|
Radiopharmaceutical
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and remain the most common of such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmacology
Radiopharmacology is radiochemistry applied to medicine and thus the pharmacology of radiopharmaceuticals ( medicinal radiocompounds, that is, pharmaceutical drugs that are radioactive). Radiopharmaceuticals are used in the field of nuclear medicine as radioactive tracers in medical imaging and in therapy for many diseases (for example, brachytherapy). Many radiopharmaceuticals use technetium-99m (Tc-99m) which has many useful properties as a gamma-emitting tracer nuclide. In the book ''Technetium'' a total of 31 different radiopharmaceuticals based on Tc-99m are listed for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood and tumors. The term ''radioisotope'', which in its general sense refers to any radioactive isotope Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmaceutical
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and remain the most common of such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide (a radioactive atom). By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, experiments that use radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments. Radioisotopes of hydrogen, carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, and iodine have been used extensively to trace the path of biochemical reactions. A radioactive tracer can also be used to track the distribution of a substance within a natural system such as a cell or tissue, or as a flow tracer to track fluid flow. Radioactive tracers are also used to determine the location of fractures created by hydraulic fracturing in nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Isotopes
A medical isotope is an isotope used in medicine. The first uses of isotopes in medicine were in radiopharmaceuticals, and this is still the most common use. However more recently, separated stable isotopes have come into use. Radioactive isotopes Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for both treatment and diagnostic scans. The most common isotope used in diagnostic scans is Technetium-99m, used in approximately 85% of all nuclear medicine diagnostic scans worldwide. It is used for diagnoses involving a large range of body parts and diseases such as cancers and neurological problems. Another well-known radioactive isotope used in medicine is Iodine-131, which is used as a radioactive label for some radiopharmaceutical therapies or the treatment of some types of thyroid cancer. Non-radioactive isotopes Examples of non-radioactive medical isotopes are: * Deuterium in deuterated drugs * Carbon-13 Carbon-13 (13C) is a natural, stable isotope of carbon with a nucleus conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Media
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In X-ray imaging, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. The types of contrast agent are classified according to their intended imaging modalities. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the most common types of contrast agent. Various sorts of iodinated contrast agents exist, with variations occurring between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polishing, polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared, infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes even at neutral pH. It is thus used to dissolve Fe- and Ca-containing scale as well as to deliver iron ions under conditions where its oxides are insoluble. EDTA is available as several salts, notably disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA, but these all function similarly. Uses EDTA is widely used in industry. It also has applications in food preservation, medicine, cosmetics, water softening, in laboratories, and other fields. Industrial EDTA is mainly used to sequester (bind or confine) metal ions in aqueous solution. In the textile industry, it prevents metal ion impurities from modifying colours of dyed products. In the pulp and paper industry, EDTA inhibits the ability of metal ions, especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
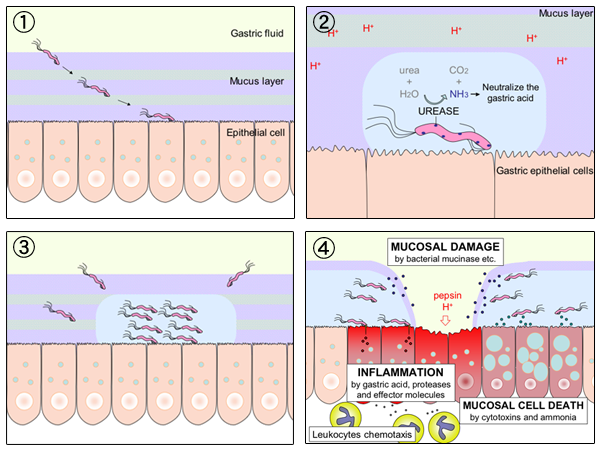
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycocholic Acid
Glycocholic acid, or cholylglycine, is a crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate of cholic acid with glycine. Its anion is called glycocholate. In a prospective study, positive associations were observed between prediagnostic plasma levels of seven conjugated bile acid metabolites, including glycocholic acid, and colon cancer Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ... risk. These findings support experimental data suggesting that high circulating bile acids promote colon cancer risk. See also * Taurocholic acid References Bile acids Cholanes {{steroid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples. Carbon-14 was discovered on February 27, 1940, by Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California Radiation Laboratory in Berkeley, California. Its existence had been suggested by Franz Kurie in 1934. There are three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon on Earth: carbon-12 (C), which makes up 99% of all carbon on Earth; carbon-13 (C), which makes up 1%; and carbon-14 (C), which occurs in trace amounts, making up about 1-1.5 atoms per 10 atoms of carbon in the atmosphere. C and C are both stable; C is unstable, with half-life years. Carbon-14 has a specific activity of 62.4 mCi/mmol (2.31 GBq/mmol), or 164.9 GBq/g. Carbon-14 decay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |