|
RAF Condover
Royal Air Force Condover or more simply RAF Condover is a former Royal Air Force Flying Training Command airfield and air navigation training establishment between August 1942 and June 1945, unusually for both fighter and bomber crews at different times. Located on the southern outskirts of Condover village in Shropshire, south of the county town Shrewsbury. Condover was used to train fighter pilots by the RAF and the USAAF as well as pilots and air navigators from Australia, South Africa and Canada. Although the runways have now been broken up and removed, many original station buildings still stand and the control tower is considered to be one of the best-preserved in Shropshire. After many years as a major part of a local riding school several of the buildings and land plots were offered for sale by auction during the summer of 2007. History The station formally opened on 21 August 1942 with three new concrete runways designed for both fighter and bomber aircraft. The ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Shrowsbury' or 'Shroosbury', the correct pronunciation being a matter of longstanding debate. The town centre has a largely unspoilt medieval street plan and over 660 listed buildings, including several examples of timber framing from the 15th and 16th centuries. Shrewsbury Castle, a red sandstone fortification, and Shrewsbury Abbey, a former Benedictine monastery, were founded in 1074 and 1083 respectively by the Norman Earl of Shrewsbury, Roger de Montgomery. The town is the birthplace of Charles Darwin and is where he spent 27 years of his life. east of the Welsh border, Shrewsbury serves as the commercial centre for Shropshire and mid-Wales, with a retail output of over £299 million per year and light industry and distributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quonset Hut
A Quonset hut is a lightweight prefabricated structure of corrugated galvanized steel having a semi cylindrical cross-section. The design was developed in the United States, based on the Nissen hut introduced by the British during World War I. Hundreds of thousands were produced during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ... and military surplus was sold to the public. The name comes from the site of their first deployment at Quonset Point at the Camp Endicott, Davisville Naval Construction Battalion Center in Davisville, Rhode Island. Design and history The first Quonset huts were manufactured in 1941 when the United States Navy needed an all-purpose, lightweight building that could be shipped anywhere and assembled without skilled labor. The George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bournville
Bournville () is a model village on the southwest side of Birmingham, England, founded by the Quaker Cadbury family for employees at its Cadbury's factory, and designed to be a "garden" (or "model") village where the sale of alcohol was forbidden. Cadbury's is well known for chocolate products – including a dark chocolate bar branded ''Bournville''. Historically in northern Worcestershire, it is also a ward within the council constituency of Selly Oak and home to the Bournville Centre for Visual Arts. Bournville is known as one of the most desirable areas to live in the UK; research by the Joseph Rowntree Foundation in 2003 found that it was "one of the nicest places to live in Britain". History Originally the area that was to become Bournville consisted of a few scattered farmsteads and cottages, linked by winding country lanes, with the only visual highlight being Bournbrook Hall, which was built during the Georgian era. The bluebell glades of Stock Wood were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egbert Cadbury
Major (Honorary Air Commodore) Sir Egbert "Bertie" Cadbury (20 April 1893 – 12 January 1967) was a British businessman, a member of the Cadbury family, who as a First World War pilot shot down two Zeppelins over the North Sea: '' L.21'' on 28 November 1916, and '' L.70'' on 6 August 1918: the latter while flying a De Havilland DH.4 with Robert Leckie as observer/gunner. Early life and background Egbert Cadbury was born in Selly Oak, Birmingham, the youngest son of George Cadbury and his second wife Elizabeth Cadbury, and the grandson of John, the founder the family business. A year after he was born the family moved to a new home, Northfield Manor House, in Northfield, Birmingham. He was educated at Leighton Park School in Reading, then went to Trinity College, Cambridge to study economics. First World War The Cadburys were Quakers, and thus pacifists, but on the outbreak of the war, Cadbury left Cambridge and volunteered to join the Royal Navy, serving as a seaman aboard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Soames, Lady Soames
Mary Soames, Baroness Soames, (; 15 September 1922 31 May 2014) was an English author. The youngest of the five children of Winston Churchill and his wife, Clementine, she worked for public organisations including the Red Cross and the Women's Voluntary Service from 1939 to 1941, and joined the Auxiliary Territorial Service in 1941. She was the wife of Conservative politician Christopher Soames. Biography Mary Spencer-Churchill was born in London, in the same week as her father, Winston Churchill, purchased Chartwell, a country house in Kent; she was brought up there, attending local schools. She worked for the Red Cross and the Women's Voluntary Service from 1939 to 1941, and joined the Auxiliary Territorial Service in 1941 with which she served in London, Belgium and Germany in mixed anti-aircraft batteries, rising to the rank of Junior Commander (equivalent to Captain). She accompanied her father as aide-de-camp on several of his overseas journeys, including his post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
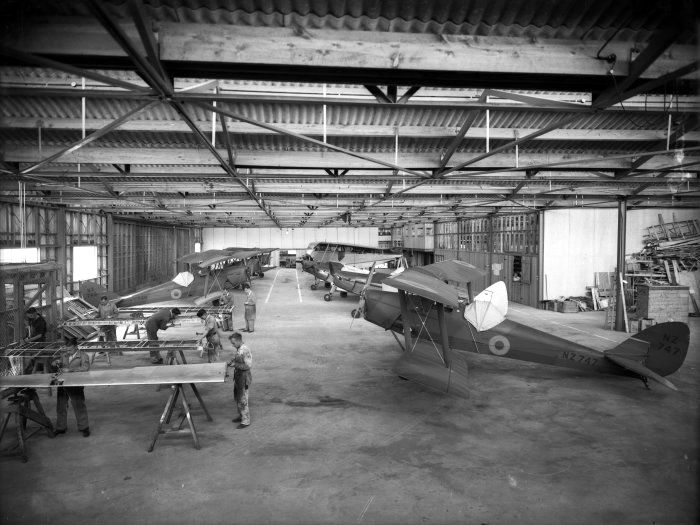
De Havilland Tiger Moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland, de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer (aircraft), trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ''ab initio'' training, the World War II, Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including Maritime patrol aircraft, maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers. The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was replaced by the de Havilland Canada DHC-1 Chipmunk, de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civilian operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civilian applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathfinder (RAF)
The Pathfinders were target-marking squadrons in RAF Bomber Command during World War II. They located and marked targets with flares, which a main bomber force could aim at, increasing the accuracy of their bombing. The Pathfinders were normally the first to receive new blind-bombing aids like Gee, Oboe and the H2S radar. The early Pathfinder Force (PFF) squadrons was expanded to become a group, No. 8 (Pathfinder Force) Group in January 1943. The initial Pathfinder Force was five squadrons, while No. 8 Group ultimately grew to a strength of 19 squadrons. While the majority of Pathfinder squadrons and personnel were from the Royal Air Force, the group also included many from the air forces of other Commonwealth countries. History Background At the start of the war in September 1939, RAF Bomber Command's doctrine was based on tight formations of heavily armed bombers attacking during daylight and fending off attacks by fighters with their defensive guns. In early mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster is a British World War II, Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same wartime era. The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry List of Air Ministry specifications, Specification P.13/36 for a medium bomber for "world-wide use" which could carry a torpedo internally, and make shallow dive-bombing attacks. Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one of the versions, Bristol Hercules engines. It first saw service with RAF Bomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Stirling
The Short Stirling was a British four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It has the distinction of being the first four-engined bomber to be introduced into service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). The Stirling was designed during the late 1930s by Short Brothers to conform with the requirements laid out in Air Ministry Specification B.12/36. Prior to this, the RAF had been primarily interested in developing increasingly capable twin-engined bombers, but had been persuaded to investigate a prospective four-engined bomber as a result of promising foreign developments in the field. Out of the submissions made to the specification, Supermarine proposed the Type 317, which was viewed as the favourite, whereas Short's submission, named the S.29, was selected as an alternative. When the preferred Type 317 had to be abandoned, the S.29, which later received the name Stirling, proceeded to production. In early 1941, the Stirling entered squadron service. During its use as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon engined Mk 24 using several wing configurations and guns. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts; around List of surviving Supermarine Spitfires, 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing with innovative sunken rivets (designed by Beverley Shenstone) to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed Oxford
The Airspeed AS.10 Oxford is a twin-engine monoplane aircraft developed and manufactured by Airspeed. It saw widespread use for training British Commonwealth aircrews in navigation, radio-operating, bombing and gunnery roles throughout the Second World War. The Oxford was developed by Airspeed during the 1930s in response to a requirement for a capable trainer aircraft that conformed with Specification T.23/36, which had been issued by the British Air Ministry. Its basic design is derived from the company's earlier AS.6 Envoy, a commercial passenger aircraft. Performing its maiden flight on 19 June 1937, it was quickly put into production as part of a rapid expansion of the Royal Air Force (RAF) in anticipation of a large-scale conflict. As a consequence of the outbreak of war, many thousands of Oxfords were ordered by Britain and its allies, including Australia, Canada, France, New Zealand, Poland, and the United States. Following the end of the conflict, the Oxford continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |