistribute large loads from an elevated region to a topographically lower area as well – thus promoting an isostatic response in the region of denudation (which can cause local bedrock uplift). The timing, magnitude, and rate of denudation can be estimated by geologists using pressure-temperature studies. Crustal thickening C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Froelich
Dr. Philip 'Flip' Nissen Froelich, Jr. is an American academic oceanographic scientist, whose research uses biogeochemistry dynamics to address human impacts on the world's oceans. Early life and career Froelich graduated from Duke University in 1968. He obtained a Ph.D. from the University of Rhode Island in 1979. He is a Francis Eppes Professor of Oceanography at Florida State University, where he is involved in the interdisciplinary Biogeochemical Dynamics Program. He is also affiliated with the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory The National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (MagLab) is a facility at Florida State University, the University of Florida, and Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, that performs magnetic field research in physics, biology, bioengineeri .... References External links Florida State University faculty profile Duke University alumni Florida State University faculty American oceanographers Living people Biogeochemists Year of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ruddiman
William F. Ruddiman is a palaeoclimatologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Virginia. Ruddiman earned an undergraduate degree in geology in 1964 at Williams College, and a Ph.D. in marine geology from Columbia University in 1969. Ruddiman worked at the US Naval Oceanographic Office from 1969 to 1976, and at Columbia's Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory from 1976 to 1991. He moved to Virginia in 1991, serving as a professor in Environmental Sciences. Ruddiman's research interests center on climate change over several time scales. He is a Fellow of both the Geological Society of America and the American Geophysical Union. Ruddiman has participated in 15 oceanographic cruises, and was co-chief of two deep-sea drilling cruises. Ruddiman is best known for his ' early anthropocene' hypothesis (or 'Ruddiman hypothesis'), the idea that human-induced changes in greenhouse gases did not begin in the eighteenth century with advent of coal-burning factories and power plants of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easton, Massachusetts
Easton is a New England town, town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 25,058 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Greater Boston area. Easton is governed by an elected Select Board. Town meeting, Open Town Meeting acts as the legislative branch of the town. The Select Board chooses a Town administrator, Town Administrator to run the day-to-day operations of the town. History Easton was first settled in 1694 and was officially incorporated in 1725. In 1694, the first settler, Clement Briggs, established his home near the Easton Green. In 1711, the Taunton North Purchase area became Norton, Massachusetts, Norton, and in 1713, the sixty-nine families settled in Easton and hired Elder William Pratt as their first minister. Prior to the settlers' establishment, the area was occupied by Native Americans as a hunting area and a burial ground. During King Philip's War, Metacomet, Metacom, also known as King Philip, used part of Easton as a headquarter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |