|
Radar Navigation
Radar navigation is the utilization of marine and aviation radar systems for vessel and aircraft navigation. When a craft is within radar range of land or special radar aids to navigation, the navigator can take distances and angular bearings to charted objects and use these to establish arcs of position and lines of position on a chart.Maloney, 2003:744. A fix consisting of only radar information is called a ''radar fix''.Bowditch, 2002:816. Some types of radar fixes include the relatively self-explanatory methods of "range and bearing to a single object,"National Imagery and Mapping Agency, 2001:163. "two or more bearings," "tangent bearings," and "two or more ranges." Parallel indexing is a technique defined by William Burger in the 1957 book ''The Radar Observer's Handbook''.National Imagery and Mapping Agency, 2001:169. This technique involves creating a line on the screen that is parallel to the ship's course, but offset to the left or right by some distance. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Screen
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), direction (geometry), direction (azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map Weather radar, weather formations, and terrain-following radar, terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym and initialism, acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an wikt:anacronym, anacronym, a common noun, Acronym#All-caps style, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio spectrum, radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna (radio), antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a radio receiver, receiver an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic Datum
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame, or terrestrial reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for unambiguously representing the position of locations on Earth by means of either geodetic coordinates (and related vertical coordinates) or geocentric coordinates. DatumsThe plural is not "data" in this case are crucial to any technology or technique based on spatial location, including geodesy, navigation, surveying, geographic information systems, remote sensing, and cartography. A horizontal datum is used to measure a horizontal position, across the Earth's surface, in latitude and longitude or another related coordinate system. A ''vertical datum'' is used to measure the elevation or depth relative to a standard origin, such as mean sea level (MSL). A three-dimensional datum enables the expression of both horizontal and vertical position components in a unified form. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Stationery Office
The Stationery Office (TSO) is a British publishing company created in 1996 when the publishing arm of Her Majesty's Stationery Office was privatised. It is the official publisher and the distributor for legislation, command and house papers, select committee reports, ''Hansard'', and the London, Edinburgh and Belfast Gazettes, the UK government's three official journals of record. With more than 9,000 titles in print and digital formats published every year, it is one of the UK's largest publishers by volume. TSO provides services, consultancy, and infrastructure to deliver all aspects of the information lifecycle. TSO developed the website legislation.gov.uk with The National Archives, providing full access to the statute book as open data. The TSO OpenUp platform is a collection of integrated services available as software as a service (SaaS), with the aim of providing a scalable and resilient platform that allows organisations to store, query, and enrich their data. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Imagery And Mapping Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) to support national security. Founded in 1996 as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA), it changed names in 2003. It is a member of the United States Intelligence Community. NGA headquarters, also known as NGA Campus East or NCE, is located at Fort Belvoir North Area in Springfield, Virginia. At , it is the third-largest government building in the Washington metropolitan area after the Pentagon and the Ronald Reagan Building. The agency also operates NGA Campus West, or NCW, in St. Louis, Missouri, and support and liaison offices worldwide. NGA also helps respond to natural and manmade disasters, helps with security planning for major events such as the Olympic Games, disseminates maritime safety information, and gathers data on climate change. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Xaver Von Zach
Baron Franz Xaver von Zach (''Franz Xaver Freiherr von Zach''; 4 June 1754 – 2 September 1832) was an Austrian astronomer born at Pest, Hungary (now Budapest in Hungary). Biography Zach studied physics at the Royal University of Pest, and served for some time in the Austrian army. He taught at the University of Lemberg (now Lviv, Ukraine) and worked in its observatory. He lived in Paris in 1780–83, and in London from 1783 to 1786 as tutor in the house of the Saxony, Saxon ambassador, Hans Moritz von Brühl. In Paris and London he entered the circles of astronomers like Jérôme Lalande, Pierre-Simon Laplace and William Herschel. In 1786 he was appointed by Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg director of the new Gotha Observatory, observatory on Seeberg hill at Gotha (town), Gotha, which was finished in 1791. At the close of the 18th century, he organised the first European congress of astronomers in 1798 and established the "celestial police", a group of twenty-four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Navigation
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio waves to geolocalization, determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of Radiodetermination-satellite service, radiodetermination. The basic principles are measurements from/to electric beacons, especially * Direction (geometry), Angular directions, e.g. by bearing, radio phases or interferometry, * Distance measuring equipment, Distances, e.g. ranging by measurement of time of flight between one transmitter and multiple receivers or vice versa, * Distance ''differences'' by measurement of multilateration, times of arrival of signals from one transmitter to multiple receivers or vice versa * Partly also velocity, e.g. by means of radio Doppler shift. Combinations of these measurement principles also are important—e.g., many radars measure range and azimuth of a target. Bearing-measurement systems These systems used some form of directional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Navigation
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometres of the Pelagic zone, open Pacific Ocean. Polynesians made contact with nearly every island within the vast Polynesian Triangle, using outrigger canoes or double-hulled canoes. The double-hulled canoes were two large hulls, equal in length, and lashed side by side. The space between the paralleled canoes allowed for storage of food, hunting materials, and nets when embarking on long voyages. Polynesian navigators used wayfinding techniques such as the navigation by the stars, and observations of birds, ocean swells, and wind patterns, and relied on a large body of knowledge from oral tradition. This island hopping was a solution to the scarcity of useful resources, such as food, wood, water, and available land, on the small islands in the Pacific Ocean. When an island’s required resources for human survival began to run low, the island's inhabitant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
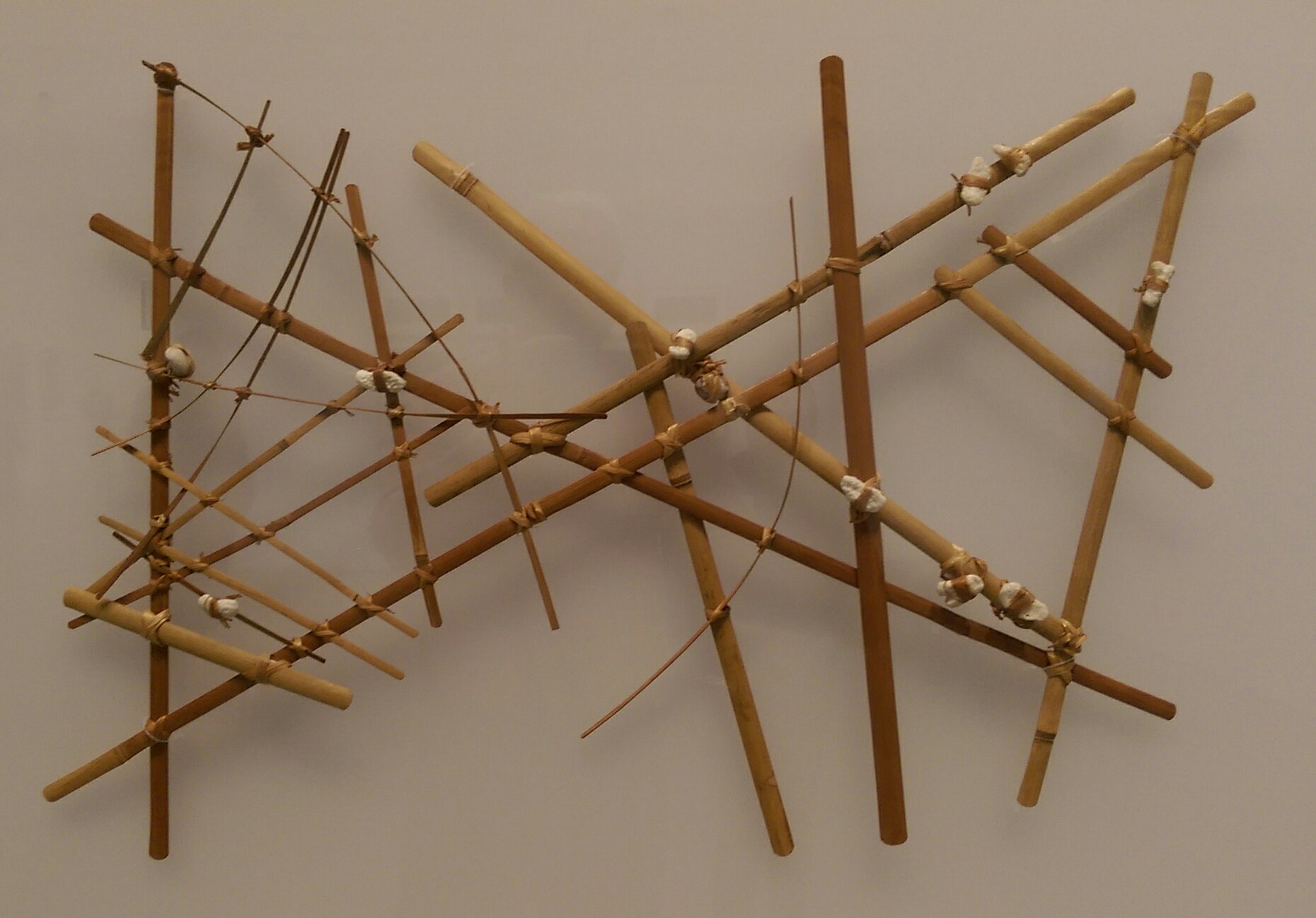
Marshall Islands Stick Chart
Stick charts were made and used by the Marshallese people, Marshallese to navigate the Pacific Ocean by canoe off the coast of the Marshall Islands. The charts represented major swell (ocean), ocean swell patterns and the ways the islands disrupted those patterns, typically determined by sensing disruptions in ocean swells by islanders during sea navigation.Asscher 2002 Most stick charts were made from the midribs of coconut fronds that were tied together to form an open framework. Island locations were represented by shells tied to the framework, or by the lashed junction of two or more sticks. The threads represented prevailing ocean surface wave-crests and directions they took as they approached islands and met other similar wave-crests formed by the ebb and flow of breakers. Individual charts varied so much in form and interpretation that the individual navigator who made the chart was the only person who could fully interpret and use it. The use of stick charts ended after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great-circle Distance
The great-circle distance, orthodromic distance, or spherical distance is the distance between two points on a sphere, measured along the great-circle arc between them. This arc is the shortest path between the two points on the surface of the sphere. (By comparison, the shortest path passing through the sphere's interior is the chord between the points.) On a curved surface, the concept of straight lines is replaced by a more general concept of geodesics, curves which are locally straight with respect to the surface. Geodesics on the sphere are great circles, circles whose center coincides with the center of the sphere. Any two distinct points on a sphere that are not antipodal (diametrically opposite) both lie on a unique great circle, which the points separate into two arcs; the length of the shorter arc is the great-circle distance between the points. This arc length is proportional to the central angle between the points, which if measured in radians can be scaled u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (satellite Navigation)
Galileo is a satellite navigation, global navigation satellite system (GNSS) created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA) and operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). It is headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, Czechia, with two ground operations centres in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany (mostly responsible for the control of the satellites), and in Fucine Lake, Fucino, Italy (mostly responsible for providing the navigation data). The €10 billion project began offering limited services in 2016. It is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the United States Global Positioning System, GPS or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |