|
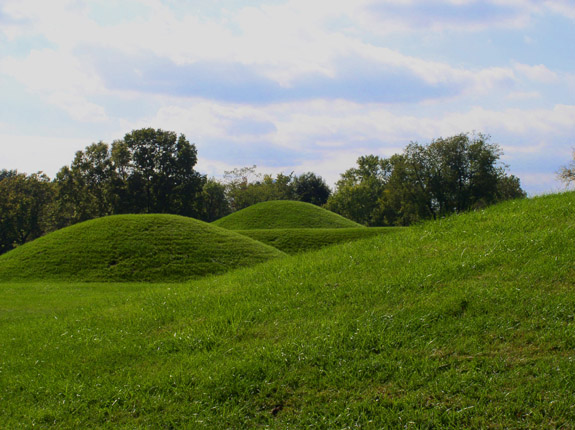
Ratcliffe Mound
The Ratcliffe Mound ( 33-Vi-3) is a Native American mound in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located in western Vinton County, it lies to the east of the community of Londonderry, at the bottom of a steep-walled valley. Sitting in the middle of farm fields near a stream, the mound is isolated in open countryside; there are no nearby woodlots. The mound is a circular cone in shape, high and in diameter.Owen, Lorrie K., ed. ''Dictionary of Ohio Historic Places''. Vol. 2. St. Clair Shores: Somerset, 1999, 1370. Unlike those of many Native American mounds, the identity of the Ratcliffe Mound's builders is unknown. Two cultures from the Woodland period, the Adena and Hopewell, built large numbers of mounds in southeastern Ohio, and the Adena are known to have built a group of six mounds in the Vinton County village of Zaleski, but the Ratcliffe Mound lacks features that enable archaeologists to identify its builders. Neither of these two cultures t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio State Route 327
State Route 327 (SR 327) is a north–south state highway in the south central portion of the U.S. state of Ohio. Its southern terminus is at U.S. Route 35 (US 35) about southeast of Jackson, at a one-quadrant interchange. It ends at its northern terminus at SR 180 in Adelphi. History SR 327 was commissioned in 1932, routed between Roads and Wellston. In 1935 the highway was extended north to Adelphi. The highway was extended south to US 35 in 1937. In 2002, work began on replacing an at-grade intersection at SR 32 into an interchange south of Wellston. The $9 million project was funded jointly by the Federal Highway Safety Infrastructure program and ODOT's Highway Safety Program (HSP). The project was completed in July 2004 at a cost of $12.5 million, an increase of $3.5 than originally estimated. It also rerouted SR 124 in a brief concurrency. Major intersections References {{Reflist 327 __NOTOC__ Year 327 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
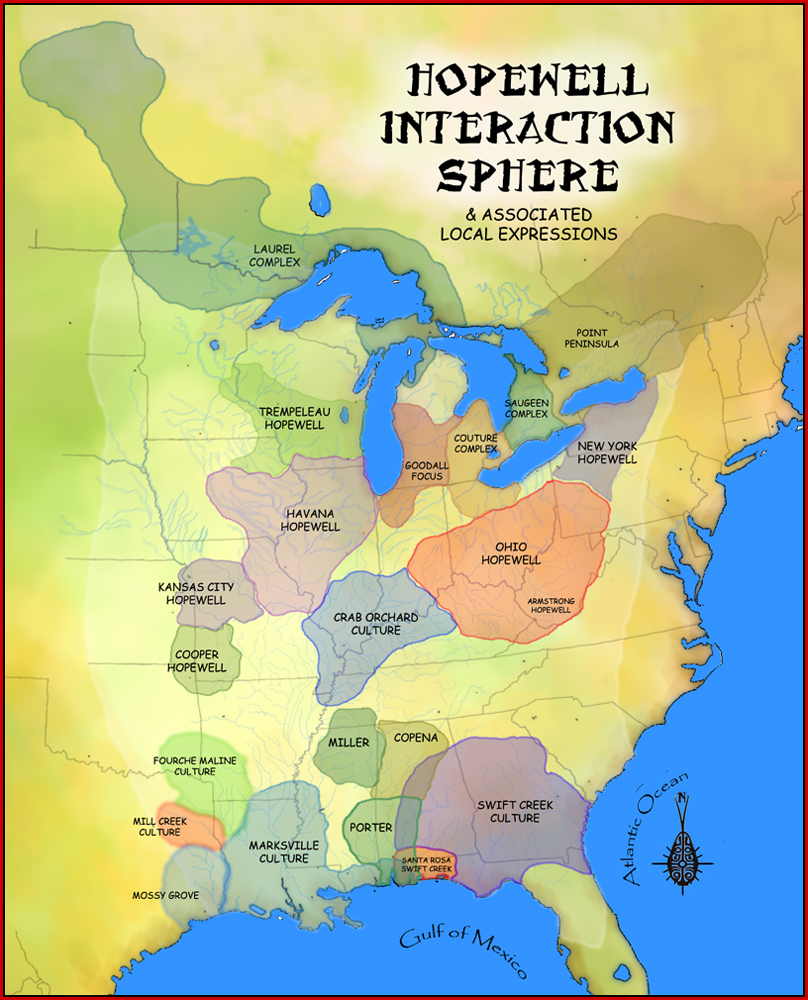
Hopewell Tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 100 BCE to 500 CE, in the Middle Woodland period. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society but a widely dispersed set of populations connected by a common network of trade routes. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell exchange system ran from the northern shores of Lake Ontario south to the Crystal River Indian Mounds in modern-day Florida. Within this area, societies exchanged goods and ideas, with the highest amount of activity along waterways, which were the main transportation routes. Peoples within the Hopewell exchange system received materials from all over the territory of what now comprises the mainland United States. Most of the items traded were exotic materials; they were delivered to peoples living in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Ohio
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Ohio
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavation (archaeology)
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be conducted over a few weeks to several years. Excavation involves the recovery of several types of data from a site. This data includes artifacts (portable objects made or modified by humans), features (non-portable modifications to the site itself such as post molds, burials, and hearths), ecofacts (evidence of human activity through organic remains such as animal bones, pollen, or charcoal), and archaeological context (relationships among the other types of data).Kelly&Thomas (2011). ''Archaeology: down to earth'' (4th ed.). Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Before excavating, the presence or absence of archaeological remains can often be suggested by, non-intrusive remote sensing, such as ground-penetrating radar. Basic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact, or artefact (see American and British English spelling differences), is a general term for an item made or given shape by humans, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest. In archaeology, the word has become a term of particular nuance and is defined as an object recovered by archaeological endeavor, which may be a cultural artifact having cultural interest. Artifact is the general term used in archaeology, while in museums the equivalent general term is normally "object", and in art history perhaps artwork or a more specific term such as "carving". The same item may be called all or any of these in different contexts, and more specific terms will be used when talking about individual objects, or groups of similar ones. Artifacts exist in many different forms and can sometimes be confused with ecofacts and features; all three of these can sometimes be found together at archaeological sites. They can also exist in differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adena Culture
The Adena culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharing a burial complex and ceremonial system. The Adena culture was centered on the location of the modern state of Ohio, but also extended into contiguous areas of northern Kentucky, eastern Indiana, West Virginia, and parts of extreme western Pennsylvania. Importance The Adena culture was named for the large mound on Thomas Worthington's early 19th-century estate located near Chillicothe, Ohio, which he named "Adena", The culture is the most prominently known of a number of similar cultures in eastern North America that began mound building ceremonialism at the end of the Archaic period. The geographic range of the Adena sites is centered on central and southern Ohio, with further sites in contiguous areas of the surrounding states of In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londonderry, Ross County, Ohio
Londonderry is an unincorporated community in eastern Liberty Township, Ross County, Ohio, United States. It has a post office with the ZIP code 45647. It lies along U.S. Route 50 at its intersection with State Route 327. History Londonderry was laid out in 1831. A post office was established under the name Gillespieville in 1833, and the name was changed to Londonderry in 1929. The present name is derived from Londonderry, Northern Ireland, the native home of a first settler. Gallery File:LondonderryOH1.JPG, Londonderry community sign. File:LondonderryOH2.JPG, Looking west at the intersection of US Highway 50 and Ohio Highway 327. Notable person *Harley Warrick Harley E. Warrick (October 5, 1924 – November 24, 2000), was an American barn painter, best known for his work painting Mail Pouch tobacco advertising on barns across 13 states in the American Midwest and Appalachian states. Over his 55-year ca ..., barn painter References Unincorporated communities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between these types is an empirical observation, but their interpretation in terms of ethnic or political groups is based on archaeologists' understanding and interpretation and is in many cases subject to long-unresolved debates. The concept of the archaeological culture is fundamental to culture-historical archaeology. Concept Different cultural groups have material culture items that differ both functionally and aesthetically due to varying cultural and social practices. This notion is observably true on the broadest scales. For example, the equipment associated with the brewing of tea varies greatly across the world. Social relations to material culture often include notions of identity and status. Advocates of culture-historical archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)