|
Radioresistance
Radioresistance is the level of ionizing radiation that organisms are able to withstand. Ionizing-radiation-resistant organisms (IRRO) were defined as organisms for which the dose of acute ionizing radiation (IR) required to achieve 90% reduction (D10) is greater than 1,000 gray (Gy) Radioresistance is surprisingly high in many organisms, in contrast to previously held views. For example, the study of environment, animals and plants around the Chernobyl disaster area has revealed an unexpected survival of many species, despite the high radiation levels. A Brazilian study in a hill in the state of Minas Gerais which has high natural radiation levels from uranium deposits, has also shown many radioresistant insects, worms and plants. Certain extremophiles, such as the bacteria '' Deinococcus radiodurans'' and the tardigrades, can withstand large doses of ionizing radiation on the order of 5,000 Gy. Induced radioresistance In the graph on left, a dose/survival curve for a hypo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinococcus Radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. ''The Guinness Book Of World Records'' listed it in January 1998 as the world's most radiation-resistant bacterium or lifeform. Several bacteria of comparable radioresistance are known, including some species of the genus '' Chroococcidiopsis'' (phylum cyanobacteria) and some species of '' Rubrobacter'' (phylum Actinomycetota); among the archaea, the species '' Thermococcus gammatolerans'' shows comparable radioresistance. Name and classification The name ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' derives from the Ancient Greek δεινός () and κόκκος () meaning "terrible grain/berry" and the Latin and , meaning "radiation-surviving". The species was formerly called ''Micrococcus radiodurans''. As a consequence of its hardiness, it has been nicknamed “Conan the Bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Biology
Radiobiology (also known as radiation biology, and uncommonly as actinobiology) is a field of clinical and basic medical sciences that involves the study of the effects of radiation on living tissue (including ionizing and non-ionizing radiation), in particular health effects of radiation. Ionizing radiation is generally harmful and potentially lethal to living things but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Its most common impact is the induction of cancer with a latent period of years or decades after exposure. High doses can cause visually dramatic radiation burns, and/or rapid fatality through acute radiation syndrome. Controlled doses are used for medical imaging and radiotherapy. Health effects In general, ionizing radiation is harmful and potentially lethal to living beings but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Most adverse health effects of radiation ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy vacuum ultraviolet, ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at Ionization energies of the elements (data page), different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cells
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'' primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40–45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to sque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and Autophagy (cellular), autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death. The word is derived from the Greek language, Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and logos, λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
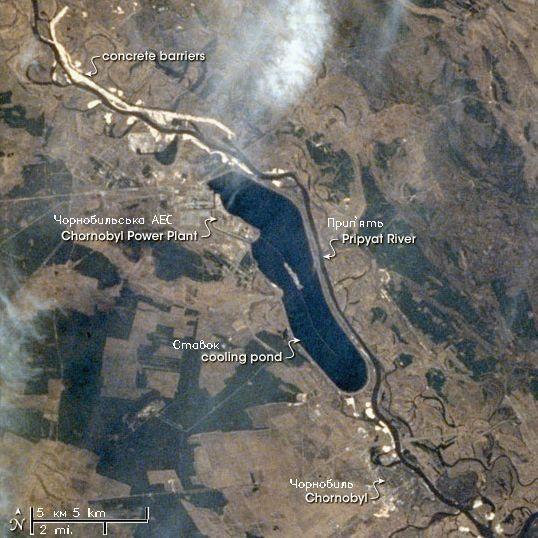
Chernobyl
Chernobyl, officially called Chornobyl, is a partially abandoned city in Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. It is located within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, to the north of Kyiv and to the southwest of Gomel in neighbouring Belarus. Prior to being evacuated in the aftermath of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, it was home to approximately 14,000 residents—considerably less than adjacent Pripyat, which was completely abandoned following the incident. Since then, although living anywhere within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone is technically illegal, Ukrainian authorities have tolerated those who have taken up living in some of the city's less irradiated areas; Chernobyl's 2020 population estimate was 150 people. First mentioned as a ducal hunting lodge in Kievan Rus' in 1193, the city has changed hands multiple times over the course of its history. In the 16th century, Jews began moving into Chernobyl, and at the end of the 18th century, it had become a major centre of Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiânia Accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, after an unsecured radiation therapy, radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site in the city. It was subsequently handled by many people, resulting in four deaths. About 112,000 people were examined for radioactive contamination and 249 of them were found to have been contaminated. In the consequent cleanup operation, topsoil had to be removed from several sites, and several houses were demolished. All the objects from within those houses, including personal possessions, were seized and incinerated. Time (magazine), ''Time'' magazine has identified the accident as one of the world's "worst Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents, nuclear disasters" and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) called it "one of the world's worst radiological incidents". The source The radiation source in the Goiânia accident was a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, ''i.e.'' observable trait. The genetic information stored in DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the "interpretation" of that informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |