|
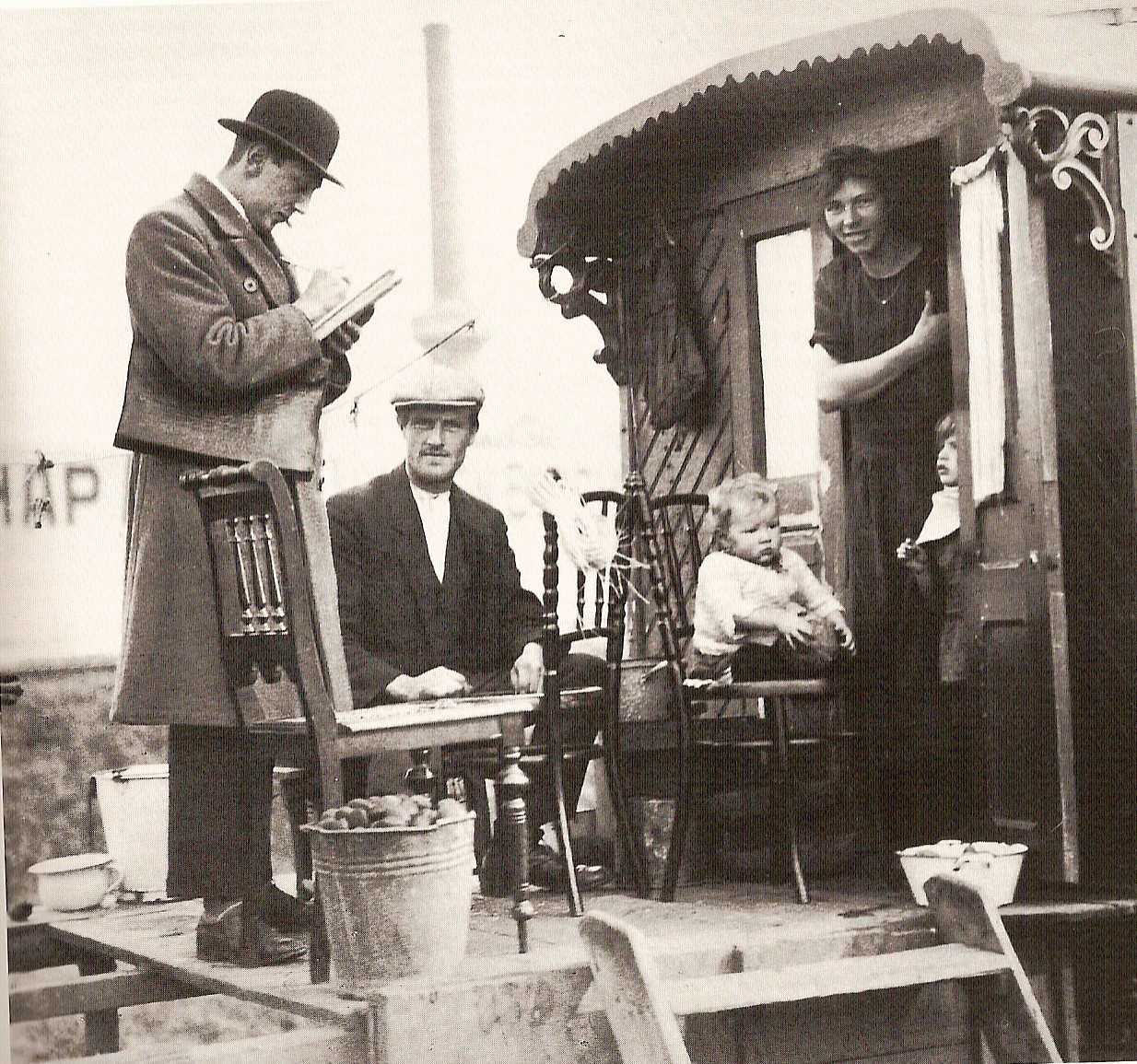
Raipur Rani Fort
Raipur Rani is a Town and Tehsil in Panchkula district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is one of three tehsils located in Panchkula District. It is located on the Panchkula city-Chandigarh-Nahan-Paonta Sahib-Dehradun highway east from the Chandigarh-Mohali-Panchkula urban cities combine. It is about from the Dera Bassi Industrial belt and from the Barwala industrial estate. Narayangarh in the Ambala District is the next large town in its proximity. Languages and Dialect Spoken The primary languages spoken in the town are Hindi and the Puadhi dialect of Haryanvi. History Raipur Rani was founded in 1420 by Rao Rai Singh who claimed to be one of the sons of Rana Har Rai Singh who came from Ajmer, and was ruled until Indian Independence by his descendants who were titled Rao Sahib. Fort of Raipur Rani Raipur Rani has a fort built by a man who came from Ajmer and was ruled until Indian Independence. The descendants of the ruling family now reside in Chandigarh. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Town
In India and some other countries, a census town is designated as a town that satisfies certain characteristics. India In India, a census town is one which is not statutorily notified and administered as a town, but nevertheless whose population has attained urban characteristics. They are characterized by the following: * Population exceeds 5,000 * At least 75% of main male working population is employed outside the agricultural sector * Minimum population density Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ... of 400 persons per km2 Census 2011 The number of census towns (CTs) in India grew from 1,362 in 2001 to 3,894 in 2011. As per Pradhan (2013), these CTs account for 30% of the urban growth in the last decade. Pradhan also notes that the largest increase in the number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paonta Sahib
Paonta Sahib is an industrial town of Himachal Pradesh in India. It is located in the south of Sirmaur district, on National Highway 72 (New NH 7). Paonta Sahib is an important place of worship for Sikhs, hosting a large Gurdwara named Gurudwara Paonta Sahib, on the banks of the river Yamuna. The river is the boundary between the states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. History The town was founded by Sikh Guru Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji. The Gurudwara Paonta Sahib has linkages to the tenth Sikh Guru, Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Sikh leader Banda Singh Bahadur. Its original name was Paontika. In Hindi language, ''Paon'' means "feet" and ''tika'' means "became stable". It is believed that Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and his horse stopped at this place, and he decided to stay here. He lived here for four and a half years, having never stayed so long at any other place in his entire life. He wrote many Sikh religious books during the stay and moved to Anandpur Sahib to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saraswati
Saraswati (, ), also spelled as Sarasvati, is one of the principal Devi, goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of knowledge, education, learning, arts, speech, poetry, music, purification, language and culture. Together with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati, she forms the trinity of chief goddesses, known as the Tridevi. Sarasvati is a pan-Indian deity, venerated not only in Hinduism but also in Jainism and Buddhism.Ludvik (2007), pp. 1, 11. She is one of the prominent goddesses in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic tradition (1500 to 500 BCE) who retains her significance in later Hinduism. In the Vedas, her characteristics and attributes are closely connected with the Sarasvati River, making her one of the earliest examples of a Rivers in Hinduism, river goddess in Indian tradition. As a deity associated with a river, Sarasvati is revered for her dual abilities to purify and to nurture fertility. In later Vedic literature, particularly the Brahmanas, Sarasvati is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Gurdwara Raipur Rani Guru Gobind Singh
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on Primary source, primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the Sikhs after his father Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed by Emperor Aurangzeb. His father was the ninth Sikh Guru. His four biological sons died during his lifetime – two in battle and two executed by the Mughal Empire, Mughal governor Wazir Khan (Sirhind), Wazir Khan.; Among his notable contributions to Sikhism are founding the ''Sikh'' warrior community called ''Khalsa'' in 1699 and introducing ''the Five Ks'', the five articles of faith that Khalsa Sikhs wear at all times. Guru Gobind Singh is credited with the ''Dasam Granth'' whose hymns are a sacred part of Sikh prayers and Khalsa rituals. He is also credited as the one who finalized and enshrined the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' as Sikhism's primary holy religious scripture and the eternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of statistics. This term is used mostly in connection with Population and housing censuses by country, national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include Census of agriculture, censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications, and other useful information to coordinate international practices. The United Nations, UN's Food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ', which itself comes from the Greek (). Anchors can either be temporary or permanent. Permanent anchors are used in the creation of a mooring, and are rarely moved; a specialist service is normally needed to move or maintain them. Vessels carry one or more temporary anchors, which may be of different designs and weights. A sea anchor is a drag device, not in contact with the seabed, used to minimize drift of a vessel relative to the water. A drogue is a drag device used to slow or help steer a vessel running before a storm in a following or overtaking sea, or when crossing a bar in a breaking sea. Anchoring Anchors achieve holding power either by "hooking" into the seabed, or weight, or a combination of the two. The weight of the anchor chain can be more than that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahib
Sahib or Saheb () is a term of address originating from Arabic (). As a loanword, ''Sahib'' has passed into several languages, including Persian, Kurdish, Turkish, Azerbaijani, Kazakh, Uzbek, Turkmen, Tajik, Crimean Tatar, Urdu, Hindi, Punjabi, Pashto, Bengali, Gujarati, Marathi, Rohingya and Somali. During medieval times, it was used either as an official title or an honorific. Now, in South and Central Asia, it is almost exclusively used to give respect to someone higher or lower. The honorific has largely been replaced with '' sir''. In the Tibeto-Burman language of Mizo, it is shorten as sâp, referring to people of European descent. Derived non-ruling princes' titles Sahibzada ''Sahibzada'' is a princely style or title equivalent to, or referring to a young prince. This derivation using the Persian suffix ''-zada(h)'', literally 'born from' (or further male/female descendant; compare ''Shahzada'') a ''Sahib'', was also (part of) the formal style for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rao (Indian Surname)
Rao is a title and a surname native to India. It is used mostly in states of Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Telangana. As a surname Notable people with this surname or title include the following: Pre-independence * Rao Tula Ram (c. 1825 – 1863) - Rewari King who fought Great Battle of 1857. * T. Madhava Rao (1829–1891) - Diwan of Travancore from 1857 to 1872. * R. Raghunatha Rao (c. February 1831 – May 3, 1912) - Diwan of Indore from 1875 to 1888 * R. Venkata Rao - Diwan of Travancore from 1821 to 1829. * T. Subba Rao - Diwan of Travancore from 1830 to 1837. * V. P. Madhava Rao - 17th Diwan of the Mysore kingdom * T. Ananda Rao - 18th Diwan of the Mysore kingdom * N. Madhava Rao - 23rd Diwan of the Mysore Kingdom * K. Krishnaswamy Rao - Diwan of Travancore from 1898 to 1904 * T. Rama Rao (administrator) - Diwan of Travancore from 1887 to 1892 * T. Ramachandra Rao (1825-1879) - Indian civil servant and first native I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puadhi Dialect
Puadhi (Gurmukhi: ; IAST: uādhī sometimes spelled as Poadhi, Powadhi, or Pwadhi) is an eastern dialect of the Punjabi language primarily spoken in the Puadh region of northern India. It is spoken between the Sutlej and Ghaggar river basins in the present day states of Punjab and Haryana, and the union territory of Chandigarh and Uttar Pradesh. Puadh extends from Rupnagar near Satluj up to the Ghaggar river and its tributaries, Markanda and Som in the east, which lie in northern Haryana up to Kala Amb in Nahan district of Himachal Pradesh. To the west it extends into the Puadh tract of Ludhiana where the westernmost spoken varieties of the Puadhi dialect form a continuum with Malwai and in north it blend with Doabi Puadhi's western boundary also extends into Fatehgarh Sahib and Patiala districts and its influence is observed in the southwest in the adjacent areas of Kaithal and Kurukshetra districts up to northern areas of Jind distinct such as Ujhana and Dhamtan Sahib. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambala
Ambala () is a city and a municipal corporation in Ambala district in the state of Haryana, India, located on the border with the Indian state of Punjab (India), Punjab and in proximity to both states capital Chandigarh. Politically, Ambala has two sub-areas: Ambala Cantonment (also known as Ambala Cantt) and Ambala City railway station, Ambala City, eight kilometres apart, therefore, it is also known as "Twin City." It has a large Indian Army and Indian Air Force presence within its cantonment area. It is located 200 km (124 mi) to the north of New Delhi, India's capital, and has been identified as a National Capital Region (India)#Counter magnets, counter-magnet city for the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region to develop as an alternative center of growth to Delhi. Ambala separates the Ganges river network from the Indus river network and is surrounded by two rivers – Ghaggar-Hakra River, Ghaggar and Dangri, Tangri – to the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barwala, Panchkula
Barwala is a town and sub-tehsil in the Panchkula district of Haryana, India. Its lies Approx. 23 km from Panchkula city and 31 Kilometers from Chandigarh state capital. The name "Barwala" is derived from "Bar", the Hindi word for Ficus benghalensis. The Barwala town is situated on the Haryana-Punjab border, near an Air Force An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ... station. The Barwala block consists of 35 gram panchayats and 10 block sameeties. The block population is 48284. References Cities and towns in Panchkula district {{Haryana-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |