|
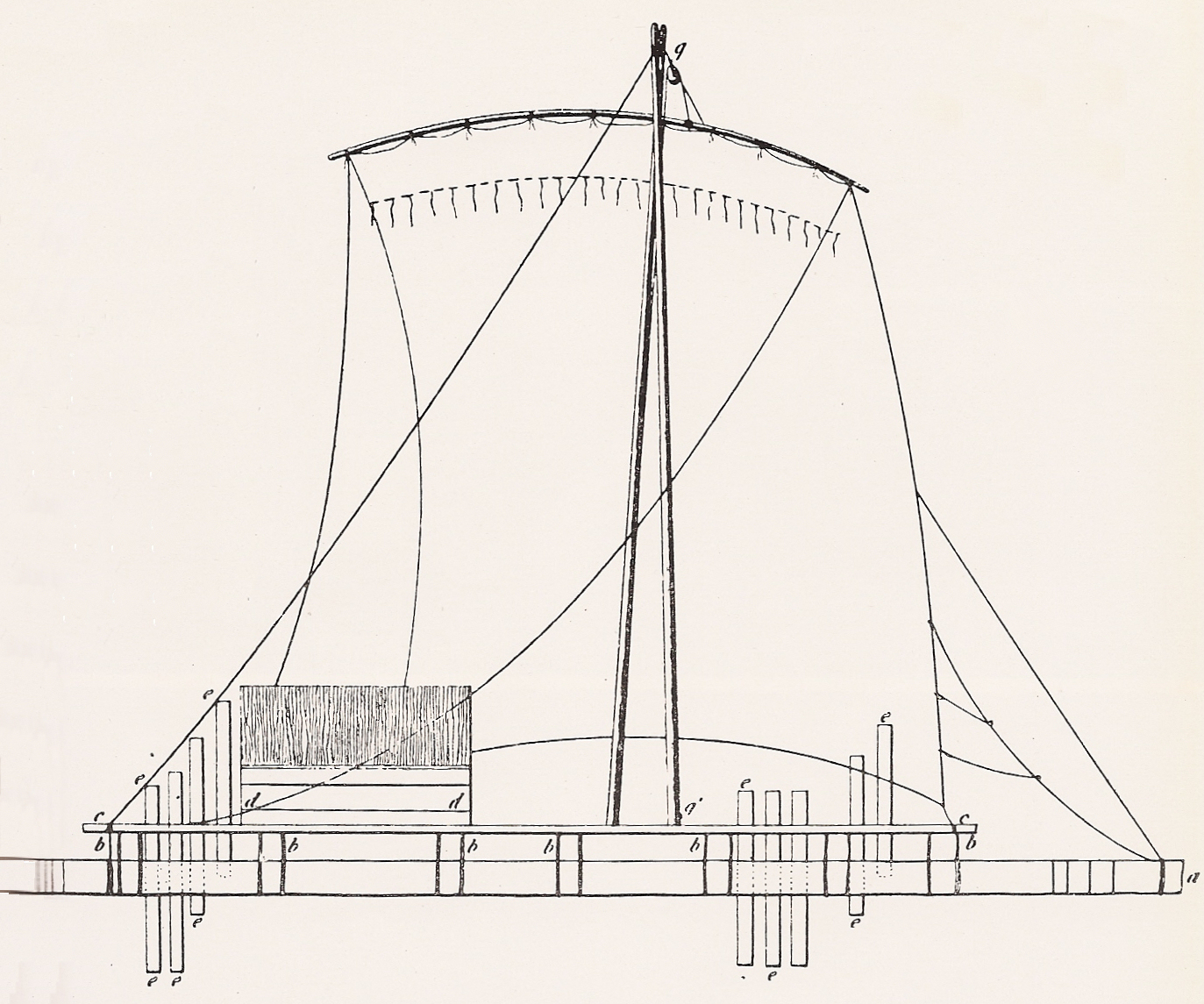
Rafts
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber Rafting
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest means of transporting felled timber. Both methods may be referred to as timber floating. The tradition of timber rafting cultivated in Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Latvia, Poland and Spain was inscribed on UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2022 Historical rafting Unlike log driving, which was a dangerous task of floating separate logs, floaters or raftsmen could enjoy relative comfort of navigation, with cabins built on rafts, steering by means of oars and possibility to make stops. On the other hand, rafting requires wider waterflows. Timber rafts were also used as a means of transportation of people and goods, both raw materials ( ore, fur, game) and man-made. Theophrastus (''Hist. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raft Guara
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a part of the experience. This activity as an adventure sport has become popular since the 1950s, if not earlier, evolving from individuals paddling to rafts with double-bladed paddles or oars to multi-person rafts propelled by single-bladed paddles and steered by a person at the stern, or by the use of oars. Rafting on certain sections of rivers is considered an extreme sport and can be fatal, while other sections are not so extreme or difficult. Rafting is also a competitive sport practiced around the world which culminates in a world rafting championship event between the participating nations. The International Rafting Federation, often referred to as the IRF, is the worldwide body which oversees all aspects of the sport. Equipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Dispersal
Oceanic dispersal is a type of biological dispersal that occurs when Terrestrial animal, terrestrial organisms transfer from one land mass to another by way of a sea crossing. Island hopping is the crossing of an ocean by a series of shorter journeys between islands, as opposed to a single journey directly to the destination. Often this occurs via large rafts of floating vegetation such as are sometimes seen floating down major rivers in the tropics and washing out to sea, occasionally with animals trapped on them. Dispersal via such a raft is sometimes referred to as a rafting event. Colonization of land masses by plants can also occur via long-distance oceanic dispersal of floating seeds. History Rafting has played an important role in the colonization of isolated land masses by mammals. Prominent examples include Madagascar, which has been isolated for ~120 million years (Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma), and South America, which was isolated for much of the Cenozoic. Both lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balsa
''Ochroma pyramidale'', commonly known as balsa, is a large, fast-growing tree native to the Americas. It is the sole member of the genus ''Ochroma'', and is classified in the subfamily Bombacoideae of the mallow family Malvaceae. The tree is famous for its wide usage in woodworking, due to its softness and its high strength compared to its low density. The name ''balsa'' is the Spanish word for "raft" and the Portuguese word for ferry. A deciduous angiosperm, ''Ochroma pyramidale'' can grow up to 30 m tall, and is classified as a hardwood despite the wood itself being very soft; it is the softest commercial hardwood and is widely used because of its light weight. Balsa trees grow extremely fast, often up to 27 metres in 10–15 years, and do not usually live beyond 30 to 40 years. In terms of volume (as opposed to height) they may be the fastest growing tree known; Streets mentions one individual which grew tall and diameter at breast height during a period of fifteen mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Float (nautical)
A float (also called a pontoon) is an airtight hollow structure, similar to a pressure vessel, designed to provide buoyancy in water. Its principal applications are in hull (watercraft), watercraft hulls, Floatplane, aircraft floats, Floating dock (jetty), floating piers, aquaculture, pontoon bridge, pontoon bridges, and marine engineering applications such as marine salvage, salvage. Applications Floats make up the multipart hulls of catamarans and trimarans and provide buoyancy for floatplanes, seaplanes and houseboats. They are used in pontoon bridges, floating piers, and floats anchored to the seabed for recreation or dockage. They are also used in shipbuilding and marine salvage, often deployed uninflated then pressurized to raise a sunken object. In military, floats are used as pontoon bridges or transportation platforms for heavier vehicles or machinery. In popular usage, the term ''pontoon'' can refer to any of several of the following objects that make use of nautical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
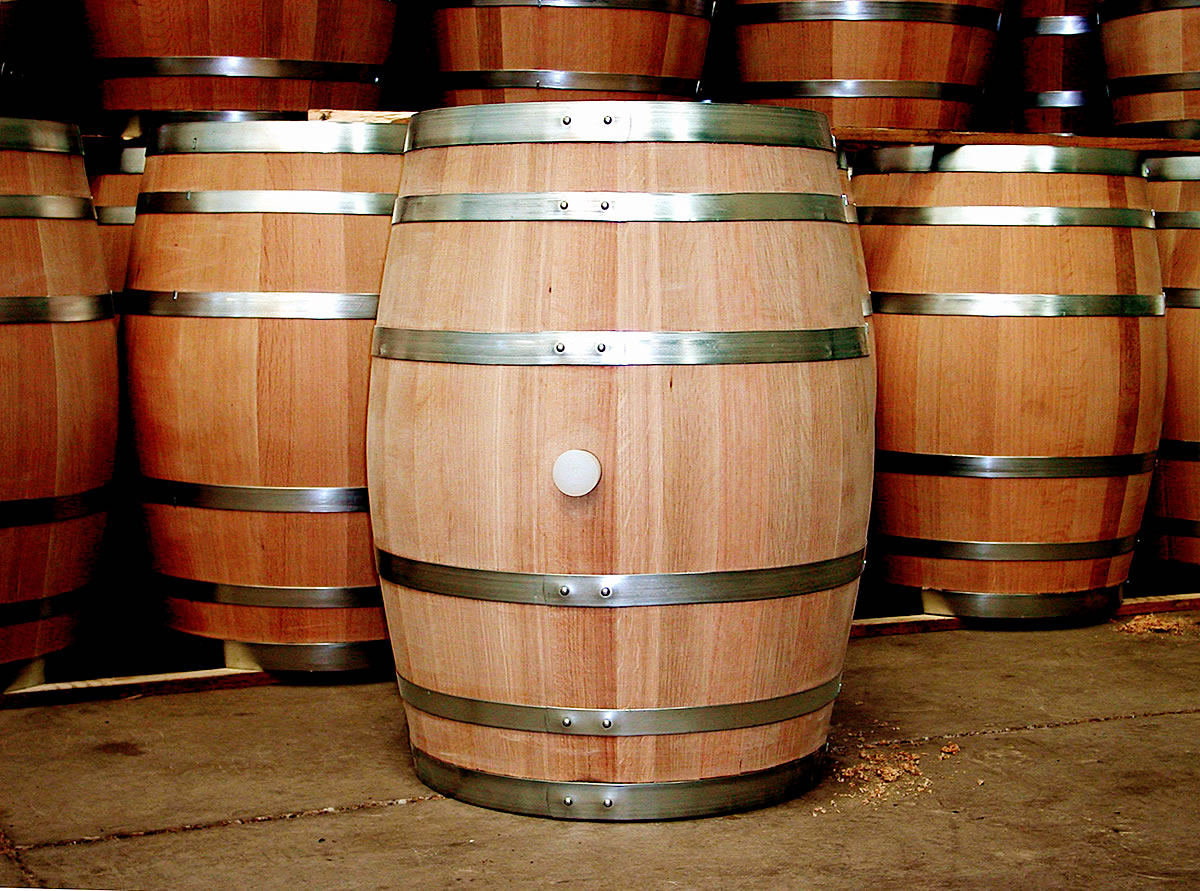
Barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden stave (wood), staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, usually alcoholic beverages; a small barrel or cask is known as a keg. Barrels have a variety of uses, including storage of liquids such as water, oil, and alcohol. They are also employed to hold maturing beverages such as wine, Cognac (brandy), cognac, Armagnac (drink), armagnac, sherry, port wine, port, whiskey, beer, arrack, and sake. Other commodities once stored in wooden casks include gunpowder, Salt-cured meat, meat, fish, paint, honey, nails, and tallow. Modern wooden barrels for wine-making are made of English oak (''Quercus robur''), white Oak (wine), oak (''Quercus petraea''), American white oak (''Quercus alba''), more exotic is mizunara oak (''Quercus crispula''), and recently Oregon oak (''Quercus garryana'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
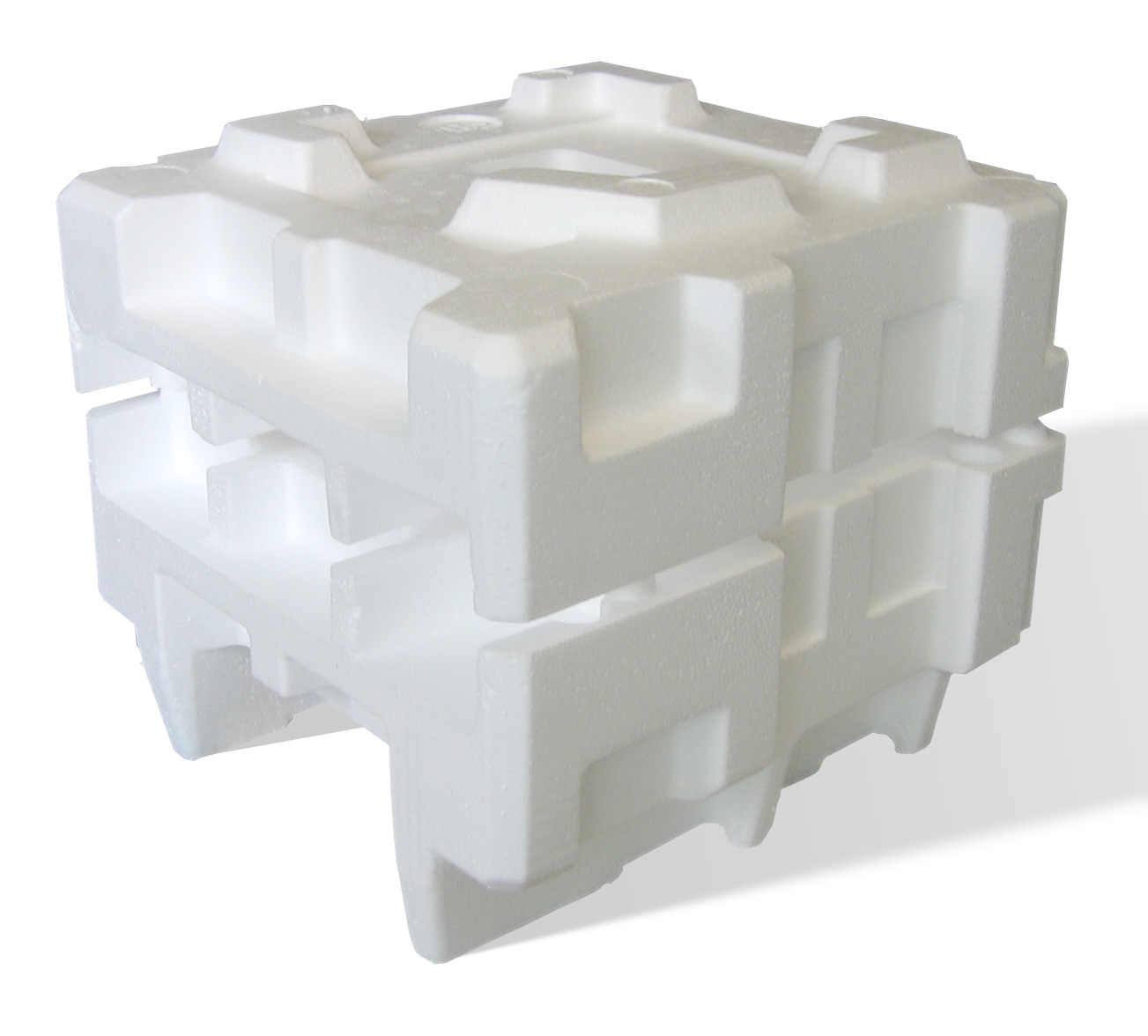
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent to visible light, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as packing peanuts and optical disc jewel cases), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature. It becomes rigid again when cooled. This te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including Polynesian languages, linguistic relations, Polynesian culture, cultural practices, and Tradition, traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and Polynesian navigation, using stars to navigate at night. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Société de Géographie of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the South Seas, southern Pacific have also often been called the South Sea Islands, and their inhabitants have been called South Sea Islanders. The Hawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |