|
Rayleigh–Kuo Criterion
The Rayleigh–Kuo criterion (sometimes called the Kuo criterion) is a stability condition for a fluid. This criterion determines whether or not a barotropic instability can occur, leading to the presence of vortices (like eddies and storms). The Kuo criterion states that for barotropic instability to occur, the gradient of the absolute vorticity must change its sign at some point within the boundaries of the current. Note that this criterion is a necessary condition, so if it does not hold it is not possible for a barotropic instability to form. But it is not a sufficient condition, meaning that if the criterion is met, this does not automatically mean that the fluid is unstable. If the criterion is not met, it is certain that the flow is stable. This criterion was formulated by Hsiao-Lan Kuo and is based on Rayleigh's equation named after the Lord Rayleigh who first introduced this equation in fluid dynamics. Barotropic instability Vortices like eddies are created by inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Flow
In solid mechanics, shear flow is the shear stress over a distance in a thin-walled structure.Higdon, Ohlsen, Stiles and Weese (1960), ''Mechanics of Materials'', article 4-9 (2nd edition), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. Library of Congress CCN 66-25222 In fluid dynamics, shear flow is the flow ''induced'' by a force in a fluid. In solid mechanics For thin-walled profiles, such as that through a beam or semi-monocoque structure, the shear stress distribution through the thickness can be neglected. Furthermore, there is no shear stress in the direction normal to the wall, only parallel. In these instances, it can be useful to express internal shear stress as shear flow, which is found as the shear stress multiplied by the thickness of the section. An equivalent definition for shear flow is the shear force ''V'' per unit length of the perimeter around a thin-walled section. Shear flow has the dimensions of force per unit of length. This corresponds to units of newtons per meter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroclinity
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity (often called baroclinicity) of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology, a baroclinic flow is one in which the density depends on both temperature and pressure (the fully general case). A simpler case, barotropic flow, allows for density dependence only on pressure, so that the Curl (mathematics), curl of the pressure-gradient force vanishes. Baroclinity is proportional to: :\nabla p \times \nabla \rho which is proportional to the sine of the angle between surfaces of constant pressure and surfaces of constant density. Thus, in a ''barotropic'' fluid (which is defined by zero baroclinity), these surfaces are parallel. In Earth's atmosphere, barotropic flow is a better approximation in the tropics, where density surfaces and pressure surfaces are both nearly level, whereas in higher latitudes the flow is more baroclinic. These midlatitude belts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
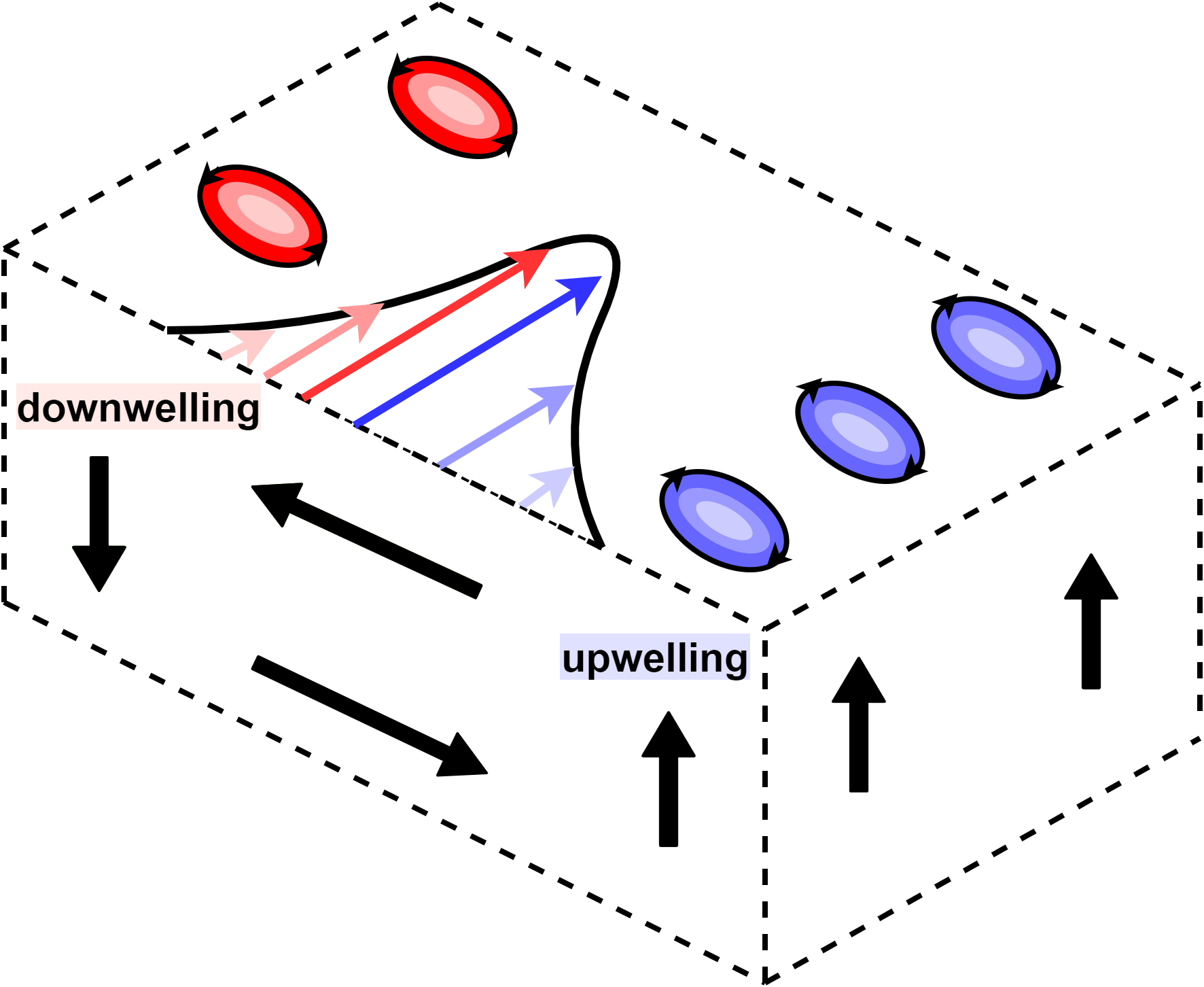
Western Boundary Currents
Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents. Eastern boundary currents Eastern boundary currents are relatively shallow, broad and slow-flowing. They are found on the eastern side of oceanic basins (adjacent to the western coasts of continents). Subtropical eastern boundary currents flow equatorward, transporting cold water from higher latitudes to lower latitudes; examples include the Benguela Current, the Canary Current, the Humboldt (Peru) Current, and the California Current. Coastal upwelling often brings nutrient-rich water into eastern boundary current regions, making them productive areas of the ocean. Western boundary currents Western boundary currents may themselves be divided into sub-tropical or low-latitude western boundary currents. Sub-tropical western boundary currents are warm, deep, narrow, and fast-flowing currents t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
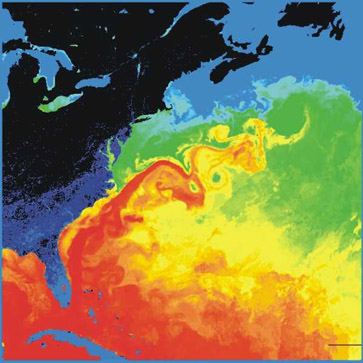
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolina) and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around , it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the coastal areas of the East Coast of the United States from Florida to southeast Virginia (near 36°N latitude), and to a greater degree, the climate of Northwest Europe. A consensus exists that the climate of Northwest Europe is warmer than other areas of similar latitude at least partially because of the stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. ''Perpendicular'' is also used as a noun: a perpendicular is a line which is perpendicular to a given line or plane. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of '' orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector quantities (in that they have Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and Direction (geometry), direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's second law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is Direct proportionality, directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is Inverse proportionality, inversely proportional to the object's mass. The International System of Units, SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy of an object or system due to the body's position relative to other objects, or the configuration of its particles. The energy is equal to the work done against any restoring forces, such as gravity or those in a spring. The term ''potential energy'' was introduced by the 19th-century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine, although it has links to the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of Potentiality and Actuality, ''potentiality''. Common types of potential energy include gravitational potential energy, the elastic potential energy of a deformed spring, and the electric potential energy of an electric charge and an electric field. The unit for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (symbol J). Potential energy is associated with forces that act on a body in a way that the total Work (physics), work done by these forces on the body depends only on the initial and final positions of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1960) ''Physics'', Section 7-5, Wiley International Edition The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, or force ( F) in the direction of motion times its displacement ( s), needed to accelerate the object from rest to its given speed. The same amount of work is done by the object when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. The SI unit of energy is the joule, while the English unit of energy is the foot-pound. In relativistic mechanics, \fracmv^2 is a good approximation of kinetic energy only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις ''kinesis'', meaning "motion". The dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby in the Earth's atmosphere in 1939. They are observed in the atmospheres and oceans of Earth and other planets, owing to the rotation of Earth or of the planet involved. Atmospheric Rossby waves on Earth are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that have a major influence on weather. These waves are associated with pressure systems and the jet stream (especially around the polar vortices). Oceanic Rossby waves move along the thermocline: the boundary between the warm upper layer and the cold deeper part of the ocean. Rossby wave types Atmospheric waves Atmospheric Rossby waves result from the conservation of potential vorticity and are influenced by the Coriolis force and pressure gradient. The image on the left sketches fundamental principles of the wave, e.g., its restorin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress or force per unit area is: \tau = ,where is the force applied and is the cross-sectional area. The area involved corresponds to the material face (geometry), face parallel to the applied force vector, i.e., with surface normal vector perpendicular to the force. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as:\tau_w := \mu\left.\frac\_,where is the dynamic viscosity, is the flow velocity, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift. Cold fronts generally move from west to east, whereas warm fronts move poleward, although any direction is possible. Occluded fronts are a hybrid merge of the two, and stationary fronts are stalled in their motion. Cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions because the dense air behind them can lift as well as push the warme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically relief, even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form ( DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |