|
Randenigala Dam
The Randenigala Dam () is a large hydroelectricity, hydroelectric embankment dam, embankment dam at Rantembe, in the Central Province, Sri Lanka, Central Province of Sri Lanka. Construction of the dam began in November 1982, and was completed in approximately . The dam and power station was ceremonially opened by then President of Sri Lanka, President J. R. Jayawardene in 1986. Construction of the dam cost approximately , of which 24.6% () was funded by the Government of Sri Lanka, local government, and the majority of the remainder by Germany. Dam The Randenigala Dam is located downstream of the Victoria Dam (Sri Lanka), Victoria Dam, and upstream of the Rantembe Dam. Randenigala measures in height, in length, with a crest and base width of and respectively. The embankment dam is made mostly of rocks, and consists of a clay core. Three large controlled tainter gate chute spillways, with a combined discharge volume of , are constructed at the southern end of the dam. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank (geography)
In geography, a bank is the land alongside a body of water. Different structures are referred to as ''banks'' in different fields of geography. In limnology (the study of inland waters), a stream bank or river bank is the terrain alongside the Stream bed, bed of a river, creek, or stream. The bank consists of the sides of the channel (geography), channel, between which the streamflow, flow is confined. Stream banks are of particular interest in fluvial geography, which studies the processes associated with rivers and streams and the Deposition (geology), deposits and landforms created by them. Bankfull discharge is a Discharge (hydrology), discharge great enough to fill the channel and overtop the banks. The descriptive terms ''left bank'' and ''right bank'' refer to the perspective of an observer looking current (stream), downstream; a well-known example of this being the southern Rive Gauche, left bank and the northern Rive Droite, right bank of the river Seine definin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Sri Lanka
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. Ancient dams were built in Mesopotamia and the Middle East for water control. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. Egyptians also built dams, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Kandy District
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka's electricity demand is currently met by nine thermal power stations, fifteen large hydroelectric power stations, and fifteen wind farms, with a smaller share from small hydro facilities and other renewables such as solar. Most hydroelectric and thermal/fossil fuel–based power stations in the country are owned and/or operated by the government via the state-run Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB), while the renewable energy sector consists mostly of privately run plants operating on a power purchase agreement with the CEB. Per CEB's 2016 generation report released in mid-2017, the country has a total combined installed generation capacity of , of which 2,115 MW (52.65%) was from thermal (900 MW/22.40% from coal and 1,215 MW/30.25% from fuel oil), 1,726 MW (42.97%) from hydroelectricity, and the remaining 176 MW (4.38%) from other renewable sources such as wind, biomass, and solar. These generation sources produced a total of of electricity during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In Sri Lanka
The following page lists most dams in Sri Lanka. Most of these dams are governed by the Mahaweli Authority, while the Ceylon Electricity Board operates dams used for Hydroelectricity#Generating methods, hydroelectric power generation. Hydroelectric dams, including small hydros, account for nearly half of the installed power capacity of Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka is pockmarked with many irrigation dams, with its water resource distributed across nearly the entirety of the island for agricultural purposes via artificial canals and streams. Utilization of hydro resources for agricultural production dates back to the History of Sri Lanka, pre-Colonial era, with the current crop production now largely dependent on these water resources. __NOTOC__ Dams in Sri Lanka Irrigation dams with a length and height of more than and are listed, including all the state-run hydroelectric power stations. Privately owned "small-hydro" facilities (which are limited to a maximum nameplate capacity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
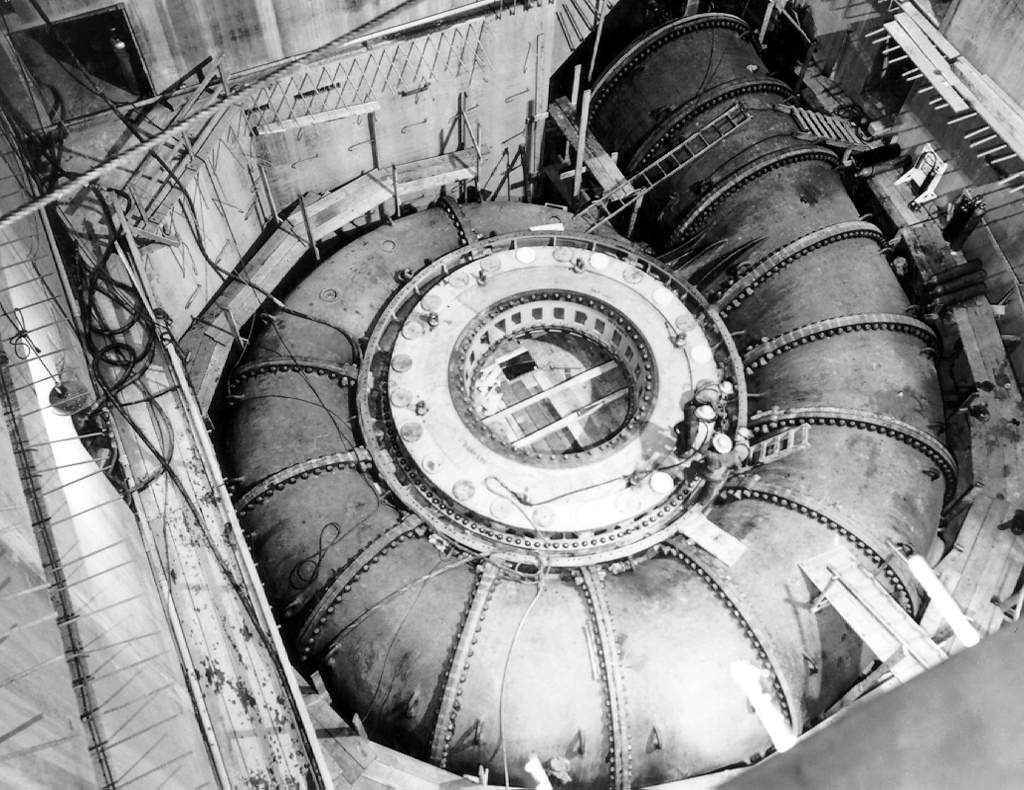
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tainter Gate
The Tainter gate is a type of radial arm floodgate used in dams and canal locks to control water flow. It is named for its inventor, the Wisconsin structural engineer Jeremiah Burnham Tainter. Tainter, an employee of the lumber firm Knapp, Stout and Co., invented the gate in 1886 for use on the company's dam that forms Lake Menomin in the United States. Description A side view of a Tainter gate resembles a slice of pie with the curved part of the piece facing the source or upper pool of water and the tip pointing toward the destination or lower pool. The curved face or skinplate of the gate takes the form of a wedge section of cylinder. The straight sides of the pie shape, the trunnion arms, extend back from each end of the cylinder section and meet at a trunnion which serves as a pivot point when the gate rotates. Principle Pressure forces on a submerged body act perpendicular to the body's surface. The design of the Tainter gate results in every pressure force acting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rantembe Dam
The Rantembe Dam () is a hydroelectric gravity dam at Rantembe, in the Central Province of Sri Lanka. Construction of the dam began in January 1987, and was completed on schedule in April 1990. The dam was constructed by the German 'Joint Venture Randenigala'; a different German joint venture has built the Randenigala Dam, further upstream. Construction of the dam cost approximately , of which 34.7% () was funded by the Ceylon Electricity Board, with the majority of the remainder funded by Germany. Dam, reservoir, and power station The Rantembe Dam, located just downstream of the Randenigala Dam, measures in height, in length, and consists of 4 tainter gate spillways with a combined discharge capacity of . The dam creates the relatively small Rantembe Reservoir, which has a catchment area of , and a total capacity of . Water from the reservoir is channelled through the dam through a steel penstock to power the two turbines. The power station's combined output of 52-mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |