|
RU-58841
__NOTOC__ RU-58841, also known as PSK-3841 or HMR-3841, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which was initially developed in the 1980s by Roussel Uclaf, the French pharmaceutical company from which it received its name. It was formerly under investigation by ProStrakan (previously ProSkelia and Strakan) for potential use as a topical treatment for androgen-dependent conditions including acne, pattern hair loss, and excessive hair growth. The compound is similar in structure to the NSAA RU-58642 but contains a different side-chain. These compounds are similar in chemical structure to nilutamide, which is related to flutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide, all of which are NSAAs similarly. RU-58841 can be synthesized either by building the hydantoin moiety or by aryl coupling to 5,5-dimethylhydantoin. RU-58841 produces cyanonilutamide (RU-56279) and RU-59416 as metabolites in animals. Cyanonilutamide has relatively low affinity for the androgen receptor but shows significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Antiandrogen
A nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) is an antiandrogen with a nonsteroidal chemical structure. They are typically selective and full or silent antagonists of the androgen receptor (AR) and act by directly blocking the effects of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). NSAAs are used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions in men and women. They are the converse of steroidal antiandrogens (SAAs), which are antiandrogens that are steroids and are structurally related to testosterone. Medical uses NSAAs are used in clinical medicine for the following indications: * Prostate cancer in men * Androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions like acne, hirsutism, seborrhea, and pattern hair loss (androgenic alopecia) in women * Hyperandrogenism, such as due to polycystic ovary syndrome or congenital adrenal hyperplasia, in women * As a component of hormone therapy for transgender women * Precocious puberty in boys * Priapism in men Available forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU-59063
RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research found that it actually possesses dose-dependent androgenic activity, albeit with lower efficacy than dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The drug is an ''N''-substituent, substituted aryl group, arylthio-, thiohydantoin and was derived from the Nonsteroidal antiandrogen#First-generation, first-generation nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) nilutamide. The Nonsteroidal antiandrogen#Second-generation, second-generation NSAAs enzalutamide, RD-162, and apalutamide were derived from RU-59063. RU-59063 has a high affinity (pharmacology), affinity for the human androgen receptor (AR) (Ki = 2.2 nM; Ka = 5.4 nM) and 1,000-fold binding selectivity, selectivity for the AR over other nuclear receptor, nuclear steroid hormone receptors, including the , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU-57073
RU-57073 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. It shows 163% of the affinity of testosterone for the androgen receptor and negligible affinity for other steroid hormone receptors. See also * Cyanonilutamide * Nilutamide * RU-56187 * RU-58642 * RU-58841 * RU-59063 RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research f ... References Abandoned drugs Primary alcohols Ketones Imidazolines Nitriles Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Organosulfur compounds Trifluoromethyl compounds {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU-58642
RU-58642 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) derived from nilutamide with very high affinity and selectivity for the androgen receptor (AR), which made it among the most potent and efficacious antiandrogens known at the time of its discovery. It was investigated for topical application for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia (male-pattern baldness), but development did not proceed past initial trial stages, and it is now only used for scientific research into the AR. See also * Cyanonilutamide * RU-56187 * RU-57073 * RU-58841 * RU-59063 RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research f ... References Abandoned drugs Hydantoins Nitriles Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Trifluoromethyl compounds {{dermatologic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU-56187
RU-56187 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. It shows 92% of the affinity of testosterone for the androgen receptor and negligible affinity for other steroid hormone receptors. The medication is a silent antagonist of the androgen receptor. RU-56187 is 3- to 10-fold more potent as an antiandrogen than bicalutamide or nilutamide in animals. Both RU-56187 and RU-58841 appear to be prodrugs of cyanonilutamide (RU-56279) ''in vivo'' in animals. See also * RU-57073 * RU-58642 * RU-59063 RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research f ... References Abandoned drugs Imidazolines Ketones Nitriles Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Organosulfur compounds Prodrugs Trifluoromethyl compounds {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanonilutamide
Cyanonilutamide (developmental code name RU-56279) is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. Both RU-56187 and RU-58841 appear to be prodrugs of cyanonilutamide ''in vivo'' in animals. It has relatively low affinity for the androgen receptor but nonetheless shows significant antiandrogenic activity in animals. See also * 5''N''-Bicalutamide * Nilutamide * RU-56187 * RU-58642 * RU-59063 RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research f ... References Abandoned drugs Human drug metabolites Imidazolines Nitriles Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Trifluoromethyl compounds {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the androgen receptor (AR) and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. They can be thought of as the functional opposites of AR agonists, for instance androgens and anabolic steroids (AAS) like testosterone, DHT, and nandrolone and selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) like enobosarm. Antiandrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiprogestogens. Antiandrogens are used to treat an assortment of androgen-dependent conditions. In men, antiandrogens are used in the treatment of prostate cancer, enlarged prostate, scalp hair loss, overly high sex drive, unusual and problematic sexual urges, and early puberty. In women, antiandrogens are used to treat acne, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanonilutamide
Cyanonilutamide (developmental code name RU-56279) is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which was never marketed. Both RU-56187 and RU-58841 appear to be prodrugs of cyanonilutamide ''in vivo'' in animals. It has relatively low affinity for the androgen receptor but nonetheless shows significant antiandrogenic activity in animals. See also * 5''N''-Bicalutamide * Nilutamide * RU-56187 * RU-58642 * RU-59063 RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potency (pharmacology), potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research f ... References Abandoned drugs Human drug metabolites Imidazolines Nitriles Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Trifluoromethyl compounds {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
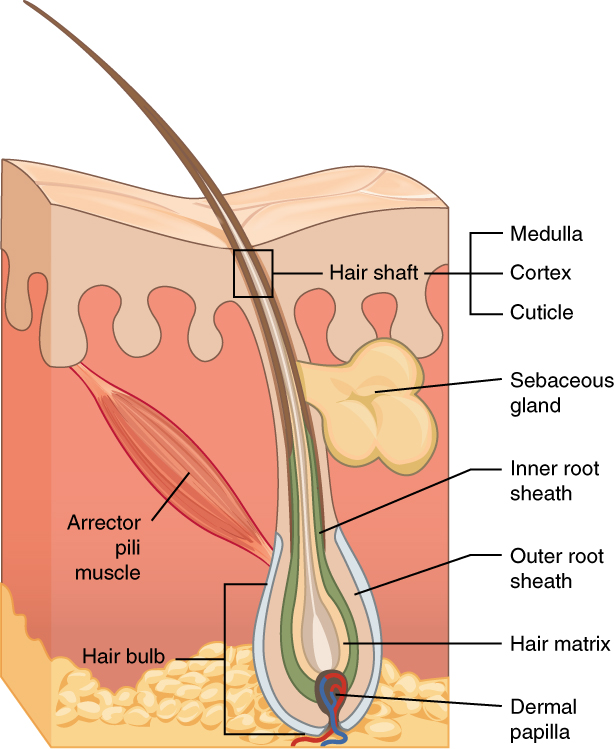
Hair Loss Medications
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, gender, or religion. Overview Meaning The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
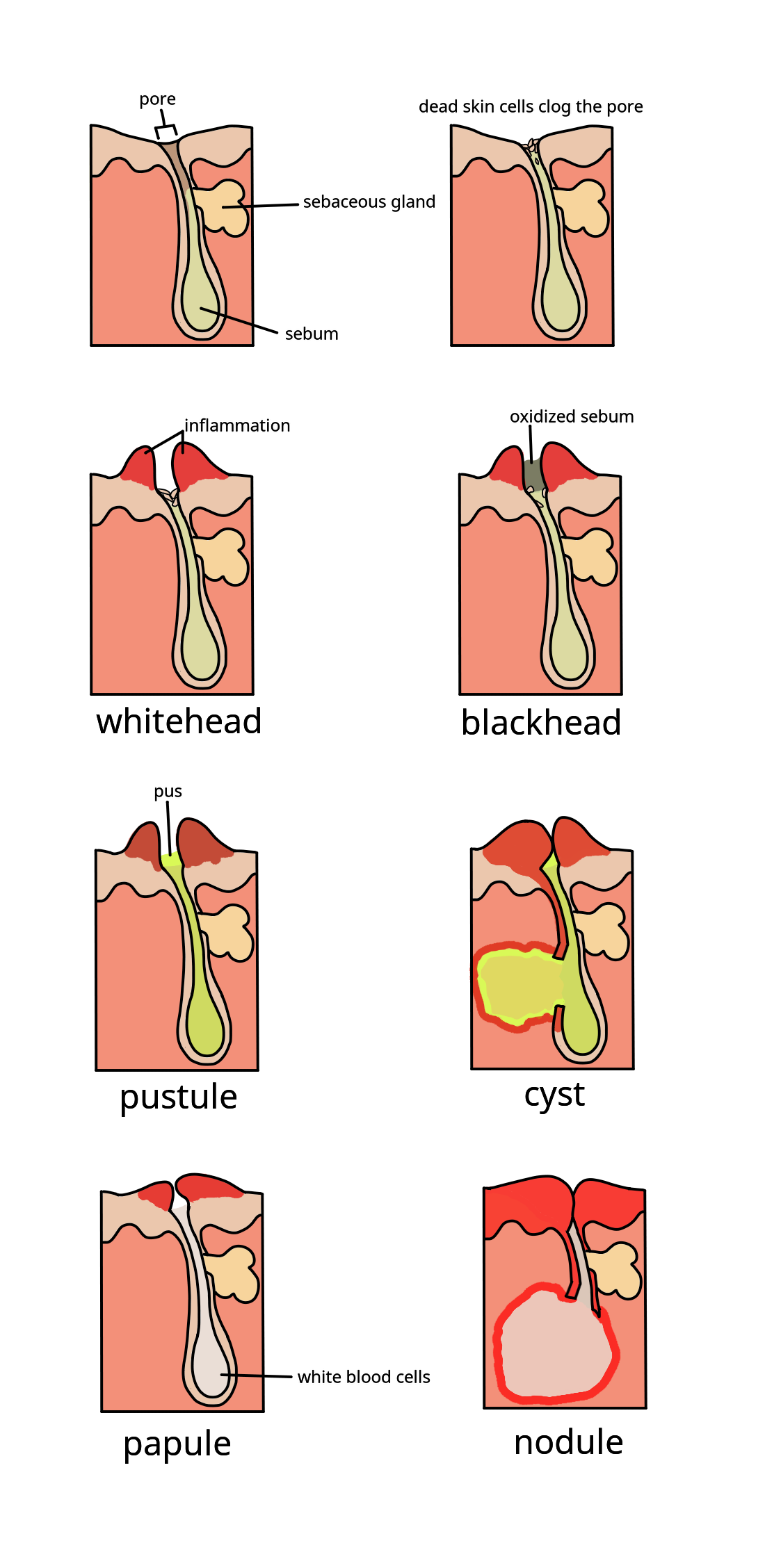
Anti-acne Preparations
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight are associated with acne. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium ''Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Alcohols
A primary alcohol is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol in which the hydroxy group is bonded to a primary carbon atom. It can also be defined as a molecule containing a “–CH2OH” group. In contrast, a secondary alcohol has a formula “–CHROH” and a tertiary alcohol has a formula “–CR2OH”, where “R” indicates a carbon-containing group. Examples of primary alcohols include ethanol, 1-propanol, and n-Butanol, 1-butanol. Methanol is also generally regarded as a primary alcohol, including by the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica. See also * Alcohol (chemistry), Alcohol (especially Nomenclature section for discussion on Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.) * Oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids References Primary alcohols, {{organic-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |