|
Quantitative Analysis (finance)
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, investment management and other related finance occupations. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns ( trend following or reversion). Although the original quantitative analysts were "sell side quants" from market maker firms, concerned with derivatives pricing and risk management, the meaning of the term has expanded over time to include those individuals involved in almost any application of mathematical finance, including the buy side. Applied quantitative analysis is commonly associated with quantitative investment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often with the help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often with the help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
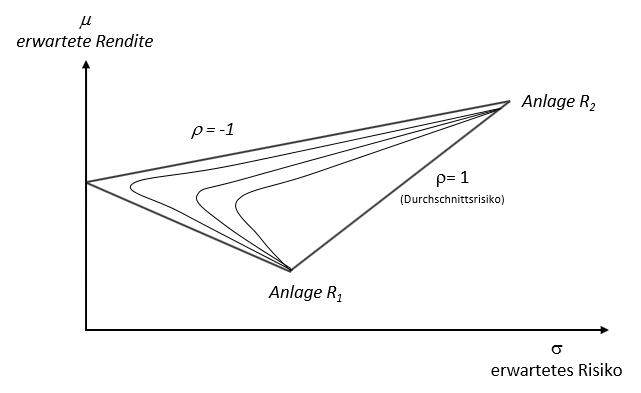
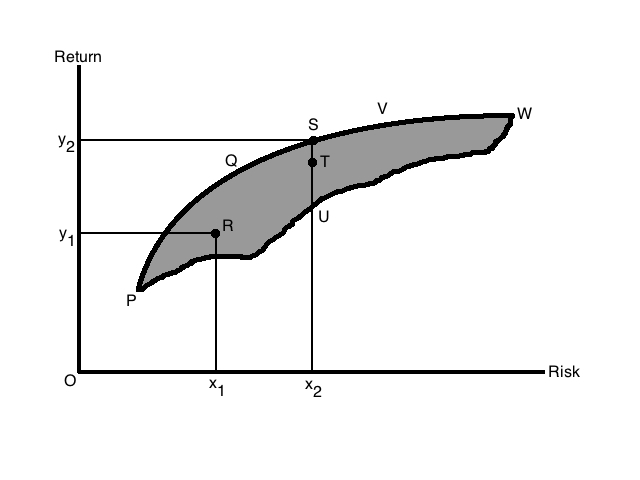
Efficient Frontier
In modern portfolio theory, the efficient frontier (or portfolio frontier) is an investment portfolio which occupies the "efficient" parts of the risk–return spectrum. Formally, it is the set of portfolios which satisfy the condition that no other portfolio exists with a higher expected return but with the same standard deviation of return (i.e., the risk). The efficient frontier was first formulated by Harry Markowitz in 1952; see Markowitz model. Overview A combination of assets, i.e. a portfolio, is referred to as "efficient" if it has the best possible expected level of return for its level of risk (which is represented by the standard deviation of the portfolio's return). Here, every possible combination of risky assets can be plotted in risk–expected return space, and the collection of all such possible portfolios defines a region in this space. In the absence of the opportunity to hold a risk-free asset, this region is the opportunity set (the feasible set) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Portfolio Theory
Modern portfolio theory (MPT), or mean-variance analysis, is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets such that the expected return is maximized for a given level of risk. It is a formalization and extension of Diversification (finance), diversification in investing, the idea that owning different kinds of financial assets is less risky than owning only one type. Its key insight is that an asset's risk and return should not be assessed by itself, but by how it contributes to a portfolio's overall risk and return. The variance of return (or its transformation, the standard deviation) is used as a measure of risk, because it is tractable when assets are combined into portfolios. Often, the historical variance and covariance of returns is used as a proxy for the forward-looking versions of these quantities, but other, more sophisticated methods are available. Economist Harry Markowitz introduced MPT in a 1952 paper, for which he was later awarded a Nobel Memorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markowitz Model
In finance, the Markowitz model ─ put forward by Harry Markowitz in 1952 ─ is a portfolio optimization model; it assists in the selection of the most efficient portfolio by analyzing various possible portfolios of the given securities. Here, by choosing securities that do not 'move' exactly together, the HM model shows investors how to reduce their risk. The HM model is also called mean-variance model due to the fact that it is based on expected returns (mean) and the standard deviation (variance) of the various portfolios. It is foundational to Modern portfolio theory. Assumptions Markowitz made the following assumptions while developing the HM model: # Risk of a portfolio is based on the variability of returns from said portfolio. # An investor is risk averse. # An investor prefers to increase consumption. # The investor's utility function is concave and increasing, due to their risk aversion and consumption preference. # Analysis is based on single period model of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Finance
''The Journal of Finance'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Finance Association. It was established in 1946. The editor-in-chief is Antoinette Schoar. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 7.870, ranking it 6th out of 111 journals in the category "Business, Finance" and 16th out of 381 journals in the category "Economics". Editors The editorial board consists of the editor, co-editors, and associate editors. The current editor is Antoinette Schoar (MIT). The following persons are or have been editor-in-chief of the journal: Awards Each year the associate editors vote for the best papers published in the journal. The Smith Breeden Prize is awarded for the best finance papers and the Brattle Prize for the best corporate finance Corporate finance is an area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of businesses, the actions that managers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Markowitz
Harry Max Markowitz (August 24, 1927 – June 22, 2023) was an American economist who received the 1989 John von Neumann Theory Prize and the 1990 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Markowitz was a professor of finance at the Rady School of Management at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). He is best known for his pioneering work in modern portfolio theory, studying the effects of asset risk, return, correlation and diversification on probable investment portfolio returns. Biography Harry Markowitz was born to a Jewish family, the son of Morris and Mildred Markowitz.Harry M. Markowitz �Autobiography The Nobel Prizes 1990, Editor Tore Frängsmyr, obel Foundation Stockholm, 1991 During high school, Markowitz developed an interest in physics and philosophy, in particular the ideas of David Hume, an interest he continued to follow during his undergraduate years at the University of Chicago. After receiving his Ph.B. in Liberal Arts, Markowitz decided t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Options Pricing
In finance, a price (premium) is paid or received for purchasing or selling options. The calculation of this premium will require sophisticated mathematics. Premium components This price can be split into two components: intrinsic value, and time value (also called "extrinsic value"). Intrinsic value The ''intrinsic value'' is the difference between the underlying spot price and the strike price, to the extent that this is in favor of the option holder. For a call option, the option is in-the-money if the underlying spot price is higher than the strike price; then the intrinsic value is the underlying price minus the strike price. For a put option, the option is in-the-money if the ''strike'' price is higher than the underlying spot price; then the intrinsic value is the strike price minus the underlying spot price. Otherwise the intrinsic value is zero. For example, when a DJI call (bullish/long) option is 18,000 and the underlying DJI Index is priced at $18,050 then there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Mathematics
The ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' (also ''EOM'' and formerly ''Encyclopaedia of Mathematics'') is a large reference work in mathematics. Overview The 2002 version contains more than 8,000 entries covering most areas of mathematics at a graduate level, and the presentation is technical in nature. The encyclopedia is edited by Michiel Hazewinkel and was published by Kluwer Academic Publishers until 2003, when Kluwer became part of Springer. The CD-ROM contains animations and three-dimensional objects. The encyclopedia has been translated from the Soviet ''Matematicheskaya entsiklopediya'' (1977) originally edited by Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov and extended with comments and three supplements adding several thousand articles. Until November 29, 2011, a static version of the encyclopedia could be browsed online free of charge. This URL now redirects to the new wiki A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and manage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Walk
In mathematics, a random walk, sometimes known as a drunkard's walk, is a stochastic process that describes a path that consists of a succession of random steps on some Space (mathematics), mathematical space. An elementary example of a random walk is the random walk on the integer number line \mathbb Z which starts at 0, and at each step moves +1 or −1 with equal probability. Other examples include the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas (see Brownian motion), the search path of a foraging animal, or the price of a fluctuating random walk hypothesis, stock and the financial status of a gambler. Random walks have applications to engineering and many scientific fields including ecology, psychology, computer science, physics, chemistry, biology, economics, and sociology. The term ''random walk'' was first introduced by Karl Pearson in 1905. Realizations of random walks can be obtained by Monte Carlo Simulation, Monte Carlo simulation. Lattice random ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Regnault
Jules Augustin Frédéric Regnault (; 1 February 1834, Béthencourt – 9 December 1894, Paris) was a French stock broker's assistant who first suggested a modern theory of stock price changes i''Calcul des Chances et Philosophie de la Bourse''(1863), using a random walk model. A key conclusion appears on Page 50: "''l'écart des cours est en raison directe de la racine carrée des temps''", in English: "the deviation of prices is directly proportional to the square root of time". He is also one of the first authors who tried to create a "stock exchange science" based on statistical and probabilistic analysis. His hypotheses were used by Louis Bachelier. Biography During the first years of his life, Jules Regnault lived in the département du Nord (France) where his father worked. When his father died on 16 January 1846 in Paris, his family moved to Brussels, where Odilon, Jules’ brother, became a writer and a student at the Université libre de Bruxelles in advanced mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is f(x) = \frac e^\,. The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma^2 is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |