|
Quirpon Island
Quirpon Island is a small Canadian island off the northeastern tip of Newfoundland's Great Northern Peninsula in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is located at the southeastern edge of the Strait of Belle Isle, south of Belle Isle. Cape Bauld is located at its northeastern point. The haunting Isle of Demons legend originates from here. Lighthouse Inn Quirpon Island is currently a tourist attraction, that is privately owned and serves as an inn (the lighthouse is owned by the Government of Canada). The inn has two buildings that can accommodate tourists, as well as a lighthouse and a few other buildings. The only way to travel there is to stay at the inn, which is accessible by dinghy only. Guests can go on tours in the boat and see icebergs, humpback whale The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newfoundland (island)
Newfoundland (, ; french: link=no, Terre-Neuve, ; ) is a large island off the east coast of the North American mainland and the most populous part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It has 29 percent of the province's land area. The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula by the Strait of Belle Isle and from Cape Breton Island by the Cabot Strait. It blocks the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, creating the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the world's largest estuary. Newfoundland's nearest neighbour is the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. With an area of , Newfoundland is the world's 16th-largest island, Canada's fourth-largest island, and the largest Canadian island outside the North. The provincial capital, St. John's, is located on the southeastern coast of the island; Cape Spear, just south of the capital, is the easternmost point of North America, excluding Greenland. It is common to consider all directly neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Peninsula
The Great Northern Peninsula ( Inuttitut: ''Ikkarumiklua'') is the largest and longest peninsula of Newfoundland, Canada, approximately 270 km long and 90 km wide at its widest point and encompassing an area of 17,483 km2. It is defined as that part of Newfoundland from Bonne Bay northwards around Cape Norman and Cape Bauld and thence southwards to the head of White Bay, bounded by the Gulf of St. Lawrence on the west, the Strait of Belle Isle on the north and the Labrador Sea and White Bay on the east. The vast majority of the peninsula is located within Division No. 9, Newfoundland and Labrador, except for the southeastern corner, which is part of Subdivision G of Division No. 5, Newfoundland and Labrador. In 1991, the peninsula had 23,854 inhabitants. By 2016, however, the population had decreased to 15,607, further decreased to 14,733 in 2021. St. Anthony is the largest population centre on the peninsula. A ferry service operates at the western part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newfoundland And Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of 405,212 square kilometres (156,500 sq mi). In 2021, the population of Newfoundland and Labrador was estimated to be 521,758. The island of Newfoundland (and its smaller neighbouring islands) is home to around 94 per cent of the province's population, with more than half residing in the Avalon Peninsula. Labrador borders the province of Quebec, and the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon lies about 20 km west of the Burin Peninsula. According to the 2016 census, 97.0 per cent of residents reported English as their native language, making Newfoundland and Labrador Canada's most linguistically homogeneous province. A majority of the population is descended from English and Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle (; french: Détroit de Belle Isle ) is a waterway in eastern Canada that separates the Labrador Peninsula from the island of Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Location The strait is the northern outlet for the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the other two being the Cabot Strait and Strait of Canso. As such, it is also considered part of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Seaway system. The strait is approximately long and ranges from a maximum width of to just at its narrowest, the average width being . Origins of name The name is derived from the island of Belle Isle (French for "Beautiful Island"), which is at the extreme eastern end of the strait and roughly equidistant from Table Head, Labrador, and Cape Bauld, Newfoundland. History Both the island of Newfoundland as well as the Labrador region which surrounds the Strait of Belle Isle have been inhabited by Indigenous Peoples for millennia. The surrounding land environment has hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle Isle (Newfoundland And Labrador)
Belle Isle (French for "Beautiful Island") is an uninhabited island slightly more than off the coast of Labrador and slightly less than north of Newfoundland at the Atlantic entrance to the Strait of Belle Isle, which takes its name. Named by the French explorer Jacques Cartier, the island lies on the shortest shipping lane between the Great Lakes and Europe and is on the main north-south shipping route to Hudson Bay and the Northwest Territories. The northern terminus of the International Appalachian Trail is on Belle Isle. Geography Belle Isle rises to about at its highest point and is in area, long and wide. It is nearly from either coast, but it is slightly closer to the Labrador side of the Strait of Belle Isle, and it has a lighthouse (supported by flying buttresses) at both its northern and its southern ends. Officially uninhabited, the island has some seasonal occupation during fishing season. Belle Isle is the northernmost peak of the Appalachian Mountains, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Bauld
Cape Bauld is a headland located at the northernmost point of Quirpon Island, an island just northeast of the Great Northern Peninsula of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Cape Bauld, slightly north and east of Cape Norman, delineates the eastern end of the Strait of Belle Isle. The English explorer John Cabot may have landed at Cape Bauld on June 24, 1497, though Cape Bonavista is also mentioned as a potential landing point. Cape Bauld is only some nine kilometers (5.6 miles) northeast of the verified Viking archeological site, the L'Anse aux Meadows coastal location, dating to five centuries earlier than Cabot's date of achievement. Lighthouse A lighthouse was constructed at the cape in 1884. The current lighthouse is the second replacement structure, constructed 1960–1961. The lightkeeper's residence is from 1920. See also * List of lighthouses in Canada This is a list of lighthouses in Canada. These may naturally be divided into l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
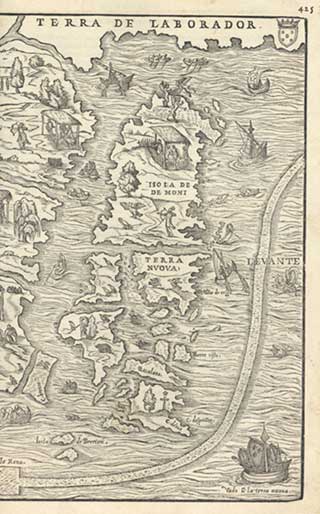
Isle Of Demons
The Isle of Demons is a phantom island once associated with Quirpon Island, Newfoundland, in Canada. It was generally shown as two islands. It began appearing on maps in the beginning of the 16th century and disappeared in the mid-17th century. It could also simply be a translation from First Nations people who often avoided areas where a person had died, believing it was haunted by spirits. This results in many islands with the same reference. It was believed that the island was populated by demons and wild beasts which would torment and attack any ships that passed or anyone that was foolish enough to wander onto the island. A French noblewoman, Marguerite de La Rocque, was marooned on an island in the mid-16th century, allegedly because of an affair with a young man on her ship. This island is a possible site of their abandonment, and residents and visitors have claimed to see the couple. Across the centuries, many historians, novelists, poets and singers have retold the stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown-in-Council''; the legislature, as the ''Crown-in-Parliament''; and the courts, as the ''Crown-on-the-Bench''. Three institutions—the Privy Council ( conventionally, the Cabinet); the Parliament of Canada; and the judiciary, respectively—exercise the powers of the Crown. The term "Government of Canada" (french: Gouvernement du Canada, links=no) more commonly refers specifically to the executive— ministers of the Crown (the Cabinet) and the federal civil service (whom the Cabinet direct)—which corporately brands itself as the ''Government of Canada'', formally known as '' Majesty's Government'' (french: Gouvernement de Sa Majesté, links=no). There are over one hundred ministries, departments and crown corporations and over 300 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Lighthouses mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, rocks, and safe entries to harbors; they also assist in aerial navigation. Once widely used, the number of operational lighthouses has declined due to the expense of maintenance and has become uneconomical since the advent of much cheaper, more sophisticated and effective electronic navigational systems. History Ancient lighthouses Before the development of clearly defined ports, mariners were guided by fires built on hilltops. Since elevating the fire would improve the visibility, placing the fire on a platform became a practice that led to the development of the lighthouse. In antiquity, the lighthouse functioned more as an entrance marker to ports than as a warning signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinghy
A dinghy is a type of small boat, often carried or towed by a larger vessel for use as a tender. Utility dinghies are usually rowboats or have an outboard motor. Some are rigged for sailing but they differ from sailing dinghies, which are designed first and foremost for sailing. A dinghy's main use is for transfers from larger boats, especially when the larger boat cannot dock at a suitably-sized port or marina. The term "dinghy towing" sometimes is used to refer to the practice of towing a car or other smaller vehicle behind a motorhome, by analogy to towing a dinghy behind a yacht. Etymology The term is a loanword from the Bengali ', Urdu ', and Hindi '. Types Dinghies usually range in length from about . Larger auxiliary vessels are generally called tenders, pinnaces or lifeboats. Folding and take-down multi-piece (nesting) dinghies are used where space is limited. Some newer dinghies have much greater buoyancy, giving them more carrying capacity than old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The sinking of the ''Titanic'' in 1912 led to the formation of the International Ice Patrol in 1914. Much of an iceberg is below the surface, which led to the expression " tip of the iceberg" to illustrate a small part of a larger unseen issue. Icebergs are considered a serious maritime hazard. Icebergs vary considerably in size and shape. Icebergs that calve from glaciers in Greenland are often irregularly shaped while Antarctic ice shelves often produce large tabular (table top) icebergs. The largest iceberg in recent history (2000), named B-15, measured nearly 300 km × 40 km. The largest iceberg on record was an Antarctic tabular iceberg of over [] sighted west of Scott Island, in the South Pacific Ocean, by the USS Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


