|
Random Pulse Width Modulation
Random pulse-width modulation (RPWM) is a modulation technique introduced for mitigating electromagnetic interference (EMI) of power converters by spreading the energy of the noise signal over a wider bandwidth, so that there are no significant peaks of the noise. This is achieved by randomly varying the main parameters of the pulse-width modulation signal. Description Electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters have been widely used for filtering out the conducted emissions generated by power converters since their advent. However, when size is of great concern like in aircraft and automobile applications, one of the practical solutions to suppress conducted emissions is to use random pulse-width modulation (RPWM). In conventional pulse-width modulation (PWM) schemes, the harmonics power is concentrated on the deterministic or known frequencies with a significant magnitude, which leads to mechanical vibration, noise, and EMI. However, by applying randomness to the conventional PWM s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
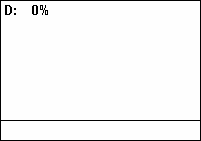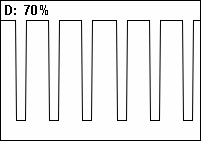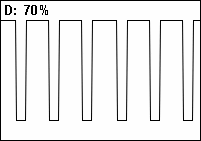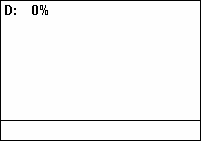
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. The duty factor for periodic signal expresses the same notion, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conducted Emissions
Conducted emissions are the effects in power quality that occur via electrical and magnetic coupling, electronic switch of semiconductor devices, which form a part of electromagnetic compatibility issues in electrical engineering. These affect the ability of all interconnected system devices in the electromagnetic environment, by restricting or limiting their intentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy. Conducted emissions consist a part of electromagnetic interference in circuits that mainly create issues in delivered power quality, owing to interference caused by harmonics arising due to ''linear'' & ''non linear'' loads present in the electric system mainly due to increasing presence of switched mode power supply and other consumer electronics. Due to these aggregated interferences, the delivered electric power quality from the mains electricity system affects the performance of electrical home appliances. These could include a decrease in lume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PWM VS RFM 20 KHz , the Polish Music Publishing House
{{disambiguation ...
PWM may refer to: Science and technology * Position weight matrix, a representation in motifs in biological sequences * Pulse-width modulation, a technique for controlling the average power delivered by an electrical signal * PWM (window manager), a Unix-based X window manager Other uses * ''Panzerwurfmine'', a type of German anti-tank hand grenade * Portland International Jetport, an airport in the U.S. * ''Professional Wealth Management'', a financial magazine * Permanent Way Machine, the British Rail Class 97/6 locomotives * Polskie Wydawnictwo Muzyczne The PWM Edition ( pl, 'Polskie Wydawnictwo Muzyczne', abbreviated as PWM) is a music publishing house based in Kraków, Poland. It was founded in 1945 and was the only music publisher in Poland for several years. In 2012 it released the twelfth vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response. A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomly
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual random events are, by definition, unpredictable, but if the probability distribution is known, the frequency of different outcomes over repeated events (or "trials") is predictable.Strictly speaking, the frequency of an outcome will converge almost surely to a predictable value as the number of trials becomes arbitrarily large. Non-convergence or convergence to a different value is possible, but has probability zero. For example, when throwing two dice, the outcome of any particular roll is unpredictable, but a sum of 7 will tend to occur twice as often as 4. In this view, randomness is not haphazardness; it is a measure of uncertainty of an outcome. Randomness applies to concepts of chance, probability, and information entropy. The fields of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switching Frequency
In electronics, switching frequency refers to the rate at which an electronic switch performs its function. Switching frequency is an important design and operating parameter in systems such as: * The Class-D amplifier, an audio power amplifier with a switched-mode output. * Various types of electric power conversion equipment: ** Boost converter ** Buck–boost converter ** Buck converter ** Chopper ** Switched-mode power supply ** Power inverter * Motor controls, such as Variable-frequency drive A variable-frequency drive (VFD) is a type of motor drive used in electro-mechanical drive systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor input frequency and, depending on topology, to control associated voltage or curre ...s {{Electronics-stub Electrical parameters This frequency is also used in different types of DC-DC converters like Battery Discharge Regulator, Universal Bus Regulator, Auxiliary Bus Regulator etc., switching frequency refers the sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage in operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering. EMC pursues three main classes of issue. Emission is the generation of electromagnetic energy, whether deliberate or accidental, by some source and its release into the environment. EMC studies the unwanted emissions and the countermeasures which may be taken in order to reduce unwanted emissions. The second class, susceptibility, is the tendency of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, to malfunction or break down in the presenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PWM VS RFM , the Polish Music Publishing House
{{disambiguation ...
PWM may refer to: Science and technology * Position weight matrix, a representation in motifs in biological sequences * Pulse-width modulation, a technique for controlling the average power delivered by an electrical signal * PWM (window manager), a Unix-based X window manager Other uses * ''Panzerwurfmine'', a type of German anti-tank hand grenade * Portland International Jetport, an airport in the U.S. * ''Professional Wealth Management'', a financial magazine * Permanent Way Machine, the British Rail Class 97/6 locomotives * Polskie Wydawnictwo Muzyczne The PWM Edition ( pl, 'Polskie Wydawnictwo Muzyczne', abbreviated as PWM) is a music publishing house based in Kraków, Poland. It was founded in 1945 and was the only music publisher in Poland for several years. In 2012 it released the twelfth vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Processes
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner. Examples include the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical current fluctuating due to thermal noise, or the movement of a gas molecule. Stochastic processes have applications in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology, neuroscience, physics, image processing, signal processing, control theory, information theory, computer science, cryptography and telecommunications. Furthermore, seemingly random changes in financial markets have motivated the extensive use of stochastic processes in finance. Applications and the study of phenomena have in turn inspired the proposal of new stochastic processes. Examples of such stochastic processes include the Wiener process or Brownian motion process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide-sense Stationary
In mathematics and statistics, a stationary process (or a strict/strictly stationary process or strong/strongly stationary process) is a stochastic process whose unconditional joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time. Consequently, parameters such as mean and variance also do not change over time. If you draw a line through the middle of a stationary process then it should be flat; it may have 'seasonal' cycles, but overall it does not trend up nor down. Since stationarity is an assumption underlying many statistical procedures used in time series analysis, non-stationary data are often transformed to become stationary. The most common cause of violation of stationarity is a trend in the mean, which can be due either to the presence of a unit root or of a deterministic trend. In the former case of a unit root, stochastic shocks have permanent effects, and the process is not mean-reverting. In the latter case of a deterministic trend, the process is cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner. Examples include the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical current fluctuating due to thermal noise, or the movement of a gas molecule. Stochastic processes have applications in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology, neuroscience, physics, image processing, signal processing, control theory, information theory, computer science, cryptography and telecommunications. Furthermore, seemingly random changes in financial markets have motivated the extensive use of stochastic processes in finance. Applications and the study of phenomena have in turn inspired the proposal of new stochastic processes. Examples of such stochastic processes include the Wiener process or Brownian motion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |