|
Rachel Bean
Rachel Bean is a cosmologist, theoretical astrophysicist, professor of astronomy, and senior associate dean for math and science at the College of Arts and Sciences at Cornell University. Education Bean received her bachelor's degree in natural sciences from the University of Cambridge in 1995. After graduation, she worked in the strategy division at Accenture, and then obtained her master's degree in 1999 and doctorate degree in 2002 in theoretical physics from Imperial College London. Following this, she was a postdoctoral research Fellow for Princeton University before being hired as a professor for Cornell's Department of Astronomy. Career In 2005, Bean became a faculty member at Cornell University, where her research focuses on cosmological tests of the nature of dark energy and gravity, and the physical origins of primordial inflation, using data from large-scale structure and the cosmic microwave background. She is actively involved in a number of international ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HONORIFIC
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an Honorary title (academic), honorary academic title. It is also often Conflation, conflated with systems of Honorifics (linguistics), honorific speech in linguistics, which are grammatical or morphology (linguistics), morphological ways of encoding the relative social status of speakers. Honorifics can be used as prefixes or suffixes depending on the appropriate occasion and presentation in accordance with Style (form of address), style and Convention (norm), customs. Typically, honorifics are used as a Style (manner of address), style in the grammatical third Grammatical person, person, and as a form of address in the second person. Some languages have anti-honorific (''despective'' or ''humilific'') first person forms (expressions such as "your most humble servant" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
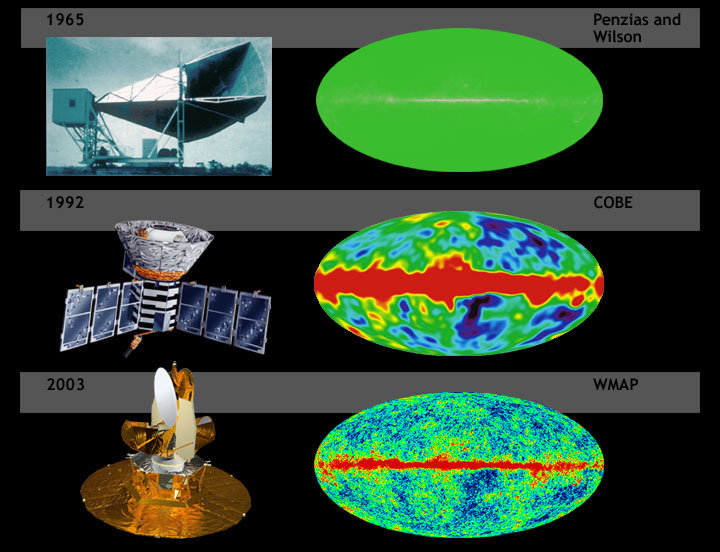
Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. It publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. It is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021, it is led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the APS was to hold scientific m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – the radiant heat remaining from the Big Bang. Headed by Professor Charles L. Bennett of Johns Hopkins University, the mission was developed in a joint partnership between the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Princeton University. The WMAP spacecraft was launched on 30 June 2001 from Florida. The WMAP mission succeeded the Cosmic Background Explorer, COBE space mission and was the second medium-class (MIDEX) spacecraft in the NASA Explorer program. In 2003, MAP was renamed WMAP in honor of cosmologist David Todd Wilkinson (1935–2002), who had been a member of the mission's science team. After nine years of operations, WMAP was switched off in 2010, following the launch of the more advanced Planck (spacecraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruber Prize In Cosmology
The Gruber Prize in Cosmology, established in 2000, is one of three prestigious international awards worth US$500,000 awarded by the Gruber Foundation, a non-profit organization based at Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut. Since 2001, the Gruber Prize in Cosmology has been co-sponsored by the International Astronomical Union. Recipients are selected by a panel from nominations that are received from around the world. The Gruber Foundation Cosmology Prize honors a leading cosmologist, astronomer, astrophysicist or scientific philosopher for theoretical, analytical or conceptual discoveries leading to fundamental advances in the field. Recipients *2000 Allan Sandage and Philip James E. Peebles *2001 Lord Martin Rees *2002 Vera Rubin *2003 Rashid Sunyaev director at the Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik *2004 Alan Guth and Andrei Linde *2005 James E. Gunn principal designer of the Hubble Space Telescope *2006 John Mather (co-recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WMAP
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – the radiant heat remaining from the Big Bang. Headed by Professor Charles L. Bennett of Johns Hopkins University, the mission was developed in a joint partnership between the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Princeton University. The WMAP spacecraft was launched on 30 June 2001 from Florida. The WMAP mission succeeded the COBE space mission and was the second medium-class (MIDEX) spacecraft in the NASA Explorer program. In 2003, MAP was renamed WMAP in honor of cosmologist David Todd Wilkinson (1935–2002), who had been a member of the mission's science team. After nine years of operations, WMAP was switched off in 2010, following the launch of the more advanced Planck spacecraft by European Space Agenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Young Submillimeter Telescope
The Cerro Chajnantor Atacama Telescope (CCAT) is a proposed diameter telescope that is intended to reveal the cosmic origins of stars, planets, and galaxies with its submillimeter cameras and spectrometers enabled by superconducting detector arrays. The telescope was originally called the Cornell Caltech Atacama Telescope, but due to lack of funding the 25 metre telescope is currently on hold. The collaboration is building a smaller diameter submillimeter/millimeter telescope, CCAT-prime, as a first step before pursuing the 25 metre CCAT at some (unknown) time in the future. CCAT-prime is based on a high optical throughput Crossed Dragone optical design, and the Simons Observatory large aperture telescope uses the same optical design. CCAT-prime will be located at the same site and share similar mission as the full sized CCAT, but naturally with reduced angular resolution compared to the 25 metre CCAT. On September 14, 2020, the CCAT-prime telescope was renamed to be the Fred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simons Observatory
The Simons Observatory is located in the high Atacama Desert in Northern Chile inside the Chajnator Science Preserve, at an altitude of 5,200 meters (17,000 ft). The Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) and the Simons Array were located nearby but these instruments have now been replaced by the current (3 small-aperture telescopes and one large-aperture telescope) telescopes of the Simons Observatory. These instruments are currently making observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Their goals are to study how the universe began, what it is made of, and how it evolved to its current state. The Simons Observatory shares many of the same goals of the previous experiments but takes advantage of advances in technology to make far more precise and diverse measurements. In addition, it is envisaged that many aspects of the Simons Observatory (optical designs, detector technologies, and so on) will be pathfinders for the future CMB-S4 array. The Simons Observatory has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atacama Cosmology Telescope
The Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) was a cosmological millimeter-wave telescope located on Cerro Toco in the Atacama Desert in the north of Chile. ACT made high-sensitivity, arcminute resolution, microwave-wavelength surveys of the sky in order to study the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), the relic radiation left by the Big Bang process. Located 40 km from San Pedro de Atacama, at an altitude of , it was one of the highest ground-based telescopes in the world. Cosmic microwave background experiments like ACT, the South Pole Telescope, the WMAP satellite, and the Planck satellite have provided foundational evidence for the standard Lambda-CDM model of cosmology. ACT first detected seven acoustic peaks in the power spectrum of the CMB, discovered the most extreme galaxy cluster and made the first statistical detection of the motions of clusters of galaxies via the pairwise kinematic Sunyaev-Zeldovich Effect. ACT was built in 2007 and saw first light in Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as the Roman Space Telescope, Roman, or RST) is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit by May 2027. It is named after former NASA Chief of Astronomy Nancy Grace Roman. The Roman Space Telescope is based on an existing wide field of view primary mirror and will carry two scientific instruments. The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-megapixel multi-band visible and near-infrared camera, providing a sharpness of images comparable to that achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope over a 0.28 square degree field of view, 100 times larger than imaging cameras on the Hubble. The Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) is a high-contrast, small field of view camera and spectrometer covering visible and near-infrared wavelengths using novel starlight-suppression technology. Stated objectives include a search for extra-solar planets using gravitational microlensing, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vera C
Vera may refer to: Names *Vera (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) *Vera (given name), a given name (including a list of people and fictional characters with the name) **Vera (), archbishop of the archdiocese of Tarragona Places Spain *Vera, Almería, a municipality in the province of Almería, Andalusia * Vera de Bidasoa, a municipality in the autonomous community of Navarra *La Vera, a comarca in the province of Cáceres, Extremadura United States * Vera, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Vera, Kansas, a ghost town * Vera, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Vera, Oklahoma, a town * Vera, Texas, an unincorporated community * Vera, Virginia, an unincorporated community * Veradale, Washington, originally known as Vera, CDP Elsewhere * Vera, Santa Fe, a city in the province of Santa Fe, Argentina * Vera Department, an administrative subdivision (departamento) of the province of Santa Fe * Vera, Mato Grosso, Brazil, a municipality * Cape Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Jayawardhana
Ray Jayawardhana is provost and professor of physics and astronomy at Johns Hopkins University. Prior to this, from 2018 to 2023, he was the Harold Tanner Dean of the College of Arts and Sciences and a Professor of Astronomy at Cornell University. Early life and education Jayawardhana was born and raised in Sri Lanka, where he attended St. John's College and Royal College Colombo prior to pursuing higher education in the United States. In 1994, he received his B.S. degree from Yale University. In 2000, he was awarded his Ph.D. from Harvard University. As a graduate student at Harvard, he led one of the two teams that discovered a dusty disk around HR 4796, a young star, with a large inner hole, which was possibly carved out during the planet formation processes. At Harvard, his group played a role in establishing that young brown dwarfs undergo a T Tauri phase, similar to young Sun-like stars, with evidence for dusty disks and signatures of disk accretion and outflow. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |