|
RGS13
Regulator of G-protein signaling 13 (RGS13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RGS13'' gene. RGS13 is a member of R4 subfamily of the Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) protein family, whose members have only short peptide sequences flanking the RGS domain. RGS13 suppresses the immunoglobulin E- mediated allergic responses. RGS family members share similarity with '' S. cerevisiae'' SST2 and ''C. elegans'' egl-10 proteins, which contain a characteristic conserved RGS domain. RGS proteins accelerate GTPase activity of G protein alpha-subunits, thereby driving G protein into their inactive GDP-bound form, thus negatively regulating G protein signaling. RGS proteins have been implicated in the fine tuning of a variety of cellular events in response to G protein-coupled receptor activation. The biological function of this gene, however, is unknown. Two transcript variants encoding the same isoform A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulator Of G Protein Signaling
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) are protein structural domains or the proteins that contain these domains, that function to activate the GTPase activity of heterotrimeric G-protein G alpha subunit, α-subunits. RGS proteins are multi-functional, GTPase-accelerating proteins that promote GTP hydrolysis by the α-subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins, thereby inactivating the G protein and rapidly switching off G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathways. Upon activation by receptors, G proteins exchange GDP for GTP, are released from the receptor, and dissociate into a free, active GTP-bound α-subunit and G beta-gamma complex, βγ-dimer, both of which activate downstream effectors. The response is terminated upon GTP hydrolysis by the α-subunit (), which can then re-bind the βγ-dimer ( ) and the receptor. RGS proteins markedly reduce the lifespan of GTP-bound α-subunits by stabilising the G protein transition state. Whereas receptors stimulate GTP binding, RGS protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. Sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence) is one of the most common indicators of homology, or common evolutionary ancestry. Some frameworks for evaluating the significance of similarity between sequences use sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families. Families are sometimes grouped together into larger clades called superfamilies based on st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Primary Structure
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences. Formation Biological Amino acids are polymerised via peptide bonds to form a long backbone, with the different amino acid side chains protruding along it. In biological systems, proteins are produced during translation by a cell's ribosomes. Some organisms can also make short peptides by non-ribosomal peptide synthesis, which often use amino acids other than the encoded 22, and may be cyclised, modified and cross-linked. Chemical Peptides can be synthesised chemically via a range of laboratory methods. Chemical methods typically synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
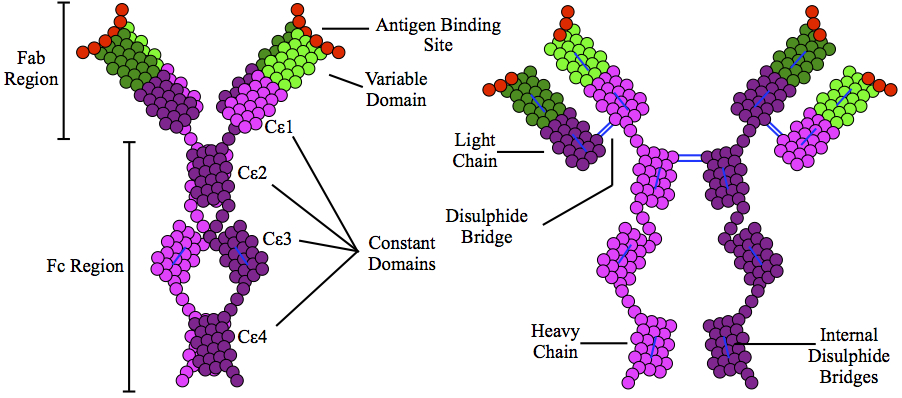
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including '' Schistosoma mansoni'', ''Trichinella spiralis'', and ''Fasciola hepatica''. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as ''Plasmodium falciparum''. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms. IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity, which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, and specific types of chronic urticaria and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergic Response
An allergic response is a hypersensitive immune reaction to a substance that normally is harmless or would not cause an immune response in everyone. An allergic response may cause harmful symptoms such as itching or inflammation or tissue injury. Mechanism Allergies are an abnormal immune reaction. The human immune system is designed to protect the body from potential harm and in people who have allergies the immune system will react to allergens (substances that trigger an immune response). The immune system will produce immunoglobulin E, IgE, antibodies for each allergen. The antibodies will cause cells in the body to produce histamine. This histamine will act on different areas of the body (eyes, throat, nose, gastrointestinal tract, skin or lungs) to produce symptoms of an allergic reaction. The allergic response is not limited to a certain amount of exposure. If the body is exposed to the allergen multiple times the immune system will react every time the allergen is pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a Hybrid word, blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Émile Maupas, Maupas initially named it ''Rhabditidae, Rhabditides elegans.'' Günther Osche, Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Ellsworth Dougherty, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicule (nematode), spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular biology, molecular and developmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein protein complex, complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''G alpha subunit, alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) protein subunit, subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable Protein dimer, dimeric complex re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |