|
RAF Gibraltar
Royal Air Force Gibraltar or more simply RAF Gibraltar (also formerly known as North Front) is a Royal Air Force List of Royal Air Force stations, station on Gibraltar. No military aircraft are currently stationed there, but RAF and aircraft of other NATO nations will periodically arrive for transient stopovers, exercises, or other temporary duty. Administered by British Forces Gibraltar, the station is a joint civil-military facility that also functions as the Rock's civilian airport – Gibraltar Airport, with the civilian airport's passenger terminal building and apron facilities located on the north side of the runway while the apron and hangar of RAF Gibraltar are located on the south side of the runway. A total of 16 personnel were reported assigned to RAF Gibraltar as of 2023. History Early history A Royal Naval Air Service seaplane base was opened at Gibraltar during the First World War. The airport was constructed during World War II when Gibraltar was an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the Atlantic Ocean (Strait of Gibraltar). It has an area of and is Gibraltar–Spain border, bordered to the north by Spain (Campo de Gibraltar). The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar, at the foot of which is a densely populated town area. Gibraltar is home to some 34,003 people, primarily Gibraltarians. Gibraltar was founded as a permanent watchtower by the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads in 1160. It switched control between the Nasrids, Crown of Castile, Castilians and Marinids in the Late Middle Ages, acquiring larger strategic clout upon the destruction of nearby Algeciras . It became again part of the Crown of Castile in 1462. In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces Capture of Gibraltar, captured Gibraltar from Spain during the War of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is the naval aviation component of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy (RN). The FAA is one of five :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, RN fighting arms. it is a primarily helicopter force, though also operating the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II, F-35 Lightning II carrier-based stealth fighter jointly with the Royal Air Force. The RAF was formed by the 1918 merger of the RN's Royal Naval Air Service with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps. The FAA did not come under the direct control of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty until mid-1939. During the Second World War, the FAA operated aircraft on ships as well as land-based aircraft that defended List of Royal Navy shore establishments, the Royal Navy's shore establishments and facilities. History Beginnings British naval flying started in 1909, with the construction of an airship for naval duties. In 1911 the Royal Navy graduated its first aeroplane pilots at the Royal Aero Club RAF Eastchu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocco border, the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to Morocco–Western Sahara border, the south. Morocco also claims the Spain, Spanish Enclave and exclave, exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Plazas de soberanía, Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab culture, Arab, Berbers, Berber, Culture of Africa, African and Culture of Europe, European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares maritime borders with Italy through the islands of Sicily and Sardinia to the north and Malta to the east. It features the archaeological sites of Carthage dating back to the 9th century BC, as well as the Great Mosque of Kairouan. Known for its ancient architecture, Souks of Tunis, souks, and blue coasts, it covers , and has a population of 12.1 million. It contains the eastern end of the Atlas Mountains and the northern reaches of the Sahara desert; much of its remaining territory is arable land. Its of coastline includes the African conjunction of the western and eastern parts of the Mediterranean Basin. Tunisia is home to Africa's northernmost point, Cape Angela. Located on the northeastern coast, Tunis is the capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Algeria–Niger border, the southeast by Niger; to Algeria–Western Sahara border, the southwest by Mali, Mauritania, and Western Sahara; to Algeria–Morocco border, the west by Morocco; and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. The capital and List of cities in Algeria, largest city is Algiers, located in the far north on the Mediterranean coast. Inhabited since prehistory, Algeria has been at the crossroads of numerous cultures and civilisations, including the Phoenicians, Numidians, Ancient Rome, Romans, Vandals, and Byzantine Greeks. Its modern identity is rooted in centuries of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arab Muslim migration waves since Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, the seventh century and the subsequent Arabization, Arabisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire", which began with the French conquest of Algeria, conquest of Algiers in 1830. On the eve of World War I, France's colonial empire was List of largest empires, the second-largest in the world after the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in the French colonization of the Americas, Americas, the Caribbean, and French India, India in the 16th century but lost most of its possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain, but Louisiana (New France), Spain later returned Louisiana to France in 1800. The territory was then Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
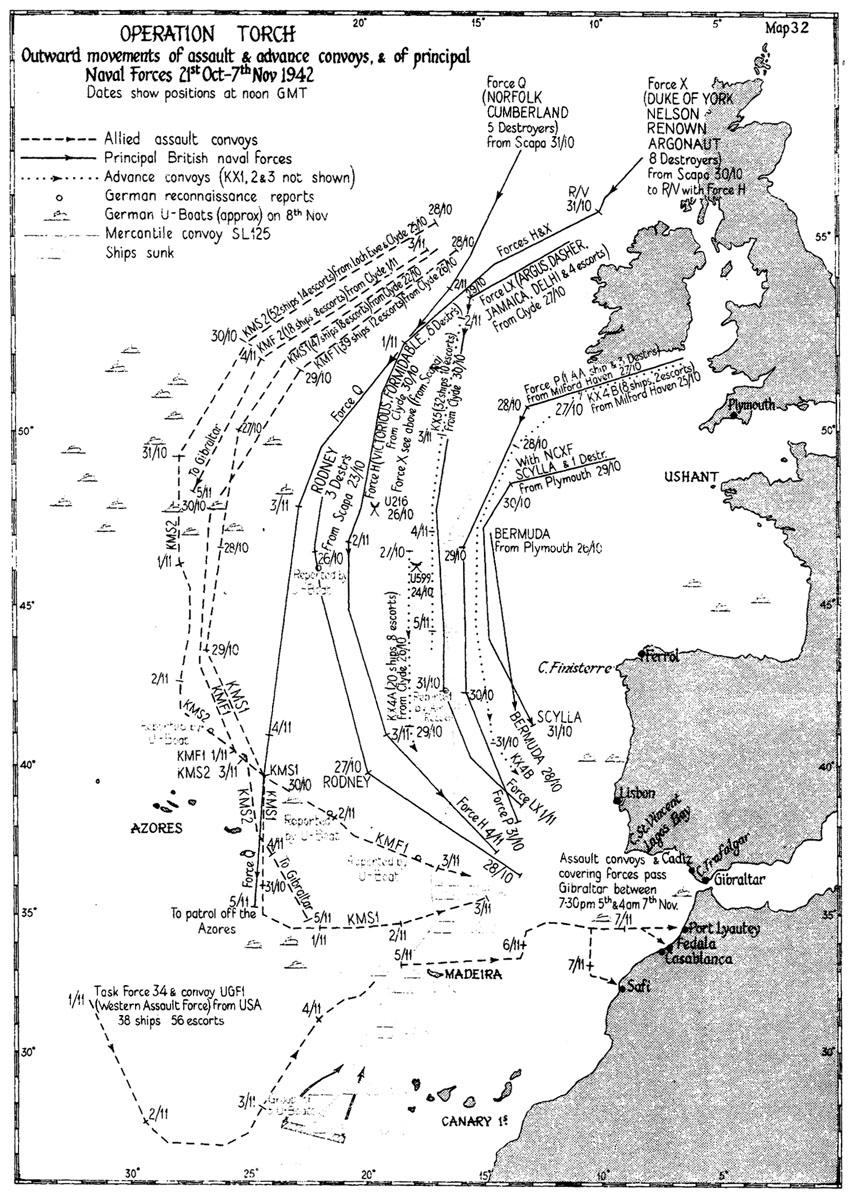
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8–16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to begin their fight against Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy on a limited scale. The French colonies were aligned with Germany via Vichy France but the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. The American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, Mediterranean theater of the war, approved plans for a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Centre) and Algiers (Eastern), then a rapid move on Tunis to catch Axis forces in North Africa from the west in conjunction with the British advance from Egypt. The Western Task Force encountered unexpected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montagu Bastion
The Montagu Bastion is one of many bastions which were designed to protect Gibraltar. Montagu was joined to Orange Bastion by a Curtain wall (fortification), curtain wall known as Montagu Curtain and this bastion was protected by the Montagu Counterguard. History Montagu Bastion was built on the remains of the Spanish ''Plataforma de San Andrés'' ('). A British bastion already existed on this site in the 1730s and was enlarged in 1773 giving it a pentagonal shape. In the 1790s, Sir William Green (general), William Green, oversaw improvements to Fortifications of Gibraltar, Gibraltar's fortifications. As part of this he had the Montagu and the Orange Bastions extended and in addition he arranged for counterguards to be constructed in front of them in the Gibraltar Harbour. The counterguard, which mirrors the shape of its bastion, had been authorised by the Charles Lennox, 3rd Duke of Richmond, Duke of Richmond in 1787. The theory behind constructing a counterguard, like the Montag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Coastal Command
RAF Coastal Command was a formation within the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was founded in 1936, when the RAF was restructured into Fighter, Bomber and Coastal commands and played an important role during the Second World War. Maritime Aviation had been neglected in the inter-war period, due to disagreements between the Royal Navy (RN) and RAF over the ownership, roles and investment in maritime air power.Buckley, 2018. p.85 The Admiralty's main concern until 1937 was the return of the Fleet Air Arm to the Royal Navy while the RAF concentrated on the development of a bombing force to provide a deterrent. Coastal Command was referred to as the "Cinderella Service" by A V Alexander, the First Lord of the Admiralty in November 1940. Soon after RAF Coastal Area was elevated to Coastal Command, its headquarters moved from Lee-on-Solent to Northwood in northwest London. During the Second World War, Coastal Command's most important contribution was the protection of Allied convoys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race Track
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also used in the study of animal locomotion. A ''racetrack'' is a permanent facility or building. ''Racecourse'' is an alternate term for a horse racing track, found in countries such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, Hong Kong, and the United Arab Emirates. Race tracks built for bicycles are known as '' velodromes''. ''Circuit'' is a common alternate term for race track, given the circuit configuration of most race tracks, allowing races to occur over several laps. Some race tracks may also be known as ''speedways'', or ''raceways''. A ''race course'', as opposed to a ''racecourse'', is a nonpermanent track for sports, particularly road running, water sports, road racing, or rallying. Many sports usually held on race tracks also can occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
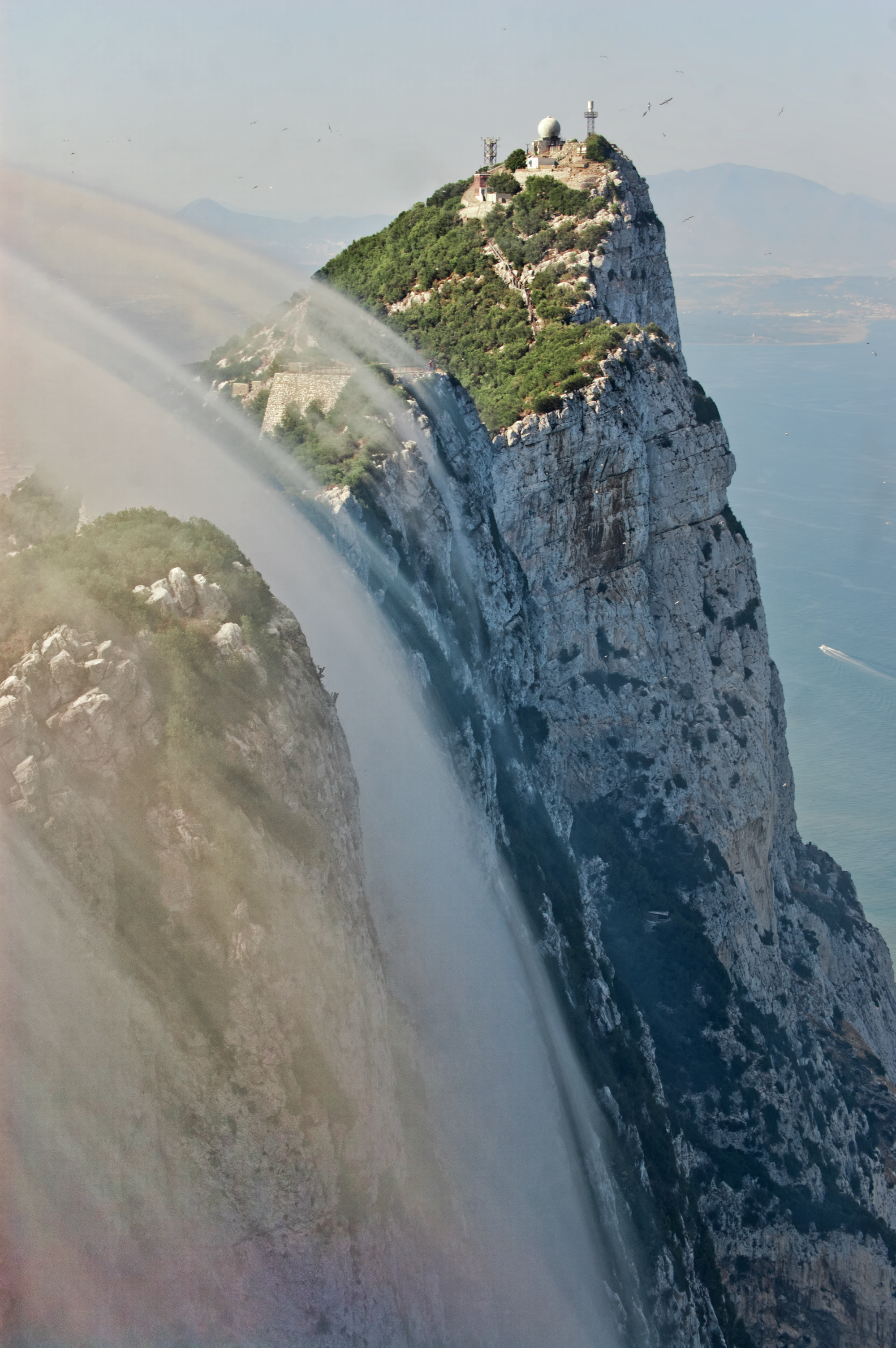
Rock Of Gibraltar
The Rock of Gibraltar (from the Arabic name Jabal Ṭāriq , meaning "Mountain of Tariq ibn Ziyad, Tariq") is a monolithic limestone mountain high dominating the western entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. It is situated near the end of a narrow -long promontory stretching due south into the Mediterranean Sea and is located within the British territory of Gibraltar. The rock is 27 km northeast of Tarifa, Spain, the southwestern tip of Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. The rock serves as a fortress and contains a labyrinthine network of man-made tunnels known as the Tunnels of Gibraltar. Most of the Rock's upper area comprises a Gibraltar Nature Reserve, nature reserve which is home to about 300 Barbary macaques in Gibraltar, Barbary macaques. It is a major tourist attraction. The Rock of Gibraltar, the northern of the two historic Pillars of Hercules, was known to the Ancient Romans, Romans as ''Mons Calpe'' ("Mount Calpe"); the southern Pillar of Hercules on the African side o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |