|
RAF Kinloss
Royal Air Force Kinloss, or more simply RAF Kinloss, is a former Royal Air Force station located near the village of Kinloss, on the Moray Firth in the north east of Scotland, UK. The RAF station opened on 1 April 1939 and served as a training establishment during the Second World War. After the war it was handed over to Coastal Command to monitor Soviet ships and submarines in the Norwegian Sea. Until 2010 it was the main base for the RAF's fleet of Hawker Siddeley Nimrod MR.2 maritime patrol aircraft. It was intended that the MR2 would be replaced by the Nimrod MRA.4, but the MRA4 was cancelled in the Strategic Defence and Security Review of October 2010. As a result, Kinloss became surplus to RAF requirements and regular flying operations ceased on 31 July 2011. In November 2011, the Ministry of Defence and 12 (Air Support) Engineer Group of the British Army announced that 930 personnel from 39 Engineer Regiment (Air Support) would move from Waterbeach Barracks, near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinloss, Scotland
Kinloss ( Gaelic: ''Cinn Lois'') is a village in Moray, Scotland. It is located near the shore of Findhorn Bay, around 3 miles (5 km) from Findhorn and 2.5 miles (4 km) from Forres. Northeast of the village is Kinloss Barracks, formerly RAF Kinloss which opened on 1 April 1939. It is believed that 1,000 aircraft were dismantled at Kinloss, after the end of the Second World War. Investigations are on for possible radioactive contamination in RAF Kinloss. The Cistercian Kinloss Abbey was created in 1150 by King David. Under abbot Robert Reid the abbey became a centre of academic excellence in the 1530s. It now lies almost completely ruined. The abbey and the town were part of the feudal Barony of Muirton. Climate Like the rest of the plains of Scotland, Kinloss has an oceanic climate (Köppen: ''Cfb''). It is one of the mildest climates in this latitude, being milder than Angoon, Alaska for almost identical latitudinal coordinates, both influenced by the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea (; ; ) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea. Unlike many other seas, most of the bottom of the Norwegian Sea is not part of a continental shelf and therefore lies at a great depth of about two kilometres on average. Rich deposits of oil and natural gas are found under the sea bottom and are being explored commercially, in the areas with sea depths of up to about one kilometre. The coastal zones are rich in fish that visit the Norwegian Sea from the North Atlantic or Barents Sea (cod) for spawning. The warm North Atlantic Current ensures relatively stable and high water temperatures, so that unlike the Arctic seas, the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Parallel (latitude), Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''Normal (geometry), normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the equatorial plane, plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Peck
Group Captain Arthur Hicks Peck, (25 April 1889 – 14 February 1975) was an officer of the Royal Air Force, who was a flying ace credited with eight aerial victories in the First World War. Family background and education Arthur Peck was born in Darjeeling, India, the only son of Lieutenant Colonel Francis Samuel Peck (1858–1908) of Bristol. His father was a surgeon in the Indian Medical Service, who died at sea aboard while returning to England. Peck attended Clifton College, Bristol, from 1903 to 1906, and was admitted to Christ's College, Cambridge, before spending the years 1908 to 1914 in Australia. First World War Peck was commissioned as a temporary (wartime only) second lieutenant in the British Army on 7 December 1914, and served in the Devonshire Regiment in France and Salonika. He eventually joined the Royal Flying Corps, being transferred to the General List and appointed a flying officer on 4 October 1916. He was appointed a flight commander with the temporar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mowlem
Mowlem was one of the largest construction and civil engineering companies in the United Kingdom. The company was established as ''John Mowlem and Co.'' by John Mowlem and initially worked on behalf of various local authorities across London. It expanded throughout the nineteenth century, taking on increasingly prestigious undertakings. The company received the first of several Royal Warrants in 1902. One year later, John Mowlem and Co. was briefly incorporated before being reorganised as a partnership once again; the business was long operated by successive generations of the Mowlem and Burt families, including George Burt, and Sir John Mowlem Burt. During 1924, the company went public on the London Stock Exchange. Throughout the Second World War, the company worked on numerous contracts issued by the British government, including the construction of the Mulberry harbour units. After the end of the conflict, it continued to developed its network of regional contracting b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compulsory Purchase Order
A compulsory purchase order (CPO; , ) is a legal function in the United Kingdom and Ireland that allows certain bodies to obtain land or property without the consent of the owner. It may be enforced if a proposed development is considered one for public betterment; for example, when building motorways where a landowner does not want to sell. Similarly, if town councils wish to develop a town centre, they may issue compulsory purchase orders. CPOs can also be used to acquire historic buildings in order to preserve them from neglect. Compensation rights usually include the value of the property, costs of acquiring and moving to a new property, and sometimes additional payments. Costs of professional advice regarding compensation are usually reimbursed by the authority, so that people affected by a compulsory purchase order can seek advice from a solicitor and a surveyor and expect to be reimbursed. Ireland In Ireland, CPOs became quite common in the early 21st century due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony Of Muirton
Baron of Muirton is a title of nobility in the Baronage of Scotland. The first known Crown charter was granted in 1532, to Robert Reid (bishop), Robert Reid, Abbot of Kinloss. In 2019, the current baron ascended to the title The M. Hon. Dr. Richard Bruce Culbert of Muirton, 32nd Baron of Muirton. Baronies originated during the Middle Ages and were lands held by barons in feu as "tenants in chief" of the monarch. The baron had the rights to the production of the land and was responsible to maintain law and order in the name of the king. He usually had to provide military forces in times of war, as well. Over time law enforcement and other powers were gradually stripped from barons. In Scotland, the Abolition of Feudal Tenure etc. (Scotland) Act 2000, Abolition of Feudal Tenures Act 2000 separated the title of baron from the land becoming a personal title and allowed it to be transferred as an incorporeal hereditament. Location The boundaries of the Barony have changed ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is the engineering arm of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Corps Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham, Kent, Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Gundulf of Rochester, Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Ensign
The Royal Air Force Ensign is the official flag that is used to represent the Royal Air Force. The ensign has a field of air force blue, with the United Kingdom's flag in the canton and the Royal Air Force's roundel in the middle of the fly. The RAF Ensign was introduced in 1921, after some opposition from senior members of the Royal Navy. Various countries' air force ensigns have been based on the RAF's ensign. Currently, it is flown from the flagstaff of every Royal Air Force station during daylight hours, and it has been permanently displayed on the Cenotaph in London since 1943. Early history and authorisation Ever since the formation of the RAF in 1918, the Air Council had wanted to introduce a flag which would be flown at RAF stations. However, the Admiralty had the right to veto the introduction of any new flag that was to be flown within the British Empire or on a British vessel. Although the Admiralty were initially opposed to granting the RAF its own flag, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
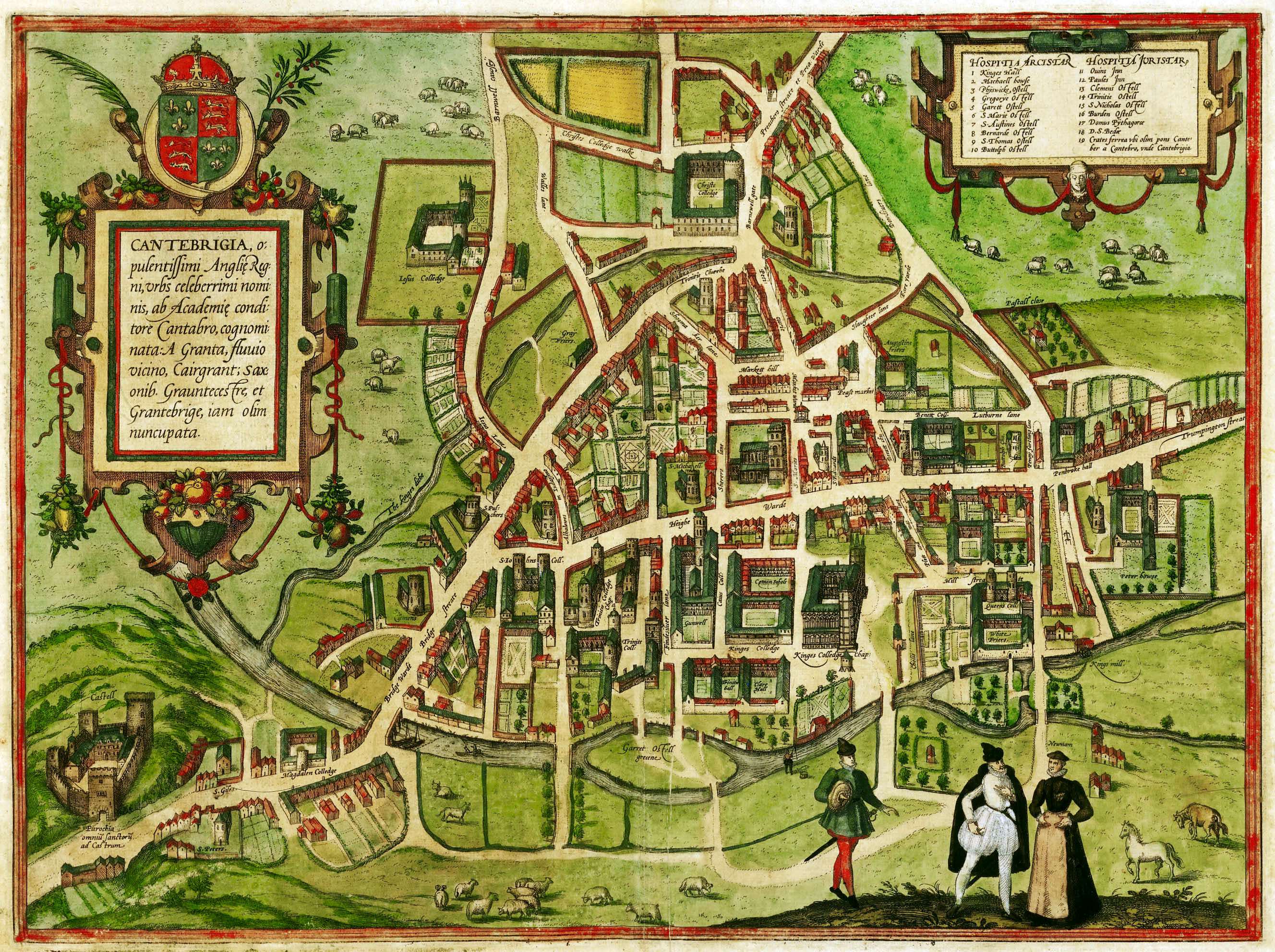
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbeach Barracks
Waterbeach Barracks was a military installation in Waterbeach, Cambridgeshire. The site was an RAF Station, RAF Waterbeach and then used by the Royal Engineers, part of the British Army, from 1966, until 2013 when the site closed to make way for housing. History In 1966 the station and airfield remained the property of the Ministry of Defence, but was transferred from the Royal Air Force to the Royal Engineers, part of the British Army. Until the closure of nearby RAF Oakington in the early 1970s, the main runway at Waterbeach remained active, along with the control tower, and was used as a relief landing ground for Varsities used in the advanced pilot training role. The barracks, airfield and surrounding quarters most recently housed 12 (Air Support) Engineer Group. The former airfield was used as a training area for troops, with occasional visits by helicopters and, in the past, by Harriers. 25 Engineer Regiment was disbanded on 19 April 2012. Two of its squadrons (34 Field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
39 Engineer Regiment (United Kingdom)
39 Engineer Regiment (39 Engr Regt) is a battalion-sized regiment of the British Army formed in 1951 and based in Kinloss in Scotland. History It was in Kenya in the early 1950s, up until 1955, and elements took part in anti- Mau Mau operations. An announcement in November 2011 confirmed that 39 Engineer Regiment (Air Support) RE would move from Waterbeach Barracks, near Cambridge, to Kinloss, in July 2012. It was expected that 930 service personnel and their families would move at this time. As of 2016, the regiment consisted of five squadrons: * 39 Engineer Regiment, Kinloss Barracks Kinloss Barracks is a military installation located near the village of Kinloss, on the Moray Firth in the north of Scotland. Until 2012 it was a Royal Air Force (RAF) station, RAF Kinloss. History RAF Kinloss The Royal Air Force statio ... ** 60 Headquarters and Support Squadron ** 34 Field Squadron ** 48 Field Squadron ** 53 Field Squadron ** 65 Field Support Squadron ** REME Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |