|
RVSV-ZEBOV
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus–Zaire Ebola virus (rVSV-ZEBOV), also known as Ebola Zaire vaccine live and sold under the brand name Ervebo, is an Ebola vaccine for adults that prevents Ebola caused by the Zaire ebolavirus. When used in ring vaccination, rVSV-ZEBOV has shown a high level of protection. Around half the people given the vaccine have mild to moderate adverse effects that include headache, fatigue, and muscle pain. rVSV-ZEBOV is a recombinant, replication-competent viral vector vaccine. It consists of rice-derived recombinant human serum albumin and live attenuated recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), which has been genetically engineered to express the main glycoprotein from the Zaire ebolavirus so as to provoke a neutralizing immune response to the Ebola virus. The vaccine was approved for medical use in the European Union and the United States in 2019. It was created by scientists at the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Manit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Vaccine
Ebola vaccines are vaccines either approved or in development to prevent Ebola. As of 2022, there are only vaccines against the Zaire ebolavirus. The first vaccine to be approved in the United States was rVSV-ZEBOV in December 2019. It had been used extensively in the Kivu Ebola epidemic under a compassionate use protocol. During the early 21st century, several vaccine candidates displayed efficacy to protect nonhuman primates (usually macaques) against lethal infection. Vaccines include replication-deficient adenovirus vectors, replication-competent vesicular stomatitis (VSV) and human parainfluenza (HPIV-3) vectors, and virus-like nanoparticle preparations. Conventional trials to study efficacy by exposure of humans to the pathogen after immunization are not ethical in this case. For such situations, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established the " animal efficacy rule" allowing licensure to be approved on the basis of animal model studies that repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kivu Ebola Epidemic
The Kivu Ebola epidemic was an outbreak of Ebola virus disease (EVD) mainly in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and in other parts of Central Africa, from 2018 to 2020. Between 1 August 2018 and 25 June 2020 it resulted in 3,470 reported cases. The Kivu outbreak also affected Ituri Province, whose first case was confirmed on 13 August 2018. In November 2018, the outbreak became the biggest Ebola outbreak in the DRC's history, and had become the second-largest Ebola outbreak in recorded history worldwide, behind only the 2013–2016 Western African Ebola virus epidemic, Western Africa epidemic. In June 2019, the virus reached Uganda, having infected a 5-year-old Congolese boy who entered Uganda with his family, but was contained. A military conflict in the region that had begun in January 2015 hindered treatment and prevention efforts. The World Health Organization (WHO) described the combination of military conflict and civilian distress as a potential "perfect st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicular Stomatitis Virus
''Indiana vesiculovirus'', formerly ''Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus'' (VSIV or VSV) is a virus in the family ''Rhabdoviridae''; the well-known '' Rabies lyssavirus'' belongs to the same family. VSIV can infect insects, cattle, horses and pigs. It has particular importance to farmers in certain regions of the world where it infects cattle. This is because its clinical presentation is identical to the very important foot and mouth disease virus. reviewed and published by WikiVet, accessed 12 October 2011. The virus is zoonotic and leads to a flu-like illness in infected humans. It is also a common laboratory virus used to study the properties of viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', as well as to study viral evolution. Properties ''Indiana vesiculovirus'' is the prototypic member of the genus ''Vesiculovirus'' of the family ''Rhabdoviridae''. VSIV is an arbovirus, and its replication occurs in the cytoplasm. Natural VSIV infections encompass two steps, cytolytic infections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Vector Vaccine
A viral vector vaccine is a vaccine that uses a viral vector to deliver genetic material (DNA) that can be transcribed by the recipient's host cells as mRNA coding for a desired protein, or antigen, to elicit an immune response. , six viral vector vaccines, four COVID-19 vaccines and two Ebola vaccines, have been authorized for use in humans. Understanding viral vectors History The first viral vector was introduced in 1972 through genetic engineering of the SV40 virus. A recombinant viral vector was first used when a hepatitis B surface antigen gene was inserted into a Vaccinia, vaccinia virus. Subsequently, other viruses including Adenoviridae, adenovirus, adeno-associated virus, retrovirus, cytomegalovirus, sendai virus, and lentiviruses have been designed into vaccine vectors. Vaccinia virus and adenovirus are the most commonly used viral vectors because of robust immune response it induces. The incorporation of several viruses in vaccination schemes has been investigated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Vaccination
Ring vaccination is a strategy to inhibit the spread of a disease by vaccinating those who are most likely to be infected. This strategy vaccinates the contacts of confirmed patients, and people who are in close contact with those contacts. This way, everyone who has been, or could have been, exposed to a patient receives the vaccine, creating a 'ring' of protection that can limit the spread of a pathogen. Ring vaccination requires thorough and rapid surveillance and Epidemiology, epidemiologic case investigation. The Intensified Smallpox Eradication Program used this strategy with great success in its efforts to eradicate smallpox in the latter half of the 20th century. Medical use When someone falls ill, people they might have infected should be vaccinated. Contacts who might have been infected typically include family, neighbours, and friends. Several layers of contacts may be vaccinated (the contacts, the contacts' contacts, the contact's contacts' contacts, etc.). Ring v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus Disease
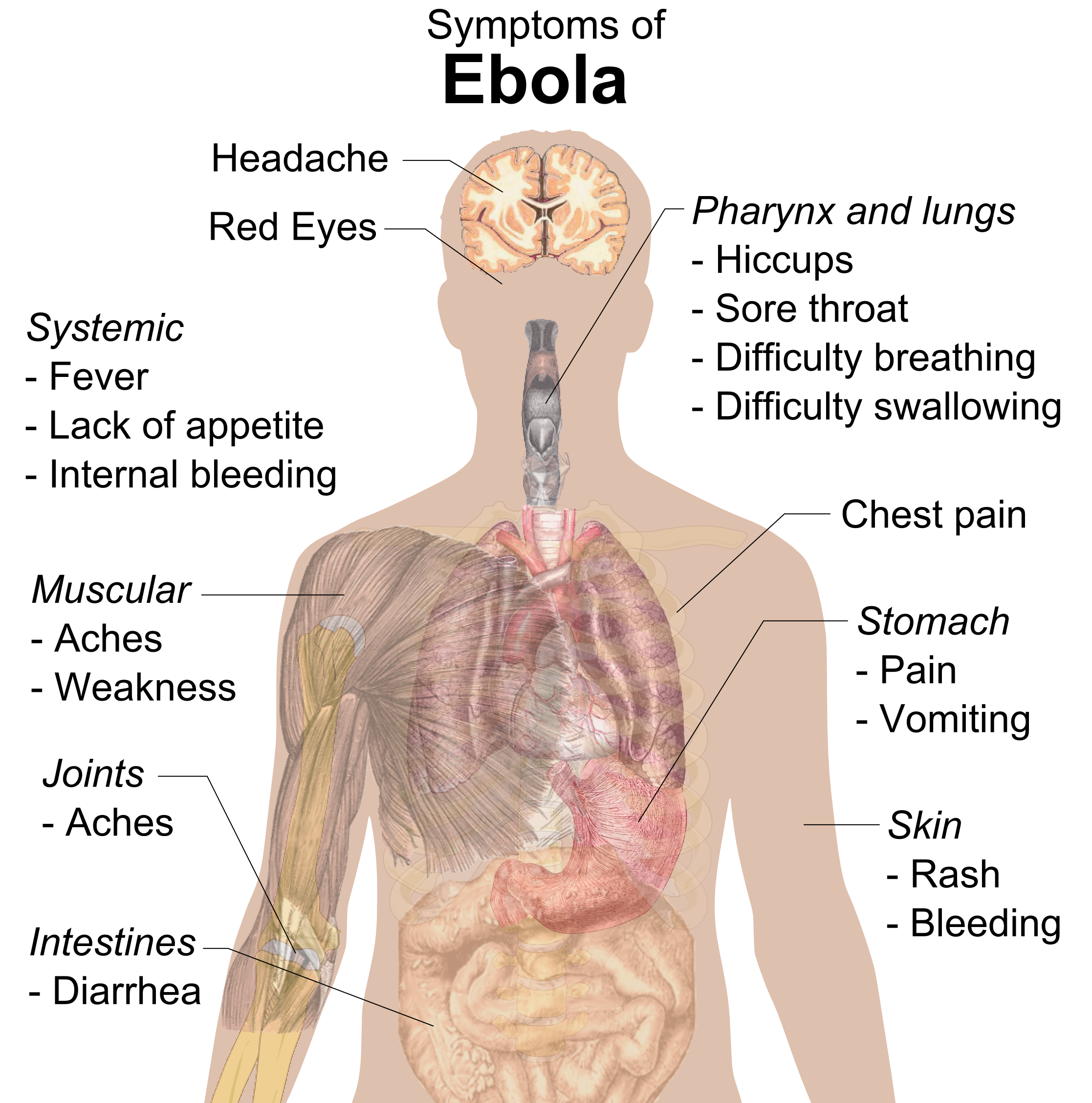
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, Myalgia, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleeding, bleed both internal bleeding, internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to hypovolemic shock, shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between 6 and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start.Ebola in Uganda: An Ebola vaccine was approved by the US FDA in December 2019. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 Democratic Republic Of The Congo Ebola Virus Outbreak
On 11 May 2017, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was identified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as having one Ebola-related death. As of 8 June 2017, there were five confirmed cases and three probable cases. Of these, four survived and four died. The affected areas of the DRC are Mabongo (one confirmed), Ngayi (one probable), and Nambwa (four confirmed and two probable) in Likati health zone. According to the WHO, "Modelling suggests the risk of further cases is currently low but not negligible.... As of ... June 83% of simulated scenarios predict no further cases in the next 30 days." According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, "Ebola ... is a rare and deadly disease caused by infection with one of the Ebola virus species. Ebola can cause disease in humans and nonhuman primates (monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees)." Ebola was first identified in 1976 near the Ebola River in the DRC. More than 11,300 people died in the 2013 to 2016 E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut National Pour La Recherche Biomedicale
The Institut National de la Recherche Biomédicale (INRB) is the national medical research organization of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The responsible ministry is the Ministry of Scientific Research and Technology. The National Biomedical Research Institute (INRB) was founded in 1984, it is a 70,000 m² establishment. It has been a collaborating center of the World Health Organization since 2018, headed by Professor Jean-Jacques Muyembe-Tamfum, MD, Ph., Which serves as a national biomedical research laboratory for the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) ). It is a multidisciplinary institute which collectively has hundreds of years of experience both in the identification, treatment and prevention of diseases in the DRC. Its foundations are the performance of medical and biological analyzes, applied and translational research, the surveillance of communicable diseases and the promotion of professional growth and development. The INRB has continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
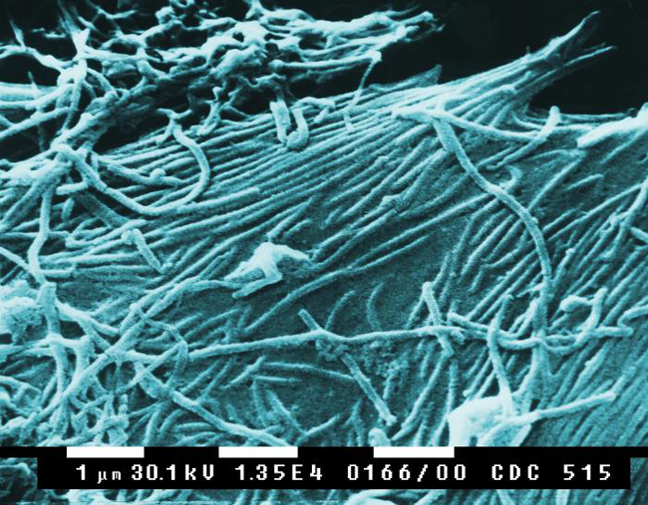
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBOV
''Orthoebolavirus zairense'' or Zaire ebolavirus, more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the Western African Ebola virus epidemic, 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was List of Ebola outbreaks, first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |