|
Rational Pricing
Rational pricing is the assumption in financial economics that asset prices – and hence asset pricing models – will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away". This assumption is useful in pricing fixed income securities, particularly bonds, and is fundamental to the pricing of derivative instruments. Arbitrage mechanics Arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of a state of imbalance between two (or possibly more) markets. Where this mismatch can be exploited (i.e. after transaction costs, storage costs, transport costs, dividends etc.) the arbitrageur can "lock in" a risk-free profit by purchasing and selling simultaneously in both markets. In general, arbitrage ensures that "the law of one price" will hold; arbitrage also equalises the prices of assets with identical cash flows, and sets the price of assets with known future cash flows. The law of one price The same asset must trade at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade".William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus:Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of Financial capital, capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama and Miller (1972), ''The Theory of Finance'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield Curves
In finance, the yield curve is a graph which depicts how the Yield to maturity, yields on debt instruments – such as bonds – vary as a function of their years remaining to Maturity (finance), maturity. Typically, the graph's horizontal or x-axis is a time line of months or years remaining to maturity, with the shortest maturity on the left and progressively longer time periods on the right. The vertical or y-axis depicts the annualized yield to maturity. Those who issue and trade in forms of debt, such as loans and bonds, use yield curves to determine their value. Shifts in the shape and slope of the yield curve are thought to be related to investor expectations for the economy and interest rates. Ronald Melicher and Merle Welshans have identified several characteristics of a properly constructed yield curve. It should be based on a set of securities which have differing lengths of time to maturity, and all yields should be calculated as of the same point in time. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Rate
A reference rate is a rate that determines pay-offs in a financial contract and that is outside the control of the parties to the contract. It is often some form of LIBOR rate, but it can take many forms, such as a consumer price index, a house price index or an unemployment rate. Parties to the contract choose a reference rate that neither party has power to manipulate. Examples of use The most common use of reference rates is that of short-term interest rates such as LIBOR in floating rate notes, loans, swaps, short-term interest rate futures contracts, etc. The rates are calculated by an independent organisation, such as the British Bankers Association (BBA) as the average of the rates quoted by a large panel of banks, to ensure independence. Another example is that of swap reference rates for constant maturity swaps. The ISDAfix rates used are calculated daily for an independent organisation, the International Swaps and Derivatives Association, from quotes from a large pane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike Price
In finance, the strike price (or exercise price) of an option is a fixed price at which the owner of the option can buy (in the case of a call), or sell (in the case of a put), the underlying security or commodity. The strike price may be set by reference to the spot price, which is the market price of the underlying security or commodity on the day an option is taken out. Alternatively, the strike price may be fixed at a discount or premium. The strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the market price of the underlying instrument at that time. Moneyness Moneyness is the value of a financial contract if the contract settlement is financial. More specifically, it is the difference between the strike price of the option and the current trading price of its underlying security. In options trading, terms such as ''in-the- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often with the help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivatives Market
The derivatives market is the financial market for derivatives - financial instruments like futures contracts or options - which are derived from other forms of assets. The market can be divided into two, that for exchange-traded derivatives and that for over-the-counter derivatives. The legal nature of these products is very different, as well as the way they are traded, though many market participants are active in both. The derivatives market in Europe has a notional amount of €660 trillion. Participants in a derivative market Participants in a derivative market can be segregated into four sets based on their trading motives. * Hedgers * Speculators * Margin Traders * Arbitrageurs Types of trades in a derivative market * Directional Trades * Spreads * Arbitrage positions * Hedged Trades Futures markets Futures exchanges, such as Euronext.liffe and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, trade in standardized derivative contracts. These are options contracts, swaps c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spot Price
In finance, a spot contract, spot transaction, or simply spot, is a contract of buying or selling a commodity, security or currency for immediate settlement (payment and delivery) on the spot date, which is normally two business days after the trade date. The settlement price (or rate) is called spot price (or spot rate). A spot contract is in contrast with a forward contract or futures contract where contract terms are agreed now but delivery and payment will occur at a future date. Spot prices and future price expectations Depending on the item being traded, spot prices can indicate market expectations of future price movements in different ways. For a security or non-perishable commodity (e.g. silver), the spot price reflects market expectations of future price movements. In theory, the difference in spot and forward prices should be equal to the finance charges, plus any earnings due to the holder of the security, according to the cost of carry model. For example, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (finance)
In finance, a derivative is a contract between a buyer and a seller. The derivative can take various forms, depending on the transaction, but every derivative has the following four elements: # an item (the "underlier") that can or must be bought or sold, # a future act which must occur (such as a sale or purchase of the underlier), # a price at which the future transaction must take place, and # a future date by which the act (such as a purchase or sale) must take place. A derivative's value depends on the performance of the underlier, which can be a commodity (for example, corn or oil), a financial instrument (e.g. a stock or a bond), price index, a price index, a currency, or an interest rate. Derivatives can be used to insure against price movements (Hedge (finance)#Etymology, hedging), increase exposure to price movements for speculation, or get access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Most derivatives are price guarantees. But some are based on an event or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Risk
In finance, model risk is the risk of loss resulting from using insufficiently accurate models to make decisions, originally and frequently in the context of valuing financial securities. Here, Rebonato (2002) defines model risk as "the risk of occurrence of a significant difference between the mark-to-model value of a complex and/or illiquid instrument, and the price at which the same instrument is revealed to have traded in the market". However, model risk is increasingly relevant in contexts other than financial securities valuation, including assigning consumer credit scores, real-time prediction of fraudulent credit card transactions, and computing the probability of an air flight passenger being a terrorist. In fact, Burke regards failure to use a model (instead over-relying on expert judgment) as a type of model risk.http://www.siiglobal.org/SII/WEB5/sii_files/Membership/PIFs/Risk/Model%20Risk%2024%2011%2009%20Final.pdf Types Derman describes various types of model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
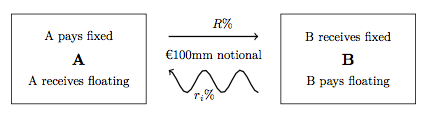
Multi-curve Framework
In finance, an interest rate swap (finance), swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative, interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a Interest rate derivative#Linear and non-linear, "linear" IRD and one of the most Market liquidity, liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreement, forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swap, zero coupon swaps (ZCSs). In its December 2014 statistics release, the Bank for International Settlements reported that interest rate swaps were the largest component of the global Over-the-counter (finance), OTC Derivative (finance), derivative market, representing 60%, with the notional amount outstanding in OTC interest rate swaps of $381 trillion, and the gross market value of $14 trillion. Interest rate swaps can be traded as an index through the FTSE MTIRS Index. Interest rate swaps General description An interest rate swap's (IRS's) effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootstrapping (finance)
In finance, bootstrapping is a method for constructing a ( zero-coupon) fixed-income yield curve from the prices of a set of coupon-bearing products, e.g. bonds and swaps. A ''bootstrapped curve'', correspondingly, is one where the prices of the instruments used as an ''input'' to the curve, will be an exact ''output'', when these same instruments are valued using this curve. Here, the term structure of spot returns is recovered from the bond yields by solving for them recursively, by forward substitution: this iterative process is called the ''bootstrap method''. The usefulness of bootstrapping is that using only a few carefully selected zero-coupon products, it becomes possible to derive par swap rates (forward and spot) for ''all'' maturities given the solved curve. Methodology As stated above, the selection of the input securities is important, given that there is a general lack of data points in a yield curve (there are only a fixed number of products in the market). Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Analysis (finance)
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, investment management and other related finance occupations. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns ( trend following or reversion). Although the original quantitative analysts were "sell side quants" from market maker firms, concerned with derivatives pricing and risk management, the meaning of the term has expanded over time to include those individuals involved in almost any application of mathematical finance, including the buy side. Applied quantitative analysis is commonly associated with quantitative investment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |