|
Random Cluster Model
In statistical mechanics, probability theory, graph theory, etc. the random cluster model is a random graph that generalizes and unifies the Ising model, Potts model, and percolation model. It is used to study random combinatorial structures, electrical networks, etc. It is also referred to as the RC model or sometimes the FK representation after its founders Cees Fortuin and Piet Kasteleyn. The random cluster model has a critical limit, described by a conformal field theory. Definition Let G = (V,E) be a graph, and \omega: E \to \ be a bond configuration on the graph that maps each edge to a value of either 0 or 1. We say that a bond is ''closed'' on edge e\in E if \omega(e)=0, and open if \omega(e)=1. If we let A(\omega) = \ be the set of open bonds, then an open cluster or FK cluster is any connected component in A(\omega) union the set of vertices. Note that an open cluster can be a single vertex (if that vertex is not incident to any open bonds). Suppose an edge is open i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applications include many problems in a wide variety of fields such as biology, neuroscience, computer science Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ..., information theory and sociology. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion. Statistical mechanics arose out of the development of classical thermodynamics, a field for which it was successful in explaining macroscopic physical properties—such as temperature, pressure, and heat capacity—in terms of microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutte Polynomial
The Tutte polynomial, also called the dichromate or the Tutte–Whitney polynomial, is a graph polynomial. It is a polynomial in two variables which plays an important role in graph theory. It is defined for every undirected graph G and contains information about how the graph is connected. It is denoted by T_G. The importance of this polynomial stems from the information it contains about G. Though originally studied in algebraic graph theory as a generalization of counting problems related to graph coloring and nowhere-zero flow, it contains several famous other specializations from other sciences such as the Jones polynomial from knot theory and the partition functions of the Potts model from statistical physics. It is also the source of several central computational problems in theoretical computer science. The Tutte polynomial has several equivalent definitions. It is essentially equivalent to Whitney’s rank polynomial, Tutte’s own dichromatic polynomial and Fortuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Graph
In the mathematics, mathematical discipline of graph theory, the dual graph of a planar graph is a graph that has a vertex (graph theory), vertex for each face (graph theory), face of . The dual graph has an edge (graph theory), edge for each pair of faces in that are separated from each other by an edge, and a self-loop when the same face appears on both sides of an edge. Thus, each edge of has a corresponding dual edge, whose endpoints are the dual vertices corresponding to the faces on either side of . The definition of the dual depends on the choice of embedding of the graph , so it is a property of plane graphs (graphs that are already embedded in the plane) rather than planar graphs (graphs that may be embedded but for which the embedding is not yet known). For planar graphs generally, there may be multiple dual graphs, depending on the choice of planar embedding of the graph. Historically, the first form of graph Duality (mathematics), duality to be recognized was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planar Graph
In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph (discrete mathematics), graph that can be graph embedding, embedded in the plane (geometry), plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect only at their endpoints. In other words, it can be drawn in such a way that no edges cross each other. Such a drawing is called a plane graph, or a planar embedding of the graph. A plane graph can be defined as a planar graph with a mapping from every node to a point on a plane, and from every edge to a plane curve on that plane, such that the extreme points of each curve are the points mapped from its end nodes, and all curves are disjoint except on their extreme points. Every graph that can be drawn on a plane can be drawn on the sphere as well, and vice versa, by means of stereographic projection. Plane graphs can be encoded by combinatorial maps or rotation systems. An equivalence class of topologically equivalent drawings on the sphere, usually with addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Critical Exponents
In the context of the physical and mathematical theory of percolation, a percolation transition is characterized by a set of ''universal'' critical exponents, which describe the fractal properties of the percolating medium at large scales and sufficiently close to the transition. The exponents are universal in the sense that they only depend on the type of percolation model and on the space dimension. They are expected to not depend on microscopic details such as the lattice structure, or whether site or bond percolation is considered. This article deals with the critical exponents of random percolation. Percolating systems have a parameter p\,\! which controls the occupancy of sites or bonds in the system. At a critical value p_c\,\!, the mean cluster size goes to infinity and the percolation transition takes place. As one approaches p_c\,\!, various quantities either diverge or go to a constant value by a power law in , p - p_c, \,\!, and the exponent of that power law is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometrical Frustration
In condensed matter physics, geometrical frustration (or in short, frustration) is a phenomenon where the combination of conflicting inter-atomic forces leads to complex structures. Frustration can imply a plenitude of distinct ground states at absolute zero, zero temperature, and usual thermal ordering may be suppressed at higher temperatures. Much-studied examples include amorphous materials, glasses, and dilute magnets. The term ''frustration'', in the context of magnetism, magnetic systems, was introduced by Gerard Toulouse in 1977. Frustrated magnetism, magnetic systems had been studied even before. Early work includes a study of the Ising model on a triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor Spin (physics), spins coupled Antiferromagnetism, antiferromagnetically, by Gregory Wannier, G. H. Wannier, published in 1950. Related features occur in magnets with ''competing interactions'', where both ferromagnetic as well as antiferromagnetic couplings between pairs of Spin (physics), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
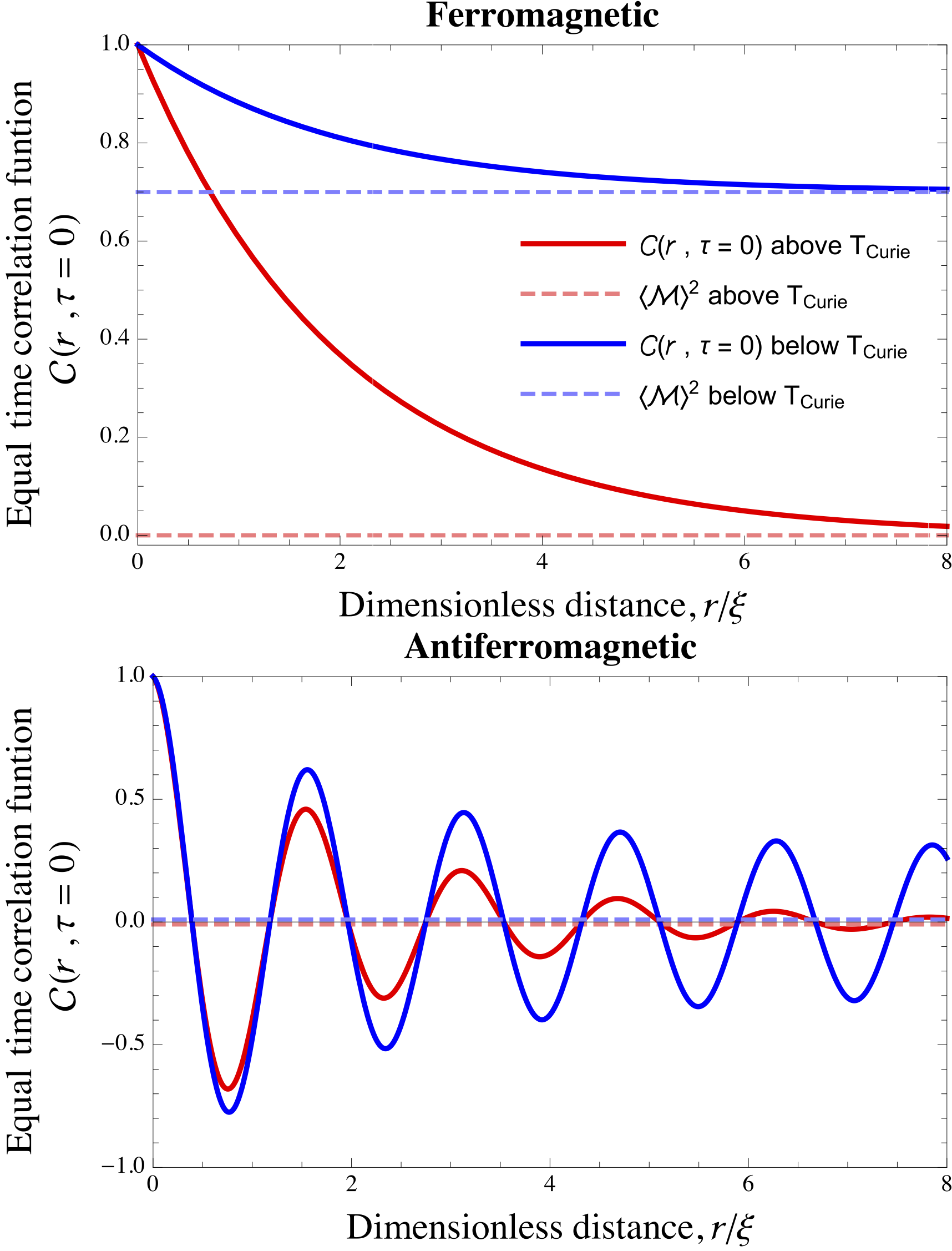
Correlation Function (statistical Mechanics)
In statistical mechanics, the correlation function is a measure of the order in a system, as characterized by a mathematical correlation function. Correlation functions describe how microscopic variables, such as spin and density, at different positions or times are related. More specifically, correlation functions measure quantitatively the extent to which microscopic variables fluctuate together, on average, across space and/or time. Keep in mind that correlation doesn’t automatically equate to causation. So, even if there’s a non-zero correlation between two points in space or time, it doesn’t mean there is a direct causal link between them. Sometimes, a correlation can exist without any causal relationship. This could be purely coincidental or due to other underlying factors, known as confounding variables, which cause both points to covary (statistically). A classic example of spatial correlation can be seen in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic materials. In these ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the conditional probability distribution is a probability distribution that describes the probability of an outcome given the occurrence of a particular event. Given two jointly distributed random variables X and Y, the conditional probability distribution of Y given X is the probability distribution of Y when X is known to be a particular value; in some cases the conditional probabilities may be expressed as functions containing the unspecified value x of X as a parameter. When both X and Y are categorical variables, a conditional probability table is typically used to represent the conditional probability. The conditional distribution contrasts with the marginal distribution of a random variable, which is its distribution without reference to the value of the other variable. If the conditional distribution of Y given X is a continuous distribution, then its probability density function is known as the conditional density function. The prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Distribution
In statistical mechanics and mathematics, a Boltzmann distribution (also called Gibbs distribution Translated by J.B. Sykes and M.J. Kearsley. See section 28) is a probability distribution or probability measure that gives the probability that a system will be in a certain state as a function of that state's energy and the temperature of the system. The distribution is expressed in the form: :p_i \propto \exp\left(- \frac \right) where is the probability of the system being in state , is the exponential function, is the energy of that state, and a constant of the distribution is the product of the Boltzmann constant and thermodynamic temperature . The symbol \propto denotes proportionality (see for the proportionality constant). The term ''system'' here has a wide meaning; it can range from a collection of 'sufficient number' of atoms or a single atom to a macroscopic system such as a natural gas storage tank. Therefore, the Boltzmann distribution can be used to sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. It gives the probabilities of various values of the variables in the subset without reference to the values of the other variables. This contrasts with a conditional distribution, which gives the probabilities contingent upon the values of the other variables. Marginal variables are those variables in the subset of variables being retained. These concepts are "marginal" because they can be found by summing values in a table along rows or columns, and writing the sum in the margins of the table. The distribution of the marginal variables (the marginal distribution) is obtained by marginalizing (that is, focusing on the sums in the margin) over the distribution of the variables being discarded, and the discarded variables are said to have been marginalized out. The context here is that the theoreti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swendsen–Wang Algorithm
The Swendsen–Wang algorithm is the first non-local or cluster algorithm for Monte Carlo simulation for large systems near criticality. It has been introduced by Robert Swendsen and Jian-Sheng Wang in 1987 at Carnegie Mellon. The original algorithm was designed for the Ising and Potts models, and it was later generalized to other systems as well, such as the XY model by Wolff algorithm and particles of fluids. The key ingredient was the random cluster model, a representation of the Ising or Potts model through percolation models of connecting bonds, due to Fortuin and Kasteleyn. It has been generalized by Barbu and Zhu to arbitrary sampling probabilities by viewing it as a Metropolis–Hastings algorithm and computing the acceptance probability of the proposed Monte Carlo move. Motivation The problem of the critical slowing-down affecting local processes is of fundamental importance in the study of second-order phase transitions (like ferromagnetic transition in the Isin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Probability Distribution
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as suture (joint), sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Joints play a vital role in the human body, contributing to movement, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |