|
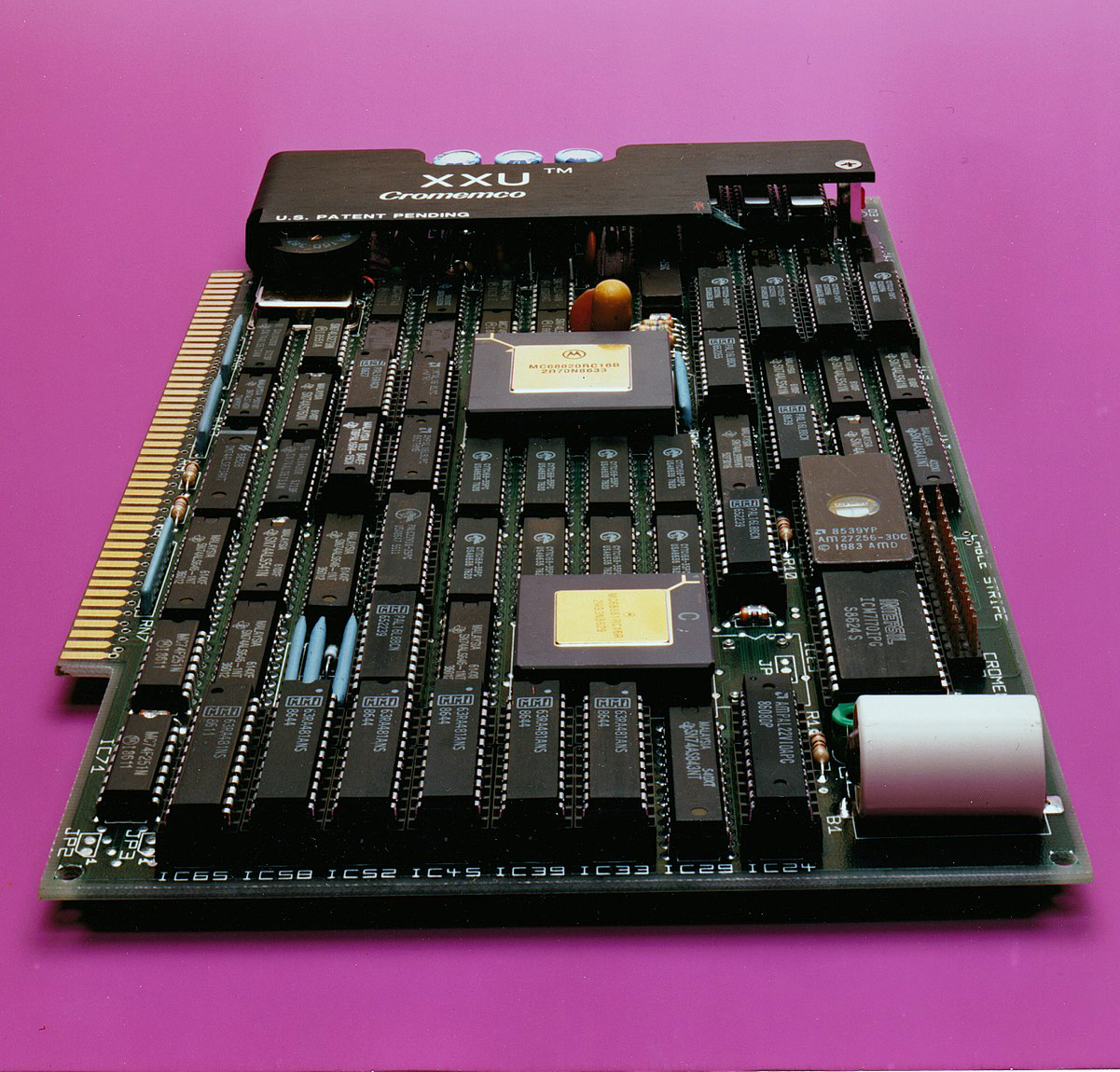
RGS-008
The RGS-008, also written as the RGS-008A, is an early microcomputer released as a kit by RGS Electronics of Santa Clara, California, in 1974. Based on the Intel 8008 microprocessor, the RGS-008 was among the first wave of microcomputers released to the public in the early-to-mid-1970s. It holds the distinction of being the first computer system reviewed in the charter issue of ''Byte'', a highly influential computer magazine. Specifications The RGS-008, as shipped, comprises six printed circuit boards and all the necessary components (including ICs, Molex connectors, switches, and LEDs) to build up the CPU board, the memory board, the backplane, the front panel, and the power supply. The CPU board sports an Intel 8008 microprocessor, while the stock RAM board features 1 KB worth of RAM (later increased to 4 KB of RAM stock). The backplane's bus is based on double-sided, 72-pin edge connectors; it can theoretically accommodate a total of 256 peripheral devices. Develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backplane
A backplane or backplane system is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications. A backplane is generally differentiated from a motherboard by the lack of on-board processing and storage elements. A backplane uses plug-in cards for storage and processing. Usage Early microcomputer systems like the Altair 8800 used a backplane for the processor and expansion cards. Backplanes are normally used in preference to cables because of their greater reliability. In a cabled system, the cables need to be flexed every time that a card is added or removed from the system; this flexing eventually cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
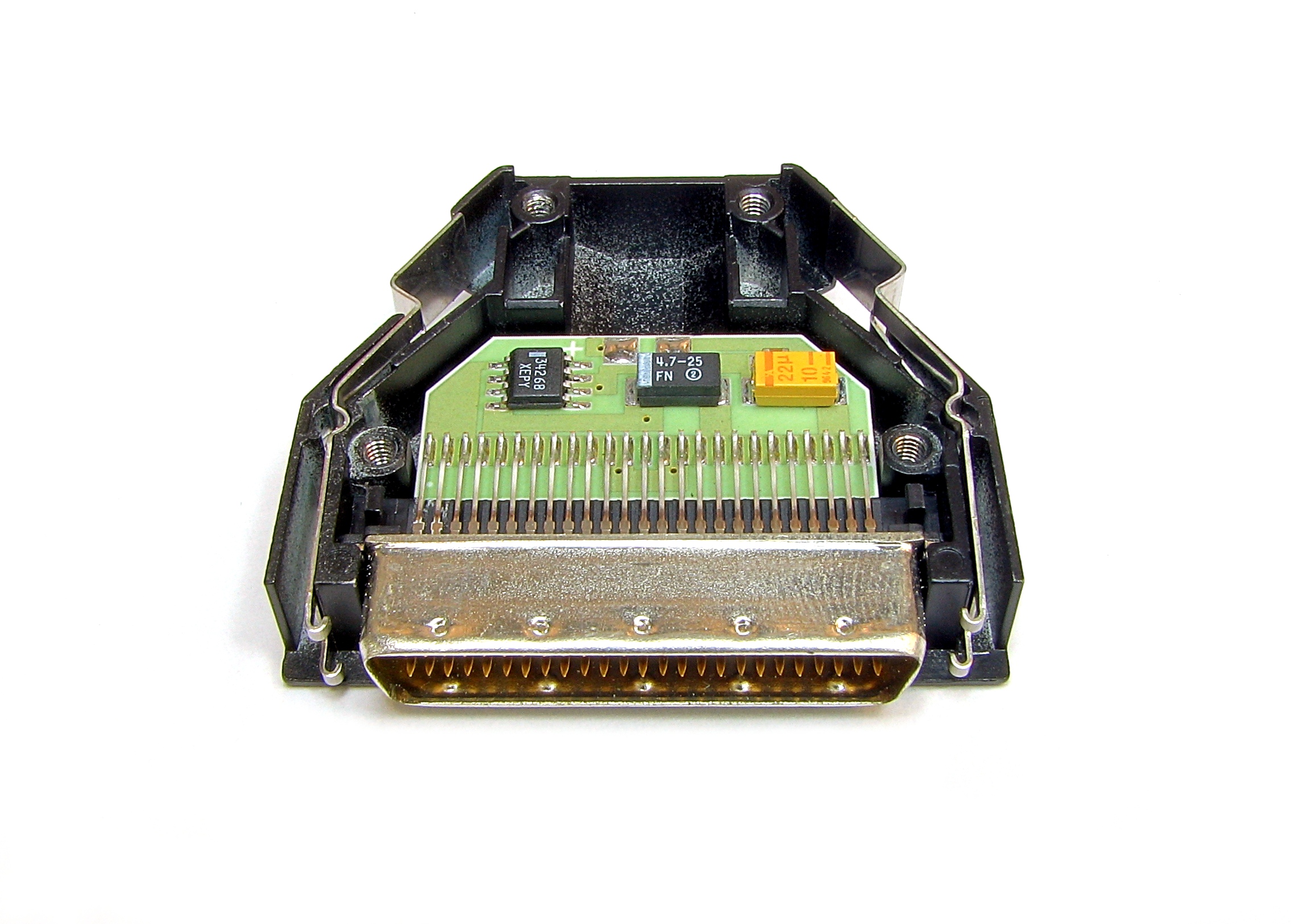
Edge Connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board (PCB) consisting of signal trace, traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching jack (connector), socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector (the male connector is formed out of the edge of the PCB), and they also tend to be fairly robust and durable. They are commonly used in computers for expansion slots for peripheral cards, such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI Express, and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP cards. Socket design Edge connector sockets consist of a plastic "box" open on one side, with pins on one or both sides of the longer edges, sprung to push into the middle of the open center. Connectors are often Key (engineering), keyed to ensure the correct Electrical polarity, polarity, and may contain bumps or notches both for polarity and to ensure that the wrong type of device is not inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain View, California
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States, part of the San Francisco Bay Area. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, the population was 82,376 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Mountain View was integral to the early history and growth of Silicon Valley, and is the location of many high technology companies. In 1956, William Shockley established Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory in Mountain View, the first company to develop silicon semiconductor devices in Silicon Valley. Mountain View houses the headquarters of many of the world's largest technology companies, including Google and Alphabet Inc., Unicode Consortium, Intuit, Applied Intuition, NASA Ames Research Center, and former or existing headquarters for NortonLifeLock, Symantec, 23andMe, LinkedIn, Samsung, Quora and Synopsys. History The fertile land between the Santa Cruz Mountains and the shores of the southern San Francisco Bay once supported multiple village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a computer museum in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the Information Age, and explores the Digital Revolution, computing revolution and its impact on society. History The museum's origins date to 1968 when Gordon Bell began a quest for a historical collection and, at that same time, others were looking to preserve the Whirlwind (computer), Whirlwind computer. The resulting ''Museum Project'' had its first exhibit in 1975, located in a converted coat closet in a Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC lobby. In 1978, the museum, now ''The Digital Computer Museum'' (TDCM), moved to a larger DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts and opened to the public in September 1979. Maurice Wilkes presented the first lecture at TDCM in 1979 – the presentation of such lectures has continued to the present time. TDCM incorporated as ''The Computer Museum, Boston, The Computer Museum'' (TCM) in 1982. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blinkenlights
In computer jargon, blinkenlights are diagnostic lights on front panels of old mainframe computers. More recently the term applies to status lights of modern network hardware (modems, network hubs, etc.). Blinkenlights disappeared from more recent computers for a number of reasons, the most important being the fact that with faster CPUs a human can no longer interpret the processes in the computer on the fly. Though more sophisticated UI mechanisms have since been developed, blinkenlights may still be present as additional status indicators and familiar skeuomorphs. Etymology The term has its origins in hacker humor and is taken from a famous (often blackletter-Gothic) mock warning sign written in a mangled form of German. Variants of the sign were relatively common in computer rooms in English-speaking countries from the early 1960s. One version read: Some versions of the sign end with the word ''blinkenlights''. The sign dates back as far as 1955 at IBM, and a copy wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDN (magazine)
''EDN'' is an electronics industry website and formerly a magazine owned by AspenCore Media, an Arrow Electronics company. The editor-in-chief is Majeed Ahmad. ''EDN'' was published monthly until, in April 2013, EDN announced that the print edition would cease publication after the June 2013 issue. History it was the first issue of ''Electrical Design News'', the original name, was published in May 1956 by Rogers Corporation of Englewood, Colorado. In January 1961, Cahners Publishing Company, Inc., of Boston, acquired Rogers Publishing Company. In February 1966, Cahners sold 40% of its company to International Publishing Company in London London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ... In 1970, the Reed Group merged with International Publishing Corporation and changed its name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer Revolution
The history of the personal computer as a mass-market consumer electronic device began with the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. A personal computer is one intended for interactive individual use, as opposed to a mainframe computer where the end user's requests are filtered through operating staff, or a time-sharing system in which one large processor is shared by many individuals. After the development of the microprocessor, individual personal computers were low enough in cost that they eventually became affordable consumer goods. Early personal computers – generally called microcomputers – were sold often in electronic kit form and in limited numbers, and were of interest mostly to hobbyists and technicians. Etymology There are several competing claims as to the origins of the term "personal computer". Yale Law School librarian Fred Shapiro notes an early published use of the phrase in a 1968 Hewlett-Packard advertisement for a programmable calculator, which they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons. Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground to protect users from electrical shock hazards. If internal insulation fails, dangerous voltages may appear on the exposed conductive parts. Connecting exposed conductive parts to a "ground" wire which provides a low-impedance path for current to flow back to the incoming neutral (which is also connected to ground, close to the point of entry) will allow circuit breakers (or RCDs) to interrupt power supply in the event of a fault. In electric power distribution systems, a protective earth (PE) conductor is an essential part of the safety provided by the earthing system. Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Termination
In electronics, electrical termination is the practice of ending a transmission line with a device that matches the characteristic impedance of the line. Termination prevents signals from Signal reflection, reflecting off the end of the transmission line. Reflections at the ends of unterminated transmission lines cause distortion, which can produce ambiguous digital signal levels and misoperation of digital systems. Reflections in analog signal systems cause such effects as ghosting (television), video ghosting, or Power margin, power loss in radio transmitter transmission lines. Transmission lines Signal termination often requires the installation of a terminator at the beginning and end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from each end, causing Interference (communication), interference, or power loss. The terminator is usually placed at the end of a transmission line or Daisy chain (electrical engineering), daisy chain Bus (computing), bus (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altair 8800
The Altair 8800 is a microcomputer introduced in 1974 by Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS) based on the Intel 8080 CPU. It was the first commercially successful personal computer. Interest in the Altair 8800 grew quickly after it was featured on the cover of the January 1975 issue of ''Popular Electronics''. It was sold by mail order through advertisements in ''Popular Electronics'', ''Radio-Electronics'', and in other hobbyist magazines. The Altair 8800 had no built-in screen or video output, so it would have to be connected to a serial terminal (such as a VT100-compatible terminal) to have any output. To connect it to a terminal, a serial interface card had to be installed. Alternatively, the Altair could be programmed using its front-panel switches. According to the personal computer pioneer Harry Garland, the Altair 8800 was the product that catalyzed the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. The computer bus designed for the Altair became a ''de facto'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-100 Bus
The S-100 bus or Altair bus, later standardized as IEEE 696-1983 ''(inactive-withdrawn)'', is an early computer bus designed in 1974 as a part of the Altair 8800. The bus was the first industry standard expansion bus for the microcomputer industry. computers, consisting of processor and peripheral cards, were produced by a number of manufacturers. The bus formed the basis for homebrew computers whose builders (e.g., the Homebrew Computer Club) implemented drivers for CP/M and MP/M. These microcomputers ran the gamut from hobbyist toy to small business workstation and were common in early home computers until the advent of the IBM PC. Architecture The bus is a passive backplane of 100-pin printed circuit board edge connectors wired in parallel. Circuit cards measuring serving the functions of CPU, memory, or I/O interface plugged into these connectors. The bus signal definitions closely follow those of an 8080 microprocessor system, since the Intel 8080 microproce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Godbout
Bill Godbout (October 2, 1939 – November 8, 2018) was an early computer pioneer and entrepreneur known for manufacturing and selling computer equipment, parts, and electronic kits in Silicon Valley, during the 1970s and 1980s. He and his company, Godbout Electronics (and later CompuPro and Viasyn), were very influential in the early years of the personal computer market. Together with George Morrow, he worked on the IEEE696 (withdrawn) better known as the very popular S-100 bus. He is featured in the book ''The Silicon Boys, 1999'' by David A. Kaplan about the pioneers of Silicon Valley. Early life He was born on October 2, 1939, in Providence, Rhode Island. Career After college, he went straight into a job at IBM, but found himself "involuntarily recalled" to active military duty in 1961 and subsequently spending most of the 1960s in the military, being discharged in 1968. Deciding not to return to a big company, although still holding IBM in esteem, he moved to the San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |