|
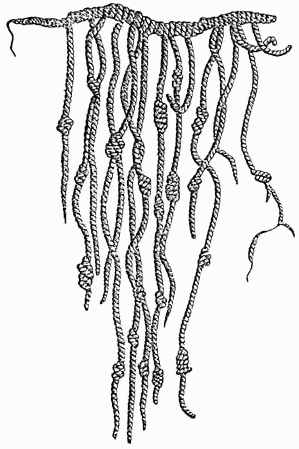
Quipus
''Quipu'' ( ), also spelled ''khipu'', are record keeping devices fashioned from knotted cords. They were historically used by various cultures in the central Andes of South America, most prominently by the Inca Empire. A ''quipu'' usually consists of cotton or Camelidae, camelid fiber cords, and contains categorized information based on dimensions like color, order and number. The Inca, in particular, used knots tied in a decimal positional system to store numbers and other values in ''quipu'' cords. Depending on its use and the amount of information it stored, a given ''quipu'' may have anywhere from a few to several thousand cords. Objects which can unambiguously be identified as ''quipus'' first appear in the archaeological record during 1st millennium CE,Urton, Gary. (2011). "Tying the Archive in Knots, or: Dying to Get into the Archive in Ancient Peru likely attributable to the Wari Empire. ''Quipus'' subsequently played a key part in the administration of the Kingdom of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Urton
Gary Urton (born July 7, 1946) is an American anthropologist. He was the Dumbarton Oaks Professor of Pre-Columbian Studies at Harvard University and the chair of its anthropology department between 2012 and 2019. Urton retired from Harvard in 2020, after multiple former students accused him of sexual harassment. Despite much controversy and opposition, he was given an emeritus title after retirement. Following internal investigation, Urton was stripped of his emeritus status by Harvard in June 2021. Education and career Urton received his B.A. from the University of New Mexico in 1969, and his M.A. and Ph.D. degrees from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in 1971 and 1979, respectively. He was a professor at Colgate University from 1978 to 2002. He is married to artist and anthropologist Julia Meyerson. Urton is a specialist in Andes, Andean archaeology, particularly the quipu (''khipu'') rope-based recording system used in the Inca empire in the 15th and 16th centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of statistics. This term is used mostly in connection with Population and housing censuses by country, national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include Census of agriculture, censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications, and other useful information to coordinate international practices. The United Nations, UN's Food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Orthography
Spanish orthography is the orthography used in the Spanish language. The alphabet uses the Latin script. The spelling is fairly phonemic orthography, phonemic, especially in comparison to more opaque orthographies like English orthography, English, having a relatively consistent mapping of graphemes to phonemes; in other words, the pronunciation of a given Spanish-language word can largely be predicted from its spelling and to a slightly lesser extent vice versa. Spanish punctuation uniquely includes the use of inverted question and exclamation marks: . Spanish uses capital letters much less often than English; they are not used on adjectives derived from proper nouns (e.g. ''francés'', ''español'', ''portugués'' from ''Francia'', ''España'', and ''Portugal'', respectively) and book titles capitalize only the first word (e.g. ''The Revolt of the Masses, La rebelión de las masas''). Spanish uses only the acute accent over any vowel: . This accent is used to mark the tonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechuan And Aymaran Spelling Shift
In recent years, Peru has revised the official spelling for place-names originating from Aymara and the Quechuan languages. A standardized alphabet for done Quechua was adopted by the Peruvian government in 1975; a revision in 1985 moved to a three-vowel orthography. The major changes are to replace the digraph with the single letter , and to replace the consonants ''c''/''q ' with either or , as appropriate in the word in question. ''K'' and ''q'' represent different sounds in most Andean languages: k is a velar stop , as in Spanish and English; q is a uvular stop . As Spanish does not have uvular , traditional spellings lose this distinction (although sometimes a double ''cc'' was used to represent the k-like sounds of Quechua that differed from the "plain k" sound known in Spanish; e.g., in place names such as Ccarhuacc, Chopcca, Cconocc, Llacce, Manyacc, Chihuilluyocc, Chilcahuaycco, etc.), and Quechua or Aymara sources must be consulted to select the right consonant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispanicized
Hispanicization () refers to the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by Hispanic culture or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-Hispanic becomes Hispanic. Hispanicization is illustrated by spoken Spanish, production and consumption of Hispanic food, Spanish language music, and participation in Hispanic festivals and holidays. In the former Spanish colonies, the term is also used in the narrow linguistic sense of the Spanish language replacing indigenous languages. Spain Within Spain, the term "Hispanicization" can refer to the cultural and linguistic absorption of the ethnically Berber Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands in the century following their subjugation in the 15th century. It is relatively rarely used as a synonym for "Castilianization" (''castellanización'') i.e. the historical process whereby speakers of minority Spanish languages such as Catalan, Basque, Galician, Astur-Leonese or Aragonese are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of Peru
The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as the Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spaniards, Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, along with his brothers in arms and their Indigenous peoples of South America, indigenous Indian auxiliaries, allies, captured the last Sapa Inca, Atahualpa, at the Battle of Cajamarca in 1532. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire (called "Tahuantinsuyu" or "Tawantinsuyu" in Quechuan languages, Quechua, meaning "Realm of the Four Parts"), led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions to the Amazon basin, Amazon Basin and surrounding rainforest. When the Spanish arrived at the borders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nueva Corónica Y Buen Gobierno (1936 Facsimile) P360
{{disambig, geo ...
Nueva is the Spanish feminine form of the word for " new" and may refer to: * Isla Nueva, an uninhabited island in Chile * The Nueva School, a school in Hillsborough, California, USA * Nueva (Llanes), a parish in Llanes, Asturias, Spain * Nueva, a restaurant in Delhi, India by Indian cricketer Virat Kohli Virat Kohli (born 5 November 1988) is an Indian Cricket, international cricketer who plays One Day International, ODI cricket for the India national cricket team, national team and is a former Captain (cricket), captain in all formats. He is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesians
Polynesians are an ethnolinguistic group comprising closely related ethnic groups native to Polynesia, which encompasses the islands within the Polynesian Triangle in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Southeast Asia and are part of the larger Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, with an Urheimat in Taiwan. They speak the Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic subfamily within the Austronesian language family. The Indigenous Māori people form the largest Polynesian population, followed by Samoans, Native Hawaiians, Tahitians, Tongans, and Cook Islands Māori. , there were an estimated 2 million ethnic Polynesians (both full and part) worldwide. The vast majority either inhabit independent Polynesian nation-states (Samoa, Niue, Cook Islands, Tonga, and Tuvalu) or form minorities in countries such as Australia, Chile (Easter Island), New Zealand, France (French Polynesia and Wallis and Futuna), and the United States (Hawaii and Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |