|
Ray J. Ball
Raymond J. (Ray) Ball is a researcher and educator in accounting and financial economics. He is the Sidney Davidson Distinguished Service Professor of Accounting in the University of Chicago’s Booth School of Business. He has published foundational research on the economics of financial reporting and financial markets. Early life Ball was born in 1944 on the outskirts of Sydney, Australia. He became the first member of his family with an opportunity to graduate high school, and a corporate sponsorship by Rheem (Australia) afforded the opportunity to attend university. He has pursued an academic career ever since. Education Ball studied Accounting at the University of NSW (Australia), graduating with First Class Honors and the University Medal. He obtained an MBA degree in 1968 and Ph.D. in economics and accounting in 1972 from the University of Chicago, where his doctoral supervisor was Eugene F. Fama. He is a CPA and Fellow of CPA Australia. Major Research Ray Ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the best universities in the world and it is among the most selective in the United States. The university is composed of College of the University of Chicago, an undergraduate college and five graduate research divisions, which contain all of the university's graduate programs and interdisciplinary committees. Chicago has eight professional schools: the University of Chicago Law School, Law School, the Booth School of Business, the Pritzker School of Medicine, the Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy, and Practice, the Harris School of Public Policy, the University of Chicago Divinity School, Divinity School, the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and the Pritzker School of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPA Australia
CPA Australia ("Certified Practising Accountant") is a professional accounting body in Australia founded in 1886. As of 31 December 2020, it has 168,736 members working in 150 countries and regions around the world. CPA Australia currently has 19 staffed offices across Australia, China, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Vietnam, New Zealand and the UK. History The current form of CPA Australia dates from 1952, when the Commonwealth Institute and Federal Institute merged to create the Australian Society of Accountants. In July 1990 the name changed to the Australian Society of Certified Practising Accountants, and in April 2000, the name became CPA Australia. The main predecessor bodies of the Society, with year of formation, were: *Incorporated Institute of Accountants, 1886 *Federal Institute of Accountants, 1894 *Association of Accountants of Australia, 1910 *Australasian Institute of Cost Accountants, 1920 CEO controversy The CEO of CPA Australia from 2008, Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Accounting Research
The ''Journal of Accounting Research'' is a leading peer-reviewed academic journal associated with the University of Chicago. It was established in 1963 and is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Accounting Research Center (Formerly the Institute of Professional Accounting) at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business. Its current senior editors are Philip G. Berger, Luzi Hail, Christian Leuz, Haresh Sapra, Douglas J. Skinner, Rodrigo Verdi, and Regina Wittenberg Moerman. It is listed as one of the 50 journals used by the ''Financial Times'' to compile its business-school research ranks and ''Bloomberg Businessweeks Top 20 Journals. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', it has a 2018 impact factor of 4.891, ranking it third out of 103 journals in the category "Business, Finance". Former Editors * Sidney Davidson * David O. Green *Nicholas Dopuch *Katherine Schipper Katherine Schipper is an American accounting researcher and educator. Currently the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Accounting And Economics
The ''Journal of Accounting and Economics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal focusing on the fields of accounting Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "languag ... and economics. The editors-in-chief are J. Core ( Massachusetts Institute of Technology), E. deHann ( University of Washington), and W. R. Guay ( University of Pennsylvania). According to the '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 7.239. See also * Accounting research References External links * Elsevier academic journals Accounting journals Bimonthly journals Publications established in 1979 English-language journals {{accounting-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fama–French Three-factor Model
In asset pricing and portfolio management the Fama–French three-factor model is a statistical model designed in 1992 by Eugene Fama and Kenneth French to describe stock returns. Fama and French were colleagues at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, where Fama still works. In 2013, Fama shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his empirical analysis of asset prices. The three factors are (1) market excess return, (2) the outperformance of small versus big companies, and (3) the outperformance of high book/market versus low book/market companies. There is academic debate about the last two factors. Background and development Factor models are statistical models that attempt to explain complex phenomena using a small number of underlying causes or factors. The traditional asset pricing model, known formally as the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) uses only one variable to describe the returns of a portfolio or stock with the returns of the marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
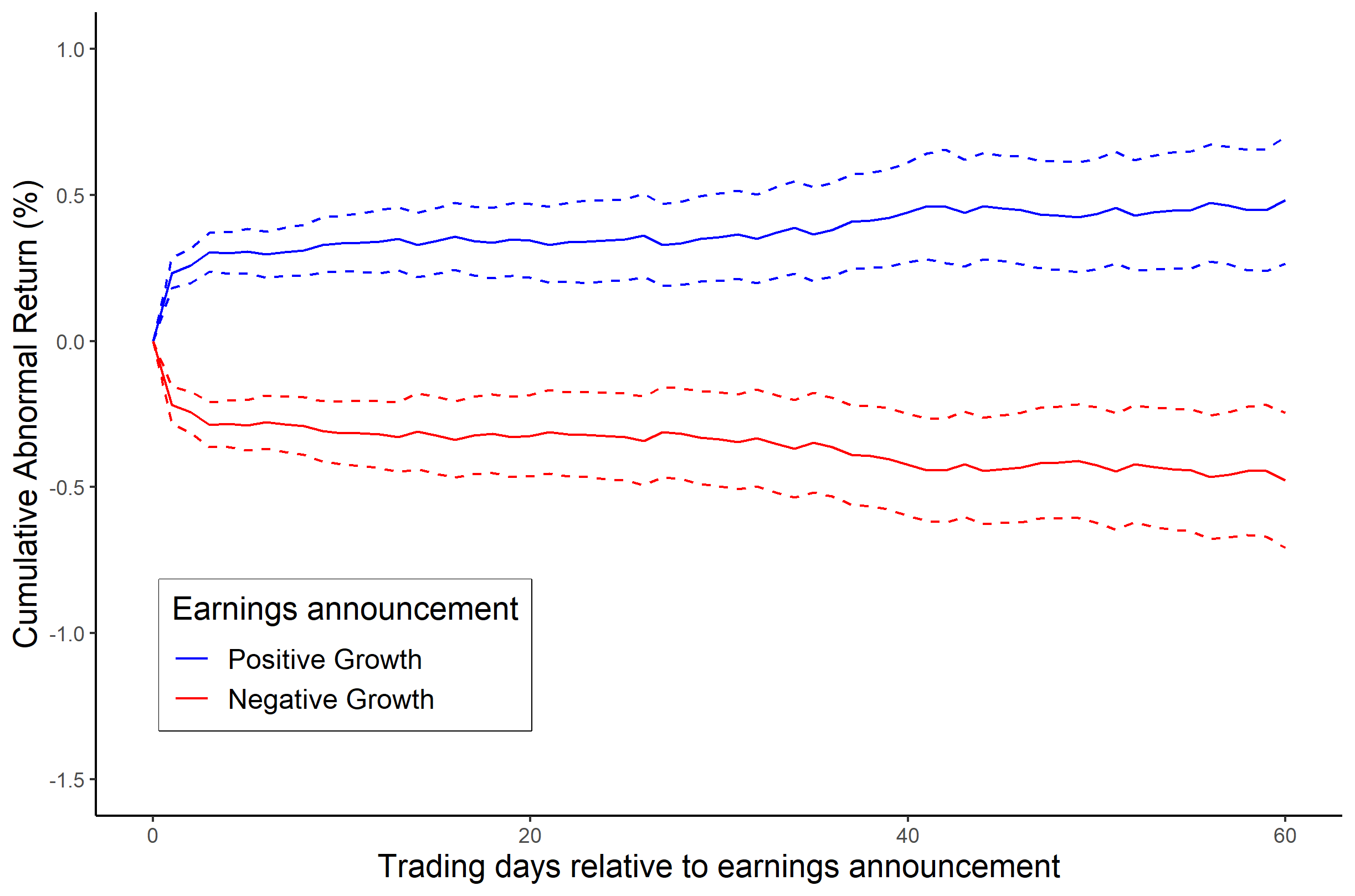
Post–earnings-announcement Drift
In financial economics and accounting research, post–earnings-announcement drift or PEAD (also named the SUE effect) is the tendency for a stock’s cumulative abnormal returns to drift in the direction of an earnings surprise for several weeks (even several months) following an earnings announcement. Cause and effect Once a firm's current earnings become known, the information content should be quickly digested by investors and incorporated into the efficient market price. However, it has long been known that this is not exactly what happens. For firms that report good news in quarterly earnings, their abnormal security returns tend to drift upwards for at least 60 days following their earnings announcement. Similarly, firms that report bad news in earnings tend to have their abnormal security returns drift downwards for a similar period. This phenomenon is called post-announcement drift. This was initially proposed by the information content study of Ray J. Ball & P. Brown, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Kuhn
Thomas Samuel Kuhn (; July 18, 1922 – June 17, 1996) was an American philosopher of science whose 1962 book ''The Structure of Scientific Revolutions'' was influential in both academic and popular circles, introducing the term '' paradigm shift'', which has since become an English-language idiom. Kuhn made several claims concerning the progress of scientific knowledge: that scientific fields undergo periodic "paradigm shifts" rather than solely progressing in a linear and continuous way, and that these paradigm shifts open up new approaches to understanding what scientists would never have considered valid before; and that the notion of scientific truth, at any given moment, cannot be established solely by objective criteria but is defined by a consensus of a scientific community. Competing paradigms are frequently incommensurable; that is, they are competing and irreconcilable accounts of reality. Thus, our comprehension of science can never rely wholly upon "objecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient-market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Anomaly
A market anomaly in a financial market is predictability that seems to be inconsistent with (typically risk-based) theories of asset prices. Standard theories include the capital asset pricing model and the Fama-French Three Factor Model, but a lack of agreement among academics about the proper theory leads many to refer to anomalies without a reference to a benchmark theory (Daniel and Hirschleifer 2015 and Barberis 2018, for example). Indeed, many academics simply refer to anomalies as "return predictors", avoiding the problem of defining a benchmark theory. Academics have documented more than 150 return predictors (see '' List of Anomalies Documented in Academic Journals).'' These "anomalies", however, come with many caveats. Almost all documented anomalies focus on illiquid, small stocks. Moreover, the studies do not account for trading costs. As a result, many anomalies do not offer profits, despite the presence of predictability. Additionally, return predictability decli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Fama
Eugene Francis "Gene" Fama (; born February 14, 1939) is an American economist, best known for his empirical work on portfolio theory, asset pricing, and the efficient-market hypothesis. He is currently Robert R. McCormick Distinguished Service Professor of Finance at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business. In 2013, he shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences jointly with Robert J. Shiller and Lars Peter Hansen. The Research Papers in Economics project ranked him as the 9th-most influential economist of all time based on his academic contributions, . He is regarded as "the father of modern finance", as his works built the foundation of financial economics and have been cited widely. Early life Fama was born in Boston, Massachusetts, the son of Angelina (née Sarraceno) and Francis Fama. All of his grandparents were immigrants from Italy. Fama is a Malden Catholic High School Athletic Hall of Fame honoree. He earned his undergraduate degree in Romanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |