|
Quinomethide
A quinone methide is a type of conjugated organic compound that contain a cyclohexadiene with a carbonyl and an exocyclic methylidene or extended alkene unit. It is analogous to a quinone, but having one of the double bonded oxygens replaced with a carbon. The carbonyl and methylidene are usually oriented either ortho or para to each other. There are some examples of transient synthetic meta quinone methides. Properties Quinone methides are cross-conjugated rather than aromatic. Nucleophilic addition at the exo-cyclic double bond will result in rearomatisation, making such reactions highly favourable. As a result, quinone methides are excellent, electrophilic Michael acceptors, react quickly with nucleophiles and can be easily reduced. They are able to act as radical scavengers via a similar process, a behaviour exploited by certain polymerisation inhibitors. Quinone methides are more polar than quinones, and therefore more chemically reactive. Simple unhindered quinone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugated System
In physical organic chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases Chemical stability, stability. It is Resonance (chemistry), conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple covalent bond, bonds. Lone pairs, radical (chemistry), radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be Cyclic molecule, cyclic, acyclic, Linear molecular geometry, linear or mixed. The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele (chemist), Johannes Thiele. Conjugation is the orbital overlap, overlap of one p-orbital with another across an adjacent Sigma bond, σ bond (in transition metals, d-orbitals can be involved). A conjugated system has a region of overlapping p-orbitals, bridging the interjacent locations that simple diagrams illustrate as not having a π bond. They allow a delocalization of pi el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reactivity
In chemistry, reactivity is the impulse for which a chemical substance undergoes a chemical reaction, either by itself or with other materials, with an overall release of energy. ''Reactivity'' refers to: * the chemical reactions of a single substance, * the chemical reactions of two or more substances that interact with each other, * the systematic study of sets of reactions of these two kinds, * methodology that applies to the study of reactivity of chemicals of all kinds, * experimental methods that are used to observe these processes, and * theories to predict and to account for these processes. The chemical reactivity of a single substance (reactant) covers its behavior in which it: * decomposes, * forms new substances by addition of atoms from another reactant or reactants, and * interacts with two or more other reactants to form two or more products. The chemical reactivity of a substance can refer to the variety of circumstances (conditions that include temperature, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylation
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with alkene, olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion (carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
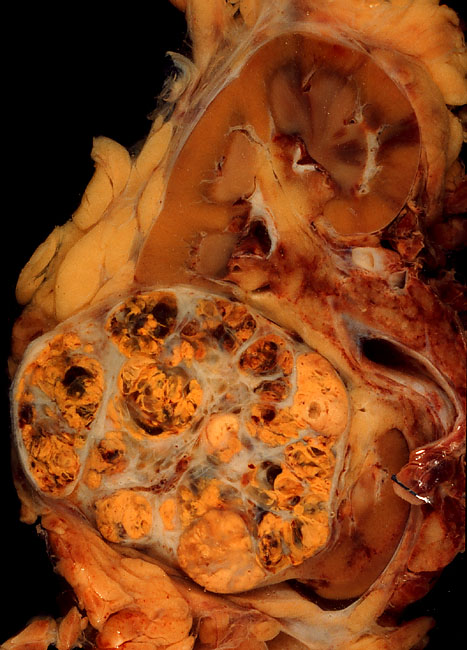
Antitumor
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy including small-molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies, and PARP inhibitors such as olaparib. Other therapies include hyperthermia, immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and stem-cell therapy. Most commonly cancer treatment involves a series of separate therapies such as chemotherapy before surgery. Angiogenesis inhibitors are sometimes used to enhance the effects of immunotherapies. The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient. Biomarker testing can help to determine the type of cancer, and indicate the best therapy. A number of experimental cancer treatments are continuously under development. In 2023 it was estimated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxin
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ... to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol (drug), alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the Bitis arietans, puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymers
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. Polymers are studied in the fields of polymer science (which includes polymer chemistry and polymer p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
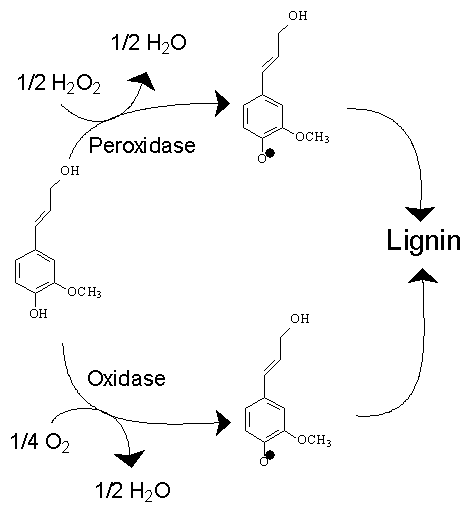
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignification
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and Bark (botany), bark, because they lend rigidity and do not decomposition, rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenols, phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle, A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be Precipitation (chemistry), precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word ''wikt:lignum, lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all List of life sciences, areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.#Voet, Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biomolecule, biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living Cell (biology), cells and between cells,#Karp, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissue (biology), tissues and organ (anatomy), organs as well as organism structure and function.#Miller, Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicyl Alcohol
Salicyl alcohol (saligenin) is an organic compound with the formula . It is a white solid that is used as a precursor in organic synthesis. Synthesis and applications Salicyl alcohol is produced by the hydroxymethylation of phenol using formaldehyde: : Air oxidation of salicyl alcohol gives salicylaldehyde. : Chemical sweeteners are formed by acetal formation with ''e.g.'' isovanillin (Cmp4). Salicyl alcohol appears as a pharmacophore in several notable β2-adrenoceptor agonists (e.g. salbutamol), as well as in synthetic estrone analogs, e.gCID:22940780oCID:154236944 Biosynthesis Salicyl alcohol is the precursor of salicylic acid. It is formed from salicin Salicin is an alcoholic β-glucoside. Salicin is produced in (and named after) willow (''Salix'') bark. It is a biosynthetic precursor to salicylaldehyde. Salicin hydrolyses into Glucose, β-d-glucose and salicyl alcohol (saligenin). Salicyl al ... by enzymatic hydrolysis by Salicyl-alcohol beta-D-glucosyltran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |