|
Racial Hygiene Association Of New South Wales
__NOTOC__ The Racial Hygiene Association of New South Wales (RHA) was an Australian-based association founded in 1926 by Lillie Goodisson and Ruby Sophia Rich of the Women's Reform League. The association was originally known as the Racial Improvement Society until 1928. It is now known as Family Planning NSW. The association was involved in promoting sex education, preventing and eradicating venereal disease and the education of the public in eugenics.Meredith FoleyGoodisson, Lillie Elizabeth (1860? - 1947) ''Australian Dictionary of Biography'', Volume 9, Melbourne University Press, 1983, pp 47-48. Goodisson served as general secretary for the association. She advocated the selective breeding of future generations for the elimination of hereditary disease and defects and campaigned unsuccessfully for the segregation and sterilisation of the mentally deficient and for the introduction of pre-marital health examinations. Although Goodisson campaigned for her association's eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Social Hygiene Council
British Social Hygiene Council (BSHC, until 1925 the National Council for Combating Venereal Diseases, NCCVD) was a British organization dedicated to eradicating venereal diseases and educating the public about them. It has been founded in 1914. See also * Social hygiene movement The social hygiene movement was an attempt by Progressive era reformers to control venereal disease, regulate prostitution and vice, and disseminate sexual education through the use of scientific research methods and modern media techniques. Soci ... References {{UK-med-org-stub 1914 establishments in the United Kingdom Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Medical and health organisations based in the United Kingdom Infectious disease organizations 1914 in health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
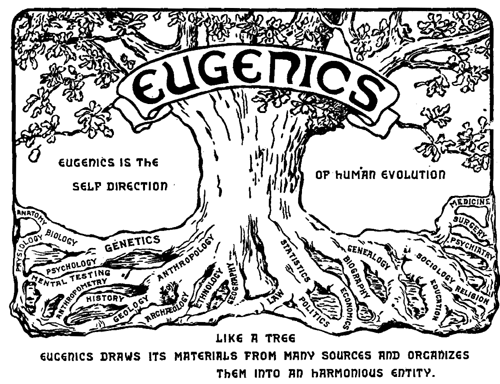
Eugenics Organizations
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenics In Australia
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Australia (1901–1945)
The history of Australia from 1901 to 1945 begins with the federation of the six colonies to create the Commonwealth of Australia. The young nation joined Britain in the First World War, suffered through the Great Depression in Australia as part of the global Great Depression and again joined Britain in the Second World War against Nazi Germany in 1939. Imperial Japan launched air raids and submarine raids against Australian cities during the Pacific War. Federation The First Fleet of British ships had arrived at Sydney Harbour in 1788, founding the first of what would evolve into six self-governed British colonies: New South Wales, Tasmania, South Australia, Western Australia, Victoria and Queensland. The last British garrisons had left Australia in 1870. At the beginning of the 20th century, nearly two decades of negotiations on Federation concluded with the approval of a federal constitution by all six Australian colonies and its subsequent ratification by the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Hygiene
The social hygiene movement was an attempt by Progressive era reformers to control venereal disease, regulate prostitution and vice, and disseminate sexual education through the use of scientific research methods and modern media techniques. Social hygiene as a profession grew alongside social work and other public health movements of the era. Social hygienists emphasized sexual continence and strict self-discipline as a solution to societal ills, tracing prostitution, drug use and illegitimacy to rapid urbanization. The movement remained alive throughout much of the 20th century and found its way into American schools, where it was transmitted in the form of classroom films about menstruation, sexually transmitted disease, drug abuse and acceptable sexual behavior in addition to an array of pamphlets, posters, textbooks and films. History The social hygiene movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries was an attempt by Progressive-era reformers to control venereal disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
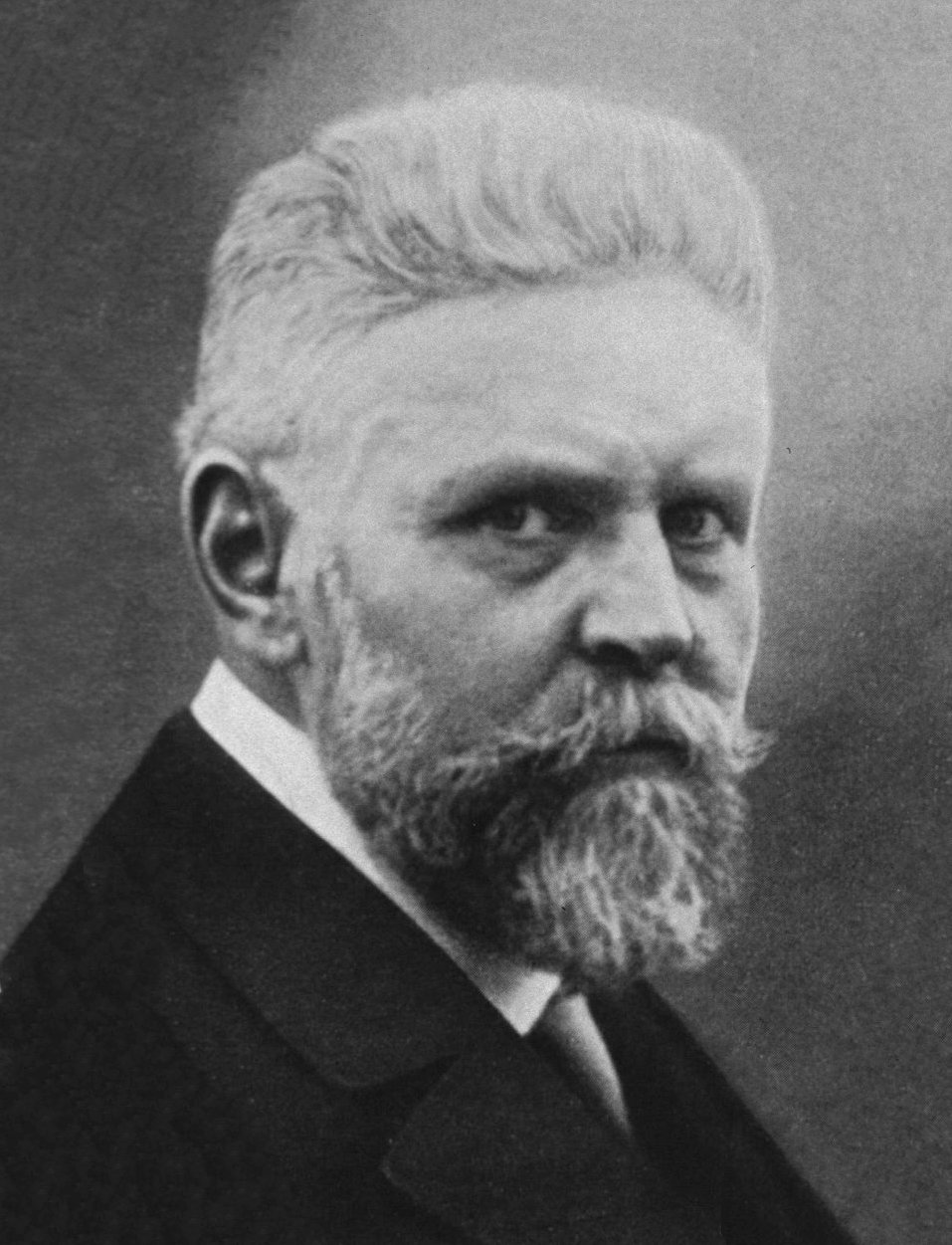
Racial Hygiene
The term racial hygiene was used to describe an approach to eugenics in the early 20th century, which found its most extensive implementation in Nazi Germany (Nazi eugenics). It was marked by efforts to avoid miscegenation, analogous to an animal breeder seeking purebred animals. This was often motivated by the belief in the existence of a racial hierarchy and the related fear that "lower races" would "contaminate" a "higher" one. As with most eugenicists at the time, racial hygienists believed that the lack of eugenics would lead to rapid social degeneration, the decline of civilization by the spread of inferior characteristics. Development The German eugenicist Alfred Ploetz introduced the term "racial hygiene" (') in 1895 in his ''Racial Hygiene Basics'' ('). He discussed the importance of avoiding "counterselective forces" such as war, inbreeding, free healthcare for the poor, alcohol and venereal disease. In its earliest incarnation it was more concerned by the declining b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
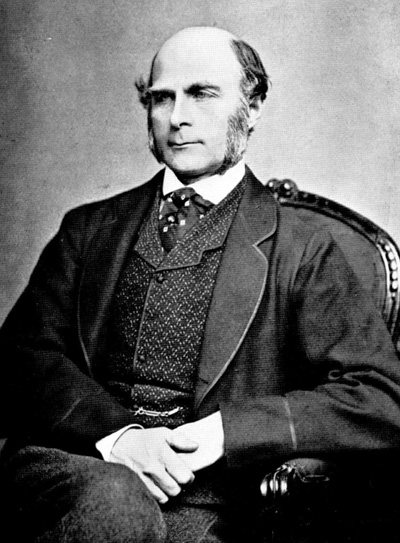
Eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marital situation, career or work considerations, financial situations. If sexually active, family planning may involve the use of contraception and other techniques to control the timing of reproduction. Family planning has been of practice since the 16th century by the people of Djenné in West Africa, when physicians advised women to space their births at three-year intervals. Others aspects of family planning aside from contraception include sex education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and management, and infertility management.World Health Organization. (n.d.)Sexual and Reproductive Health Retrieved on 30 October 2019. Family planning, as defined by the United Nations and the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. Nicknames of the city include the 'Emerald City' and the 'Harbour City'. Aboriginal Australians have inhabited the Greater Sydney region for at least 30,000 years, and Aboriginal engravings and cultural sites are common throughout Greater Sydney. The traditional custodians of the land on which modern Sydney stands ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only became available in the 20th century. Planning, making available, and using birth control is called family planning. Some cultures limit or discourage access to birth control because they consider it to be morally, religiously, or politically undesirable. The World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provide guidance on the safety of birth control methods among women with specific medical conditions. The most effective methods of birth control are Sterilization (medicine), sterilization by means of vasectomy in males and tubal ligation in females, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and contraceptive implant, implantable birth control. This is follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Scharlieb
Dame Mary Ann Dacomb Scharlieb, DBE (née Bird; 18 June 1845 – 21 November 1930) was a pioneer British female physician and gynaecologist in the late 19th/early 20th centuries. She had worked in India and by her persistence she returned to the UK to become a qualified doctor. She returned to Madras and eventually lectured in London. She was the first woman to be elected to the honorary visiting staff of a hospital in the UK and one of the most distinguished women in medicine of her generation. Biography Raised by her grandparents, following her mother's death, in a strict Evangelical Christian household, she attended a boarding school in Manchester, then to one in New Brighton, and finally at Mrs Tyndall's School at 16 Upper Hamilton Terrace in London. Hers was a conventional middle-class upbringing. Aged 19, she met William Scharlieb, "who was engaged in eating his dinners at the Middle Temple, preparatory to his call to the Bar and subsequent practice in Madras as a bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |