|
Quinizarin
1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called quinizarin or Solvent Orange 86, is an organic compound derived from anthroquinone. Quinizarin is an orange or red-brown crystalline powder. It is formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers and occurs in small amounts (as a glycoside) in the root of the madder plant, ''Rubia tinctorum''. Production Quinizarin is produced by the reaction of phthalic anhydride and 4-chlorophenol followed by hydrolysis of the chloride: It can also be prepared less efficiently from phthalic anhydride and hydroquinone. Uses Quinizarin is an inexpensive dye that is used to colour gasoline and some heating oils. It is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of indanthrene- and alizarin-derived dyes. The OH groups can be replaced by chloride. Chlorination and bromination afford other dyes. Amination (replacement of one OH by ArNH) with aniline derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Chlorophenol
4-Chlorophenol is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4OH. It is one of three monochlorophenol isomers. It is a colorless or white solid that melts easily and exhibits significant solubility in water. Its pKa is 9.14. Preparation and reaction It is prepared by chlorination of phenol, preferably in polar solvents, which tends to yield the 4-chloro derivative. Direct chlorination of molten phenol favors the formation of 2-chlorophenol. It once was produced on a large scale as a precursor to hydroquinone. It is a classic precursor, upon reaction with phthalic anhydride, to quinizarin. The commercial dye quinizarin is produced by the reaction of phthalic anhydride Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used comm ... and 4-chlorophenol followed by hydrolysis of the chloride. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthalic Anhydride
Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year. Synthesis and production Phthalic anhydride was first reported in 1836 by Auguste Laurent. Early procedures involved liquid-phase mercury-catalyzed oxidation of naphthalene. The modern industrial variant process instead uses vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) as the catalyst in a gas-phase reaction with naphthalene using molecular oxygen. The overall process involves oxidative cleavage of one of the rings and loss of two of the carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. An alternative process involves oxidation of the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alizarin
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyanthraquinone
A hydroxyanthraquinone (formula: C14H9O2(OH)) is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of an anthraquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH). The IUPAC nomenclature recommends hydroxyanthracenedione. Usually "hydroxyanthraquinone" refers to a derivative of 9,10-anthraquinone. Quoted by Khalafy and Bruce. Quoted by Khalafy and Bruce. Isomers In general, the term may mean any anthraquinone derivative where any number ''n'' of hydrogens have been replaced by ''n'' hydroxyls, so that the formula is . In this case, the number ''n'' (which is between 1 and 8) is indicated by a multiplier prefix A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particu ... (mono-, di-, tri-, up to octa-). Additional hydroxy- compounds can be derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2-Dihydroxyanthraquinone
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a ''para'' position. It is a white granular solid. Substituted derivatives of this parent compound are also referred to as hydroquinones. The name "hydroquinone" was coined by Friedrich Wöhler in 1843. Production Hydroquinone is produced industrially in two main ways.Phillip M. Hudnall "Hydroquinone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. 2005 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . * The most widely used route is similar to the cumene process in reaction mechanism and involves the dialkylation of benzene with propene to give 1,4-diisopropylbenzene. This compound reacts with air to afford the bis(hydroperoxide), which is structurally similar to cumene hydroperoxide and rearranges in acid to give acetone and hydroquinone. * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
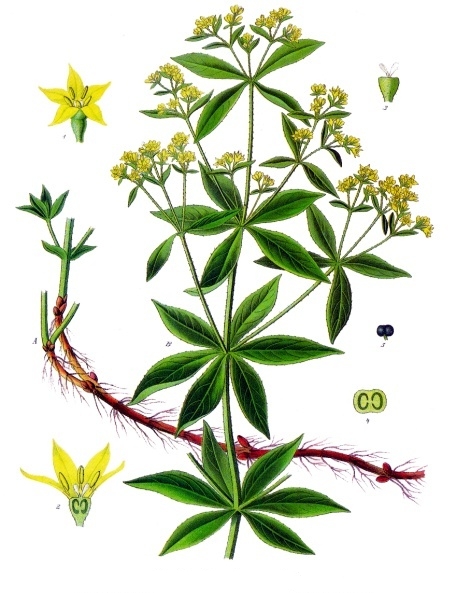
Rubia Tinctorum
''Rubia tinctorum'', the rose madder or common madder or dyer's madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae. Description The common madder can grow up to 1.5 m in height. The evergreen leaves are approximately 5–10 cm long and 2–3 cm broad, produced in whorls of 4–7 starlike around the central stem. It climbs with tiny hooks at the leaves and stems. The flowers are small (3–5 mm across), with five pale yellow petals, in dense racemes, and appear from June to August, followed by small (4–6 mm diameter) red to black berries. The roots can be over a metre long, up to 12 mm thick and the source of red dyes known as rose madder and Turkey red. It prefers loamy soils (sand and clay soil) with a constant level of moisture. Madder is used as a food plant by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the hummingbird hawk moth. Uses It has been used since ancient times as a vegetab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinalizarin
Quinalizarin or 1,2,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula . It is one of many tetrahydroxyanthraquinone isomers, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. Quinalizarin is an inhibitor of the enzyme protein kinase CK2. It is more potent and selective than emodin. It is also a potent catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor. See also * 1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone (quinizarin) * Alizarin Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Histori ..., a related simpler dye References 3-Hydroxypropenals Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors Catechols Hydroquinones Tetrahydroxyanthraquinones {{Ketone-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxyanthraquinone
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula , formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone. Isomers From 9,10-anthraquinone The unqualified term "dihydroxyanthraquinone" usually means a hydroxy derivative of 9,10-anthraquinone. The dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone functional group occurs widely in natural products, and is an important feature of the anthracycline antitumour antibiotics. In particular, 1,8-Dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone is the precursor for the important topical antipsoriatic drug anthralin, 1,8-dihydroxy-9-anthrone, There are 28 ways of choosing two of the 8 possible hydrogens, but because of the four-fold symmetry of the 9,10-an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trihydroxyanthraquinone
A trihydroxyanthraquinone or trihydroxyanthracenedione is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula , formally derived from anthraquinone by replacing three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. They include several historically important dyes. Wahl, Andre; Atack, F. W (1919) ''The Manufacture Of Organic Dyestuffs''. G. Bell And Sons, LimitedOnline versionaccessed on 2010-01-22. Hugh Alister McGuigan (1921), ''An introduction to chemical pharmacology; pharmacodynamics in relation to chemistry''. P. Blakiston's son, PhiladelphiaOnline versionat archive.org, accessed on 2010-01-30. The isomers may differ in the parent anthraquinone isomer and/or of the three hydroxyl groups. In general there are 56 ways of choosing three out of the 8 hydrogens. However, if the underlying core is symmetrical, some of these choices will give identical molecules. Isomers From 9,10-anthraquinone Due to the symmetry of the 9,10-anthraquinone core, there are only 14 isomers. CRC (1996) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |