|
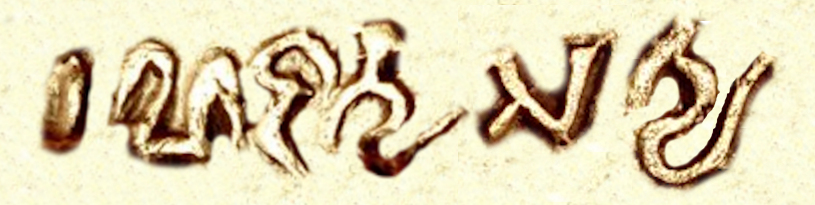
Ranadityasatya
Rāṇāditya Satya (formerly read Raṇa Datasatya on his coins), was a ruler in the area of Sindh, modern-day Pakistan, in the 5-6th centuries CE, probably circa 480 CE. The name "Rāṇāditya" is otherwise known, and it appears in several parts of the '' Rajatarangini''. His coins employ a sun symbol together with the portrait of the ruler, and have on the reverse a fire altar of the type seen on Sasanian coinage, in which the traditional attendants of Sasanian coinage are replaced by a legend in Brahmi script. The legend in Brahmi reads ''Rāṇāditya Satya''. The coins of Rāṇāditya Satya are considered as modelled on the coins of Peroz I, particularly from the portrait type. These coins are the latest known of the series of Sasanian-type "coinage of Sindh", which were minted in the area of Sindh in modern Pakistan, from Multan to the mouth of the Indus river, on the model the coinage of Sasanian Empire rulers Shapur II down to Peroz I, and are covering approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai Dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh. Scholarship Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hindrance. Under the British Raj, as bureaucrats and amateur historians mined the Chachnama to justify their invasion of Khairpur, and presence in the subcontinent, the Rai dynasty received some attention. In modern scholarship, the dynasty has attracted recent attention from a few numismatists. Background Coinage attests to the indirect influence of Sasanians over Sindh since the reign of Shapur II. In the last Sassanian mints discovered from the region — of Peroz I (r. 459–484) — a new Brahmi legend " Ranaditya Satya" appears on the reverse, which was probably the name of the local ruler. Sometime soon, Sindh appears to have fallen off the orbit of Sassanians who were reeling under Hephthalite invasions. The Rai dynasty's origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India. The invasion of India by the Huna peoples follows invasions of the subcontinent in the preceding centuries by the Yavana (Indo-Greeks), the Saka (Indo-Scythians), the Palava ( Indo-Parthians), and the Kushana (Yuezhi). The Alchon Empire was the third of four major Huna states established in Central and South Asia. The Alchon were preceded by the Kidarites and succeeded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hephthalite Huns
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE. They formed an empire, the Imperial Hephthalites, and were militarily important from 450 CE, when they defeated the Kidarites, to 560 CE, when combined forces from the First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanian Empire defeated them. After 560 CE, they established "principalities" in the area of Tokharistan, under the suzerainty of the Western Turks (in the areas north of the Oxus) and of the Sasanian Empire (in the areas south of the Oxus), before the Tokhara Yabghus took over in 625. The Imperial Hephthalites, based in Bactria, expanded eastwards to the Tarim Basin, westwards to Sogdia and southwards through Afghanistan, but they never went beyond the Hindu-Kush, which was occupied by the Alchon Huns, previously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narseh
Narseh (also spelled Narses or Narseus; pal, 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩, New Persian: , ''Narsē'') was the seventh Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 293 to 303. The youngest son of Shapur I (), Narseh served as the governor of Sakastan, Hind and Turan under his father. Shapur I was eventually succeeded by his son Hormizd I (), who died after a reign of one year. Shapur I's eldest son Bahram I, who had never been considered as a candidate for succession to the throne by his father, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir. He then made a settlement with Narseh to give up his entitlement to the throne in return for the governorship of the important frontier province of Armenia, which was a persistent cause for war between the Roman and Sasanian Empires. Narseh held the title of ''Vazurg Šāh Arminān'' ("Great King of Armenia"), which was used by the heir to the throne in the early Sasanian times. Nevertheless, Narseh most likely still viewed B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩, Šābuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the Arab city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire , and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III (), he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman Emperor Philip the Arab () to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The List of longest-reigning monarchs, longest-reigning monarch in History of Iran, Iranian history, he reigned for the entirety of his 70-year life, from 309 to 379. He was the son of Hormizd II (r. 302–309). His reign saw the military resurgence of the country, and the expansion of its territory, which marked the start of the first Sasanian golden era. He is thus along with Shapur I, Kavad I and Khosrow I, regarded as one of the most illustrious Sasanian kings. His three direct successors, on the other hand, were less successful. At the age of 16, he launched enormously successful military campaigns against Arab insurrections and tribes who knew him as 'Dhū'l-Aktāf'' ("he who pierces shoulders"). Shapur II pursued a harsh religious policy. Under his reign, the collection of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the Sasanian dynasty, House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived List of monarchs of Persia, Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions are divided by a "line of control" agreed to in 1972, although neither country recognizes it as an international boundary. In addition, China be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab. Multan is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Asia, with a history stretching deep into antiquity. The ancient city was the site of the renowned Multan Sun Temple, and was besieged by Alexander the Great during the Mallian Campaign. A historic cultural centre of the wider Punjab, it was conquered by the Ummayad military commander Muhammad bin Qasim. The city later became independent as the capital of the Emirate of Multan in 855 A.D., before subsequently coming under the rule of empires such as the Ghaznavids, the Ghurids and the Mamluks. In 1445, it became capital of the Langah Sultanate. In 1526, it was conquered by the Mughal Empire. Multan Subah would become one of the largest provinces of the Mughal Empire when it was created by administrative r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a two-year struggle. His reign was marked by war and famine. Early in his reign, he successfully quelled a rebellion in Caucasian Albania in the west, and put an end to the Kidarites in the east, briefly expanding Sasanian rule into Tokharistan, where he issued gold coins with his likeness at Balkh. Simultaneously, Iran was suffering from a seven-year famine. He soon clashed with the former subjects of the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, who possibly had previously helped him to gain his throne. He was defeated and captured twice by the Hephthalites and lost his recently acquired possessions. In 482, revolts broke out in the western provinces of Armenia and Iberia, led by Vahan Mamikonian and Vakhtang I respectively. Before Peroz cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |