|
Rapid Update Cycle
The Rapid Update Cycle (RUC) was an American atmospheric prediction system that consisted primarily of a numerical forecast model and an analysis system to initialize the model. The first operational implementation was created in 1994, with 60km resolution and a 3-hour cycle. The RUC was designed to provide accurate short-range (0- to 12-hr, later expanded to 18-hr in 2010) numerical forecast guidance for weather-sensitive users, such as those in the aviation community. Significant weather forecasting problems that occur in the 0- to 12-hr range include severe weather in all seasons (for example, tornadoes, thunderstorms, snow, and ice storms) and hazards to aviation (for example, clear air turbulence, icing, and downbursts). The RUC ran at the highest frequency of any forecast model at the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), assimilating recent observations to provide very high frequency updates of current conditions and short-range forecasts. This update ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for thousands of years and formally since the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place. Once calculated manually based mainly upon changes in atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky conditions or cloud cover, weather forecasting now relies on numerical weather prediction, computer-based models that take many atmospheric factors into account. Human input is still required to pick the best possible model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
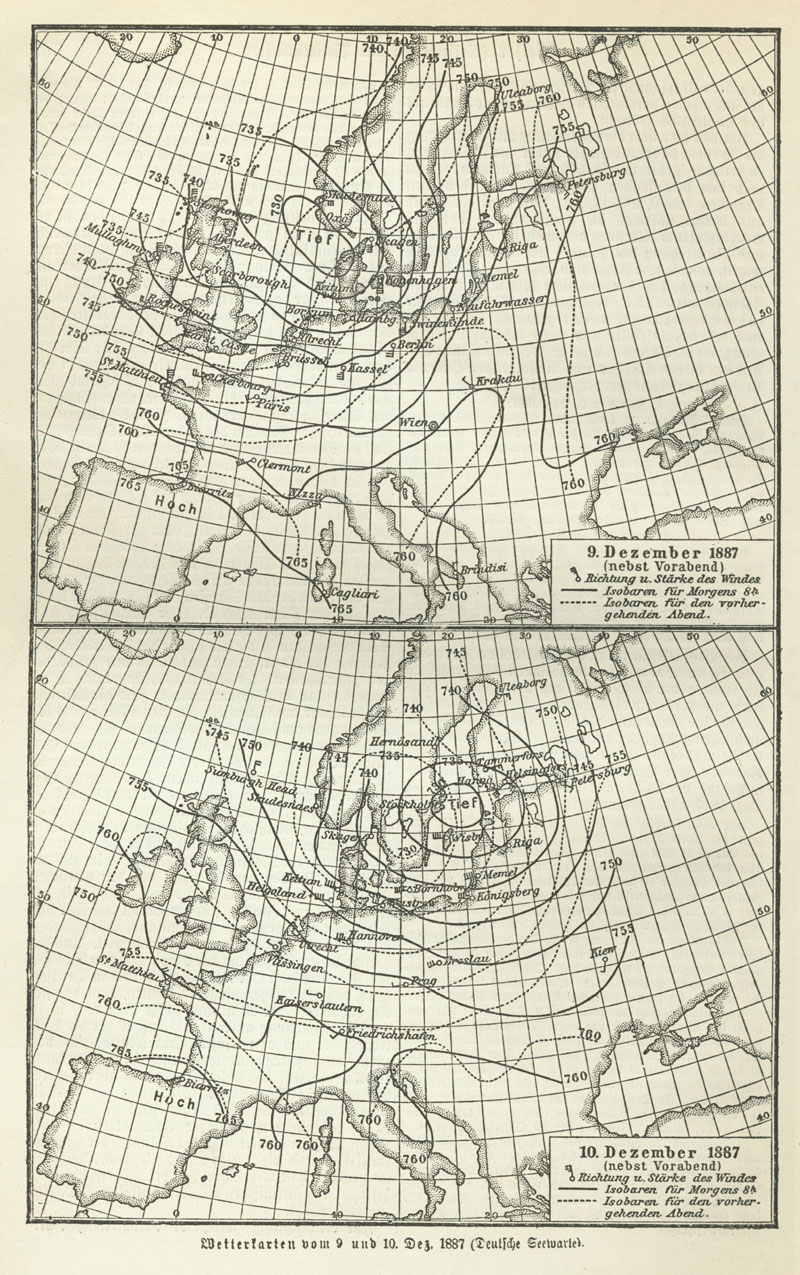
Numerical Weather Prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to weather forecasting, predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs. Mathematical models based on the same physical principles can be used to generate either short-term weather forecasts or longer-term climate predictions; the latter are widely applied for understanding and projecting climate change. The improvements made to regional models have allowed significant improvements in Tropical cyclone track forecasting, tropical cyclone track and air quality forecasts; however, atmospheric models perform poorly at han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth. Weather is driven by atmospheric pressure, air pressure, temperature, and moisture differences between one place and another. These differences can occur due to the effect of Sun angle on climate, Sun's angle at any particular spot, which varies with latitude. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest scale atmospheric circulations: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for thousands of years and formally since the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place. Once calculated manually based mainly upon changes in atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky conditions or cloud cover, weather forecasting now relies on numerical weather prediction, computer-based models that take many atmospheric factors into account. Human input is still required to pick the best possible model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often (but not always) visible in the form of a funnel cloud, condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The Tornado records#Highest winds observed in a tornado, most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in cumulonimbus clouds. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce Heavy rain (meteorology), heavy rain and sometimes Thundersnow, snow, Ice pellets, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms can produce little or Dry thunderstorm, no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may thunderstorm training, line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or #Severe thunderstorms, severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide, or Sublimation (phase transition), sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes Nucleation, nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooling, supercooled water droplets, which Freezing, freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns, and Hard rime, rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Storm
An ice storm, also known as a glaze event or a silver storm, is a type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain. The National Weather Service, U.S. National Weather Service defines an ice storm as a storm which results in the accumulation of at least of ice on exposed surfaces. They are generally not violent storms but instead are commonly perceived as gentle rains occurring at temperatures just below freezing. Formation The formation of ice begins with a layer of above-freezing air above a layer of sub-freezing temperatures closer to the surface. Frozen Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation melts to rain while falling into the warm air layer, and then begins to refreeze in the cold layer below. If the precipitate refreezes while still in the air, it will land on the ground as ice pellets, sleet. Alternatively, the liquid droplets can continue to fall without freezing, passing through the cold air just above the surface. This thin layer of air then cools the rain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear Air Turbulence
In meteorology, clear-air turbulence (CAT) is the turbulent movement of air masses in the absence of any visual clues such as clouds, and is caused when bodies of air moving at widely different speeds meet. The atmospheric region most susceptible to CAT is the high troposphere at altitudes of around as it meets the tropopause. Here CAT is most frequently encountered in the regions of jet streams. At lower altitudes it may also occur near mountain ranges. Thin cirrus clouds can also indicate high probability of CAT. CAT can be hazardous to the comfort, and occasionally the safety, of air travelers, as the aircraft pilots often cannot see and anticipate such turbulences, and a sudden encounter can impart significant stress to the airframe. CAT in the jet stream is expected to become stronger and more frequent because of climate change, with transatlantic wintertime CAT increasing by 60% (light), 95% (moderate), and 150% (severe) by the time of doubling. Definition In mete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downburst
In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface level. It originates under deep, moist convective conditions like cumulus congestus or cumulonimbus. Capable of producing damaging winds, it may sometimes be confused with a tornado, where high-velocity winds circle a central area, and air moves inward and upward. These usually last for seconds to minutes. Downbursts are particularly strong downdrafts within thunderstorms (or deep, moist convection as sometimes downbursts emanate from cumulonimbus or even cumulus congestus clouds that are not producing lightning). Downbursts are most often created by an area of significantly precipitation-cooled air that, after reaching the surface ( subsiding), spreads out in all directions producing strong winds. Dry downbursts are associated with thunderstorms that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Centers For Environmental Prediction
The United States National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) delivers national and global weather, water, climate, and space weather guidance, forecasts, warnings, and analyses to government agencies and private users. The centers form part of the National Weather Service. NCEP consists of nine centers: # Aviation Weather Center provides aviation warnings and forecasts of hazardous flight conditions at all levels within domestic and international air space. # Climate Prediction Center monitors and forecasts short-term climate fluctuations and provides information on the effects climate patterns can have on the nation. # Environmental Modeling Center develops and improves numerical weather, climate, hydrological and ocean prediction through a broad program in partnership with the research community. # National Hurricane Center provides forecasts of the movement and strength of tropical weather systems and issues watches and warnings for the North Atlantic and the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |