|
RD-253
The RD-253 () and its later variants, the RD-275 and RD-275M, are liquid-propellant rocket engines developed in the Soviet Union by Energomash. The engines are used on the first stage of the Proton launch vehicle and use an oxidizer-rich staged combustion cycle to power the turbopumps. The engine burns a hypergolic mixture of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) fuel with dinitrogen tetroxide () oxidizer, which are highly toxic, but storable at room temperature. History Development of the RD-253 started in 1961. Preliminary investigations and development of the engine and its further production was performed under the guidance of Valentin Glushko and finished in 1963. The RD-253 uses an oxidiser-rich staged combustion cycle. It was used for the first time in July 1965, when six engines powered the first stage of the Proton rocket. Development and production of RD-253 was a qualitative leap forward for rocketry of that time by achieving high levels of thrust, specific impuls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
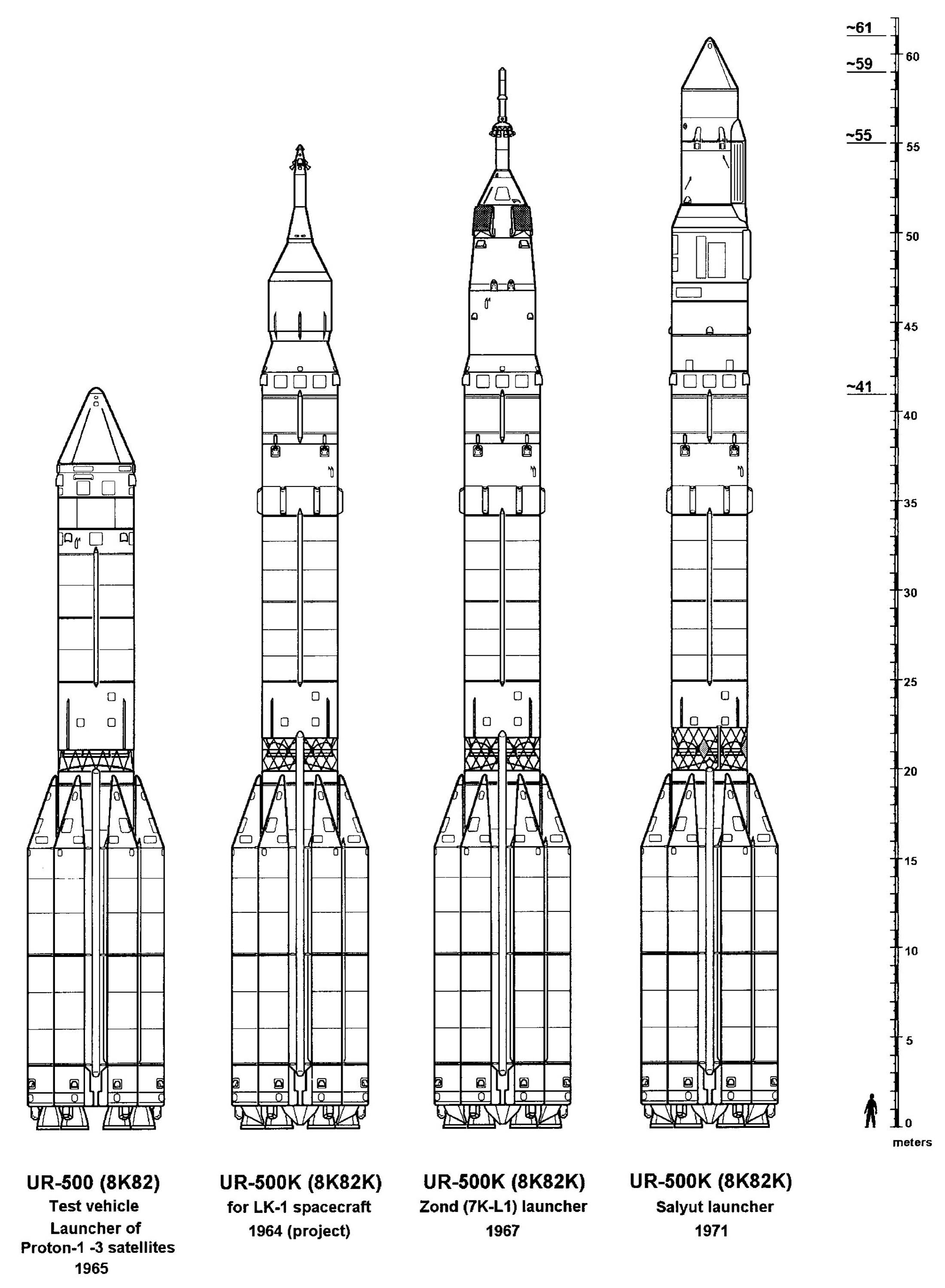
Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81/23, 81/24, 200/39 and 200/40 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The maiden flight on 10 March 1967 carried a Soyuz 7K-L1 as part of the Zond program. During the so-called Moon Race these Proton/Soyuz/Zond flights consisted of several uncrewed test flights of Soyuz spacecraft to highly elliptical or circumlunar orbits with the unrealized aim of landing Soviet cosmonauts on the Moon. It was retired from service in favour of the modernised Proton-M, making its 310th and final launch on 30 March 2012. Vehicle description The baseline Proton-K was a three-stage rocket. Thirty were launched in this configuration, with payloads including all of the Soviet Union's ''Salyut'' space stations, all Mir modules with the exception of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-PM
OJSC Proton-PM ( Russian: ) is a Russian engine and heavy machinery manufacturing plant. It is located in the city of Perm, in the Perm Krai, on the bank of the Kama River. It started in 1958 as the specialized branch of Plant No. 19 named after I. V. Stalin for the manufacturing of the RD-214 rocket engine. In 1964 it was given made a separate entity then known as Second Production. In the later years, it has branched intro producing gas turbine power plants. Products Current engines Engines in current production at the plant: * RD-276 the latest version of the RD-275. * RD-191 a liquid rocket engine, burning kerosene and LOX that powers the Angara (rocket) family of launch vehicles. Former engines Engines that are no longer produced at the plant. * RD-214 a liquid rocket engine, burning AK-27I (a mixture of 73% Nitric acid + 27% N2O4 + iodine passivant and TM-185 (a kerosene and gasoline mix), that powered the R-12 and Kosmos-2. * RD-253 a liquid rocket engine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPO Energomash
NPO Energomash "V. P. Glushko" is a major Russian rocket engine manufacturer. The company primarily develops and produces Liquid rocket engine, liquid propellant rocket engines. Energomash originates from the OKB, Soviet design bureau OKB-456, which was founded in 1946. NPO Energomash acquired its current name on May 15, 1991, in honor of its former chief designer Valentin Glushko. Energomash is noted for its long history of large scale liquid oxygen, LOX/Kerosene engine development. Notable examples are the RD-107/RD-108 engines used on the R-7 Semyorka, R-7, Molniya (rocket), Molniya and Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rocket families, and the RD-170, RD-171 and RD-180 engines used on the Energia (rocket), Energia, Zenit (rocket), Zenit and Atlas V launch vehicles. , the company remained largely owned by the Government of Russia, federal government of Russia, but RSC Energia owned approximately 14% of the total shares. , NPO Energomash employed approximately 5500 workers at its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staged Combustion Cycle (rocket)
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is thus combusted in stages. The main advantage relative to other rocket engine power cycles is high fuel efficiency, measured through specific impulse, while its main disadvantage is engineering complexity. Typically, propellant flows through two kinds of combustion chambers; the first called and the second called . In the preburner, a small portion of propellant, usually fuel-rich, is partly combusted under non- stoichiometric conditions, increasing the volume of flow driving the turbopumps that feed the engine with propellant. The gas is then injected into the main combustion chamber and combusted completely with the other propellant to produce thrust. Tradeoffs The main advantage is fuel efficiency due to all of the propellant flowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-M
The Proton-M, (Протон-М) GRAU index 8K82M or , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Russian heavy-lift launch vehicle derived from the Soviet Union, Soviet-developed Proton (rocket family), Proton. It is built by Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center, Khrunichev, and launched from sites Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 81, 81/24 and Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 200, 200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Commercial launches are marketed by International Launch Services (ILS), and generally use Site 200/39. The first Proton-M launch occurred on 7 April 2001. Proton flew its most recent mission on 12 March 2023. As of August 2020, a number of Roscosmos and other Russian government missions remain on Proton launch manifest. Vehicle description The Proton-M launch vehicle consists of three stages; all of them powered by liquid rocket engines using the hypergolic propellant combination of dinitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer, and unsymmetrical dimethylh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
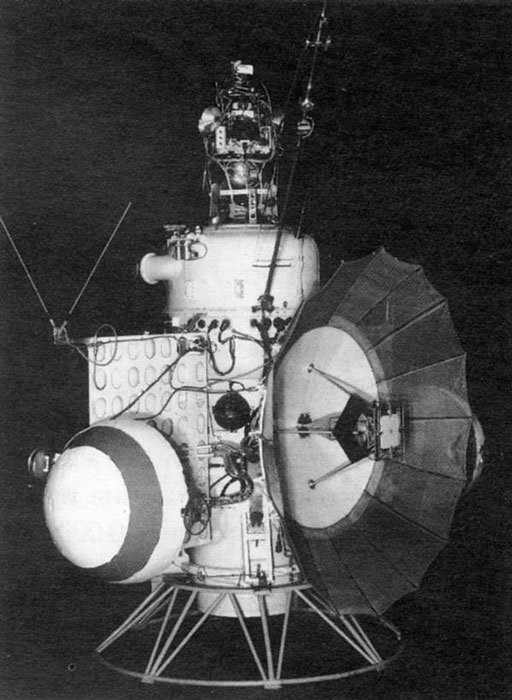
Mars Probe Program
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to exploration of Mars, explore Mars, and included planetary flyby, flyby probes, Lander (spacecraft), landers and orbiters. Early Mars spacecraft were small, and launched by Molniya (rocket), Molniya rockets. Starting with two failures in 1969, the heavier Proton-K rocket was used to launch larger 5 tonne spacecraft, consisting of an orbiter and a lander to Mars. The orbiter bus design was likely somewhat rushed into service and immature, considering that it performed very unreliably in the Venera variant after 1975. This reliability problem was common to much Soviet space hardware from the late 1960s and early 1970s and was largely corrected with a deliberate policy, implemented in the mid-1970s, of consolidating (or "debugging") existing designs rather than introducing new ones. The names of the "Mars" missions do not need to be translated, as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Mission
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflights operate either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The first spaceflights began in the 1950s with the launches of the Soviet Sputnik satellites and American Explorer and Vanguard missions. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs. Other current spaceflight are conducted to the International Space Station and to China's Tiangong Space Station. Spaceflights include the launches of Earth observation and telecommunications satellites, interplanetary missions, the rendezvouses and dockings with space stations, and crewed spaceflights on scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna Programme
The Luna programme (from the Russian word "Moon, Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called ''Lunik'' by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. The programme accomplished many Timeline of space exploration, firsts in space exploration, including Luna 1, first flyby of the Moon, Luna 2, first impact of the Moon and Luna 3, first photos of the far side of the Moon. Each mission was designed as either an orbiter or Lander (spacecraft), lander. They also performed many experiments, studying the Moon's chemical composition, gravity, temperature, and radiation. Twenty-four spacecraft were formally given the Luna designation, although more were launched. Those that failed to reach orbit were not publicly acknowledged at the time, and not assigned a Luna number. Those that failed in low Earth orbit were usually given Kosmos (satellite), Cosmos designations. The estimated cost of the Luna programme in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
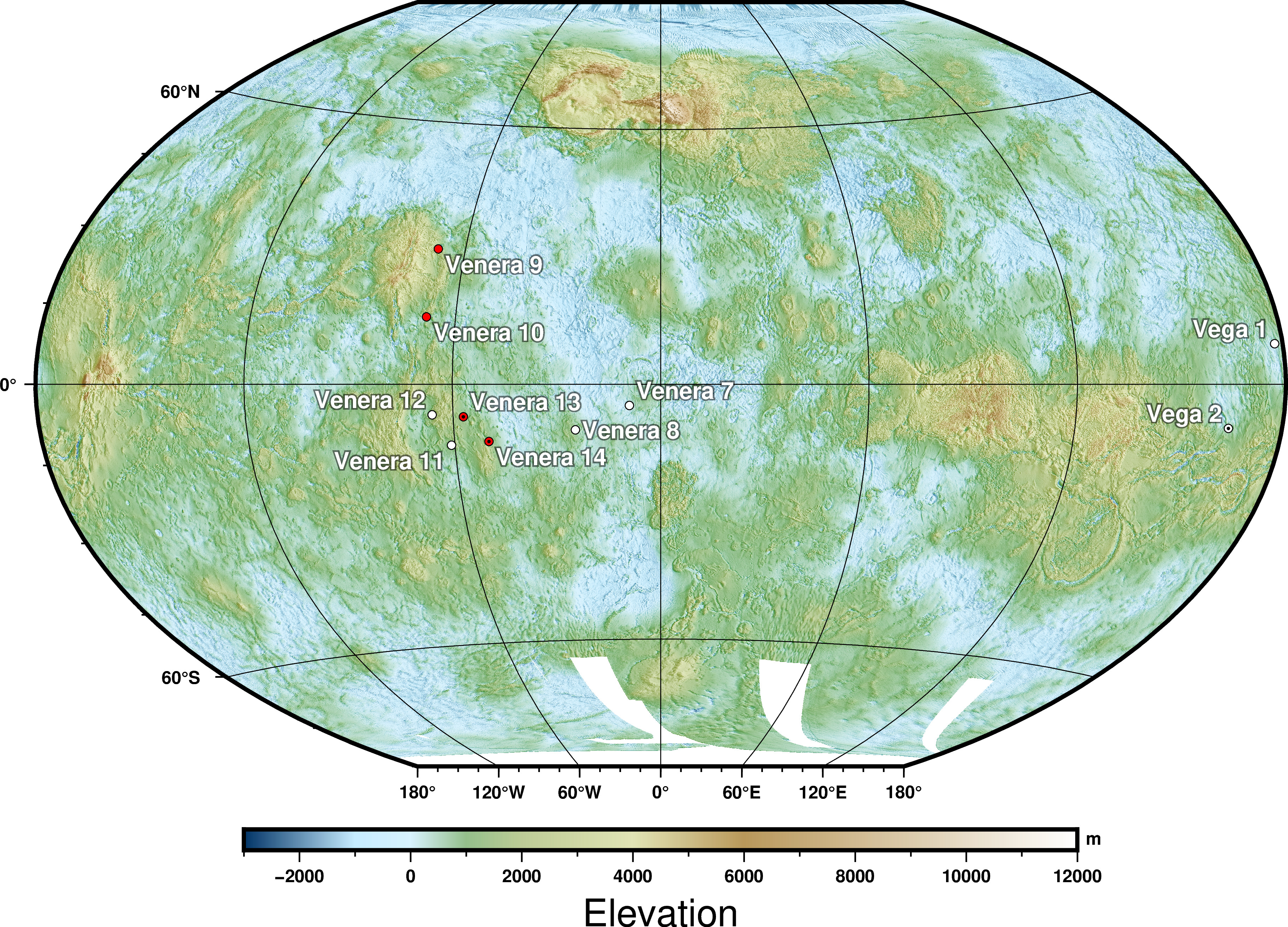
Venera
The Venera (, 'Venus') program was a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere, including the two Venera-Halley probes. Ten of those successfully landed on the surface of the planet. Due to the extreme conditions, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet ( Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet ( Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface ( Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet ( Venera 13 on 30 October 1981), and the first to perform high-resolution radar mapping scans ( Venera 15 on 2 June 1983). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Air Show
The Paris Air Show (, ''Salon du Bourget'') is a trade fair and air show held in odd years at Paris–Le Bourget Airport in France. Organized by the French aerospace industry's primary representative body, the ''Groupement des industries françaises aéronautiques et spatiales'' (GIFAS), it is the largest air show and aerospace-industry exhibition event in the world, measured by number of exhibitors and size of exhibit space, followed by UK's Farnborough Air Show, Dubai Air Show, and Singapore Airshow. First held in 1909, the Paris Air Show was held every odd year from 1949 to 2019, when the 53rd Air Show attracted 2,453 exhibitors from 49 countries and occupied more than 125,000 square meters. Organizers canceled the 2021 show due to the COVID pandemic. It resumed in 2023. It is a large trade fair, demonstrating military and civilian aircraft, and is attended by many military forces and the major aircraft manufacturers, often announcing major aircraft sales. It starts with four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Station
A space station (or orbital station) is a spacecraft which remains in orbit and hosts humans for extended periods of time. It therefore is an artificial satellite featuring habitation facilities. The purpose of maintaining a space station varies depending on the program. Most often space stations have been research stations, but they have also served military or commercial uses, such as hosting space tourists. Space stations have been hosting the only continuous presence of humans in space. The first space station was Salyut 1 (1971), hosting the first crew, of the ill-fated Soyuz 11. Consecutively space stations have been operated since Skylab (1973) and occupied since 1987 with the Salyut successor Mir. Uninterrupted human presence in orbital space through space stations have been sustained since the operational transition from the Mir to the International Space Station (ISS), with the latter's first occupation in 2000. Currently there are two fully operational space stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut Program
The ''Salyut'' programme (, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissance space stations over a period of 15 years, from 1971 to 1986. Two other ''Salyut'' launches failed. In one respect, ''Salyut'' had the space-race task of carrying out long-term research into the problems of living in space and a variety of astronomical, biological and Earth-resources experiments, and on the other hand, the USSR used this civilian programme as a cover for the highly secretive military ''Almaz'' stations, which flew under the ''Salyut'' designation. Salyut 1, ''Salyut'' 1, the first station in the program, became the world's first crewed space station. ''Salyut'' flights broke several spaceflight records, including several mission-duration records, and achieved the first orbital handover of a space station from one crew t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |